Paper:
Image Correspondence Based on Interest Point Correlation in Difference Streams: Method and Applications to Mobile Robot Localization
Helio Perroni Filho and Akihisa Ohya
Intelligent Robot Laboratory, University of Tsukuba
1-1-1 Tennodai, Tsukuba 305-8573, Japan
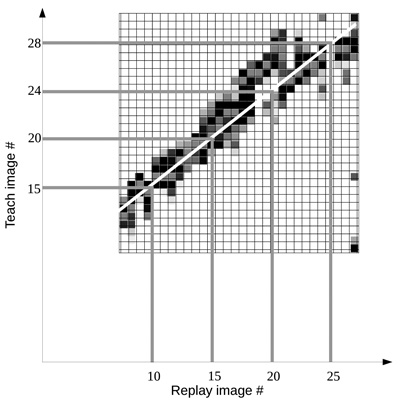
Similarity map between image sequences
- [1] E. H. Cornell, C. D. Heth, and D. M. Alberts, “Place recognition and way finding by children and adults,” Memory & Cognition, Vol.22, No.6, pp. 633-643, 1994.
- [2] R. U. Muller and J. L. Kubie, “The effects of changes in the environment on the spatial firing of hippocampal complex-spike cells,” J. Neurosci., Vol.7, No.7, pp. 1951-1968, 1987.
- [3] M. J. Milford and G. F. Wyeth, “SeqSLAM: Visual route-based navigation for sunny summer days and stormy winter nights,” 2012 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1643-1649, 2012.
- [4] R. L. Stewart, M. Mills, and H. Zhang, “Visual homing for a mobile robot using direction votes from flow vectors,” 2012 IEEE Conf. on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI), pp. 413-418, 2012.
- [5] K. Kurashiki, M. Aguilar, and S. Soontornvanichkit, “Visual Navigation of a Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Front Image in Semi-Structured Environment,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.27, No.4, pp. 392-400, 2015.
- [6] S. Lynen, M. Bosse, P. Furgale, and R. Siegwart, “Placeless place-recognition,” 2014 2nd Int. Conf. on 3D Vision (3DV), Vol.1, pp. 303-310, 2014.
- [7] D. Gálvez-López and J. D. Tardos, “Bags of binary words for fast place recognition in image sequences,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics, Vol.28, No.5, pp. 1188-1197, 2012.
- [8] K. Tanaka, Y. Chokushi, and M. Ando, “Mining Visual Phrases for Visual Robot Localization,” J. of Advanced Computational Intelligence and Intelligent Informatics, Vol.20, No.1, pp. 57-65, 2015.
- [9] E. I. Moser, E. Kropff, and M.-B. Moser, “Place cells, grid cells, and the brain's spatial representation system,” Annu. Rev. Neurosci., Vol.31, pp. 69-89, 2008.
- [10] B. Goertzel, R. Lian, I. Arel, H. De Garis, and S. Chen, “A world survey of artificial brain projects, Part II: Biologically inspired cognitive architectures,” Neurocomputing, Vol.74, No.1, pp. 30-49, 2010.
- [11] T. Fujita and C. M. Privitera, “Positional Features and Algorithmic Predictability of Visual Regions-of-Interest in Robot Hand Movement,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.21, No.6, pp. 765-772, 2009.
- [12] B. B. Murdock Jr., “Convolution and correlation in perception and memory,” Perspectives on Learning and Memory, pp. 105-119, 2014.
- [13] A. Baddeley and G. J. Hitch, “Working memory,” Scholarpedia, Vol.5, No.2, p. 3015, 2010 (revision #91945).
- [14] H. Perroni Filho and A. Ohya, “Mobile Robot Path Drift Estimation Using Visual Streams,” 2014 IEEE/SICE Int. Symposium on System Integration, pp. 192-197, 2014.
- [15] D. Burschka and G. Hager, “Vision-based control of mobile robots,” Proc. of 2001 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Vol.2, pp. 1707-1713, 2001.
- [16] R. Bajcsy, “Active perception,” Proc. of the IEEE, Vol.76, No.8, pp. 966-1005, 1988.
- [17] M. A. Fischler and R. C. Bolles, “Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography,” Communications of the ACM, Vol.24, No.6, pp. 381-395, 1981.
- [18] D. J. Parkhurst and E. Niebur, “Scene content selected by active vision,” Spatial vision, Vol.16, No.2, pp. 125-154, 2003.
- [19] H. Roger and R. J. Charles, “Topics in matrix analysis,” Cambridge University Press, 1994.
- [20] S. T. Dumais, “Latent semantic analysis,” Annual review of information science and technology, Vol.8, No.1, pp. 188-230, 2004.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.