Paper:
Probabilistic 3D Sound Source Mapping System Based on Monte Carlo Localization Using Microphone Array and LIDAR
Ryo Tanabe*,**, Yoko Sasaki**, and Hiroshi Takemura*,**
*Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tokyo University of Science
2641 Yamazaki, Noda-shi, Chiba 278-8510, Japan
**National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
2-3-26 Aomi, Kouto-ku, Tokyo 135-0064, Japan
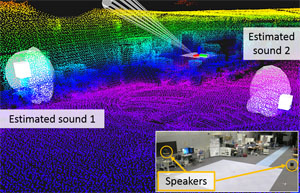
3D sound source environmental map
- [1] Y. Sasaki, S. Kagami, and H. Mizoguchi, “Map-Generation and Identification of Multiple Sound Sources from Robot in Motion,” Proc. of 2010 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 437-443, October 2010.
- [2] S. Kagami, S. Thompson, Y. Sasaki, H. Mizoguchi, and T. Enomoto, “2D sound source mapping from mobile robot using beamforming and particle filtering,” Proc. of 2009 IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 3689-3692, April 2009.
- [3] K. Takami, T. Furukawa, M. Kumon, and G. Dissanayake, “Non-field-of-view acoustic target estimation in complex indoor environment,” Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, Vol.113, pp. 577-592, 2015.
- [4] E. Martinson and A. C. Schultz, “Discovery of sound sources by an autonomous mobile robot,” Autonomous Robots, Vol.27, No.3, pp. 221-237, 2009.
- [5] T. Iyama, O. Sugiyama, T. Otsuka, K. Itoyama, and H. G. Okuno, “Visualization of auditory awareness based on sound source positions estimated by depth sensor and microphone array,” Proc. of 2014 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robot and Systems, pp. 1908-1913, September 2014.
- [6] J. Even, Y. Morales, N. Kallakuri, J. Furrer, C. T. Ishi, and N. Hagita, “Mapping sound emitting structures in 3D,” Proc. of IEEE-RAS Int. Conf. on Robots and Automation, pp. 677-682, May 2014.
- [7] R. Schmidt, “Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation,” IEEE Trans. on antennas and propagation, Vol.34, No.3, pp. 276-280, 1986.
- [8] Y. Sasaki, S. Kagami, and H. Mizoguchi, “Multiple sound source mapping for a mobile robot by self-motion triangulation,” IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 380-385, October 2006.
- [9] D. Reid, “An algorithm for tracking multiple targets,” IEEE Trans. on Automatic Control, Vol.24, No.6, pp. 843-854, 1979.
- [10] R. Kuramachi, A. Ohsato, Y. Sasaki, and H. Mizoguchi, “G-ICP SLAM: An odometry-free 3D mapping system with robust 6DoF pose estimation,” Proc. of 2015 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Biomimetics, pp. 176-181, December 2015.
- [11] Y. Sasaki, T. Fujihara, S. Kagami, H. Mizoguchi, and K. Oro, “32-channel omni-directional microphone array design and implementation,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.23, No.3, pp. 378-385, 2011.
- [12] K. Nakadai, T. Takahashi, H. G. Okuno, H. Nakajima, Y. Hasegawa, and H. Tsujino, “Design and Implementation of Robot Audition System ‘HARK’ – Open Source Software for Listening to Three Simultaneous Speakers,” Advanced Robotics, Vol.24, No.5-6, pp. 739-761, 2010.
- [13] G. Grisetti, C. Stachniss, and W. Burgard, “Improving grid-based slam with rao-blackwellized particle filters by adaptive proposals and selective resampling,” Proc. of the 2005 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2432-2437, April 2005.
- [14] Y. Chen and G. Medioni, “Object modelling by registration of multiple range images,” Image and vision computing, Vol.10, No.3, pp. 145-155, 1992.
- [15] F. Pomerleau, F. Colas, R. Siegwart, and S. Magnenat, “Comparing ICP variants on real-world data sets,” Autonomous Robots, Vol.34, No.3, pp. 133-148, 2013.
- [16] F. Moosmann and C. Stiller, “Velodyne slam,” Proc. of Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), pp. 393-398, June 2011.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.