Letter:
Speed Control of Mobile Robots Using Vibration Stimuli from Bumpy Road Surface
Ryosuke Mizoguchi, Yuki Minami
 , and Masato Ishikawa
, and Masato Ishikawa
Osaka University
2-1 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan
Speed bumps and rumble strips have been introduced into the traffic infrastructure to improve traffic safety. When a vehicle travels on a road where speed bumps and rumble strips are installed, vibration stimuli are transmitted to the driver to encourage control of the speed and position of the vehicle. In this letter, speed bumps are applied to an automated driving system. More precisely, this letter considers the speed control of a mobile robot using vibration stimuli from bumpy road surfaces. We formulated a design problem for a speed control law for a mobile robot and proposed a controller that can adjust the speed according to road surface geometry. The performance of the proposed method was verified via simulation using Unity.
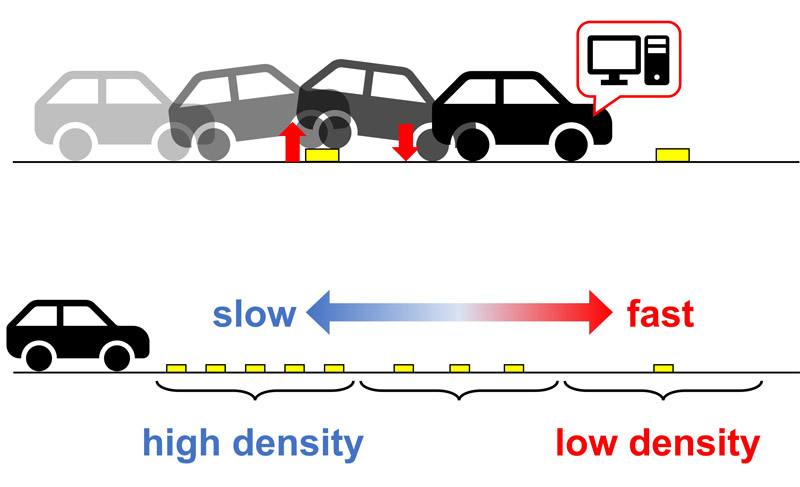
Speed control using bumpy road surface
- [1] B. N. Persaud, R. A. Retting, and C. A. Lyon, “Crash reduction following installation of centerline rumble strips on rural two-lane roads,” Accident Analysis & Prevention, Vol.36, No.6, pp. 1073-1079, 2004.
- [2] C. Xue, H. Zhou, D. Xu, and P. Liu, “Field verification of directional rumble strips to deter wrong-way freeway driving,” Trans. Engineering J. of ASCE, Vol.145, No.8, 2019.
- [3] D. K. Dewangan and S. P. Sahu, “Deep learning-based speed bump detection model for intelligent vehicle system using Raspberry Pi,” IEEE Sensors J., Vol.21, No.3, pp. 3570-3578, 2021.
- [4] A. Pirisi, M. Mussetta, F. Grimaccia, and R. E. Zich, “Novel speed-bump design and optimization for energy harvesting from traffic,” IEEE Trans. on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Vol.14, No.4, pp. 1983-1991, 2013.
- [5] Y. Mitani, Y. Minami, and M. Ishikawa, “Velocity control of mobile robots using moving light guide system,” SICE Annual Conf. 2021, pp. 1034-1035, 2021.
- [6] T. Kitaoka, Y. Minami, and M. Ishikawa, “Trajectory tracking control of mobile robot based road surface profile control,” The 62nd Japan Joint Automatic Control Conf., 2019 (in Japanese).
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.