Paper:
Variable-Corner Robotic Surfaces with Minimal Area and Their Kinematics
Masaru Miyajima, Takuya Umedachi
 , and Noriyasu Iwamoto
, and Noriyasu Iwamoto

Faculty of Textile Science and Technology, Shinshu University
3-15-1 Tokida, Ueda, Nagano 386-8567, Japan
Actuators and robots capable of representing surfaces can take various forms, depending on the types of actuators used and their arrangements. In traditional robotic surfaces, the corners on the boundary in the undeformed state remain unchanged, indicating that the number and position of the boundary corners do not vary during deformation. This paper introduces a ring-shaped actuator with three types of bending elements combined with a soap film, demonstrating the existence of robotic surfaces in which the number of boundary corners can change through actuation. We also propose forward and inverse kinematics applicable to such robotic surfaces and present simulation results. These findings suggest that inverse kinematics can be achieved in soft robots constructed with prestressed silicone rubber or fabric, including membrane-like components, stretched over a frame.
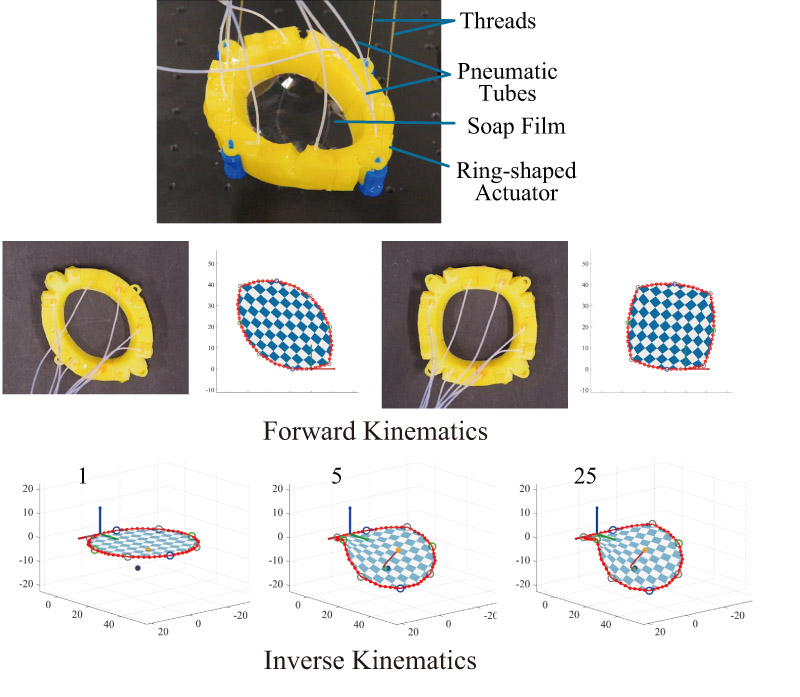
Variable-corner robotic surface and its forward and inverse kinematics
- [1] M. Cianchetti, T. Ranzani, G. Gerboni, I. De Falco, C. Laschi, and A. Menciassi, “STIFF-FLOP surgical manipulator: Mechanical design and experimental characterization of the single module,” 2013 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 3576-3581, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2013.6696866
- [2] F. Renda, M. Giorelli, M. Calisti, M. Cianchetti, and C. Laschi, “Dynamic model of a multibending soft robot arm driven by cables,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics, Vol.30, Issue 5, pp. 1109-1122, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2014.2325992
- [3] P. E. Dupont, J. Lock, B. Itkowitz, and E. Butler, “Design and control of concentric-tube robots,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics, Vol.26, Issue 2, pp. 209-225, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2009.2035740
- [4] T. Nakamura, “Fluid-Driven Soft Actuators for Soft Robots,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.36, No.2, pp. 251-259, 2024. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2024.p0251
- [5] K. Tadakuma, M. Kawakami, and H. Furukawa, “From a Deployable Soft Mechanism Inspired by a Nemertea Proboscis to a Robotic Blood Vessel Mechanism,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.34, No.2, pp. 234-239, 2022. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2022.p0234
- [6] R. J. Webster III and B. A. Jones, “Design and kinematic modeling of constant curvature continuum robots: A review,” The Int. J. of Robotics Research, Vol.29, Issue 13, pp. 1661-1683, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1177/0278364910368147
- [7] S. Follmer, D. Leithinger, A. Olwal, N. Cheng, and H. Ishii, “Jamming User Interfaces: Programmable Particle Stiffness and Sensing for Malleable and Shape-Changing Devices,” Proc. of the 25th Annual ACM Symp. on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST ’12), pp. 519-528, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1145/2380116.2380181
- [8] A. A. Stanley and A. M. Okamura, “Controllable surface haptics via particle jamming and pneumatics,” IEEE Trans. on Haptics, Vol.8, Issue 1, pp. 20-30, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/TOH.2015.2391093
- [9] A. A. Stanley, K. Hata, and A. M. Okamura, “Closed-loop shape control of a haptic jamming deformable surface,” 2016 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2718-2724, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2016.7487433
- [10] A. A. Stanley and A. M. Okamura, “Deformable model-based methods for shape control of a haptic jamming surface,” IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol.23, Issue 2, pp. 1029-1041, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2016.2525788
- [11] H. Habibi, C. Yang, I. S. Godage, R. Kang, I. D. Walker, and D. T. Branson III, “A lumped-mass model for large deformation continuum surfaces actuated by continuum robotic arms,” J. of Mechanisms and Robotics, Vol.12, Issue 1, Article No.011014, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4045037
- [12] Y. Funabora, “Prototype of a fabric actuator with multiple thin artificial muscles for wearable assistive devices,” 2017 IEEE/SICE Int. Symp. on System Integration (SII), pp. 356-361, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/SII.2017.8279238
- [13] E. Steltz, A. Mozeika, N. Rodenberg, E. Brown, and H. M. Jaeger, “JSEL: Jamming skin enabled locomotion,” 2009 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 5672-5677, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2009.5354790
- [14] C. Freeman, M. Maynard, and V. Vikas, “Topology and Morphology Design of Spherically Reconfigurable Homogeneous Modular Soft Robots,” Soft Robotics, Vol.10, No.1, pp. 52-65, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2021.0125
- [15] H. Kimura, M. Kataoka, and N. Inou, “Hermetically-Sealed Flexible Mobile Robot “MOLOOP” for Narrow Terrain Exploration,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.34, No.2, pp. 361-372, 2022. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2022.p0361
- [16] U. Pinkall and K. Polthier, “Computing discrete minimal surfaces and their conjugates,” Experimental Mathematics, Vol.2, No.1, pp. 15-36, 1993.
- [17] G. Dziuk and J. Hutchinson, “The Discrete Plateau Problem: Algorithm and Numerics,” Mathematics of Computation, Vol.68, No.225, pp. 1-23, 1999.
- [18] F. Ilievski, A. D. Mazzeo, R. F. Shepherd, X. Chen, and G. M. Whitesides, “Soft robotics for chemists,” Angewandte Chemie Int. Editiion, Vol.50, Issue 8, pp. 1890-1895, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201006464
- [19] M. Botsch, L. Kobbelt, M. Pauly, P. Alliez, and B. Lévy, “Polygon Mesh Processing,” CRC Press, 2010.
- [20] U. Pinkall and K. Polthier, “Computing discrete minimal surfaces and their conjugates,” Experimental Mathematics, Vol.2, Issue 1, pp. 15-36, 1993. https://doi.org/10.1080/10586458.1993.10504266
- [21] M. Meyer, M. Desbrun, P. Schröder, and A. H. Barr, “Discrete Differential-Geometry Operators for Triangulated 2-Manifolds,” H.-C. Hege and K. Polthier (Eds.), “Visualization and Mathematics III,” pp. 35-57, Springer, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-05105-4_2
- [22] M. P. do Carmo, “Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces: Revised and Updated Second Edition,” Dover Publications, 2016.
- [23] S. J. Callens, N. Tümer, and A. A. Zadpoor, “Hyperbolic origami-inspired folding of triply periodic minimal surface structures,” Applied Materials Today, Vol.15, pp. 453-461, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2019.03.007
- [24] N. Iwamoto, “Geometric Modeling and Estimation of Robotic Fin Shape with Bending Actuators and Passive Elements,” Sensors and Materials, Vol.35, No.9, pp. 3125-3135, 2023. https://doi.org/10.18494/SAM4387
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.