Paper:
Study on a Pneumatically Actuated Robot for Simulating Evolutionary Developmental Process of Musculoskeletal Structures
Hideyuki Ryu, Yoshihiro Nakata, Yuya Okadome, Yutaka Nakamura, and Hiroshi Ishiguro
Department of Systems Innovation, Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University
1-3 Machikaneyama-cho, Toyonaka, Osaka 560-8531, Japan
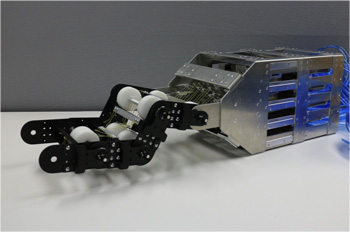
A pneumatic musculoskeletal robot
- [1] C. Darwin, “On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life,” John Murray, Nov. 24, 1859.
- [2] N. Saito, “From selectionism to neutralism: paradigm shift of evolutionary studies,” NTT Publishing Co., Ltd., 2009.
- [3] M. Kumamoto, “Revolution in humanoid robotics: evolution of motion control,” Tokyo Denki University Press, 2006.
- [4] I. Nara, M. Kumamoto, N. Hata, and Y. Uchiyama, “Biarticular muscles: Motion control and Rehabilitation,” IGAKU-SHOIN Ltd., 2008.
- [5] R. Pfeifer, M Lungarella, and F Iida, “The Challenges Ahead for Bio-Inspired `Soft' Robotics,” Communications of the ACM, Vol.55, No.11, pp. 76-87, Nov. 2012.
- [6] T. Oshima, K. Toriumi, T. Fujikawa, and N. Momose, “Effects of the Lower Leg Bi-Articular Muscle in Jumping,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.16, No.6, pp. 643-648, 2004.
- [7] V. Salvucci, Y. Kimura, S. Oh, and Y. Hori, “BiWi: Bi-Articularly Actuated and Wire Driven Robot Arm,” IEEE Int. Conf. on Mechatronics 2011, Istanbul, Turkey, Apr. 2012.
- [8] A. Ide, Y. Nakata, Y. Nakamura, K. Hirata, and H. Ishiguro, “Compliant physical interaction of a musculoskeletal robotic arm based on control of the stiffness ellipse at the end effector,” Proc. of the 2012 JSME Conf. on Robotics and Mechatronics, 1P1-T07, Hamamatsu, Japan, May 2012.
- [9] K. Urai, Y. Okadome, Y. Nakata, Y. Nakamura, and H. Ishi-guro, “Estimation of Physical Interaction between a Musculoskeletal Robot and Its Surroundings,” Artificial Life and Robotics, Vol.19, No.2, pp. 193-200, Sept. 2014.
- [10] Y. Nakata, A. Ide, Y. Nakamura, K. Hirata, and H. Ishiguro, “Hopping of a Monopedal Robot with a Biarticular Muscle Driven by Electromagnetic Linear Actuators,” IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation 2012, pp. 3153-3160, St. Paul, MN, USA, May 2012.
- [11] Y. Nakata, A. Ide, Y. Nakamura, K. Hirata, and H. Ishiguro, “Hopping by a Monopedal Robot with a Biarticular Muscle by Compliance Control – An Application of an Electromagnetic Linear Actuator –,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.25, No.1, pp. 106-114, 2013.
- [12] H. Ryu, Y. Nakata, Y. Okadome, Y. Nakamura, and H. Ishi-guro, “Development of pneumatically actuated robot for simulating evolutionary developmental process of musculoskeletal structures,” Proc. of the 2014 JSME Conf. on Robotics and Mechatronics, 1A1-J03, Toyama, Japan, May 2014.
- [13] H. Ryu, Y. Nakata, Y. Okadome, Y. Nakamura, and H. Ishiguro, “A Physically Connected Actuator Network: A Self-organizing Mechanism for Robotic Musculoskeletal Systems,” IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robotics and Systems (IROS 2014), Workshop: From Active Impedance to Intrinsically Compliant and Variable Impedance Actuators: Pros, Cons and Trade-offs, Chicago, IL, USA, Sept. 14th, 2014.
- [14] S. Hagio, M. Fukuda, and M. Kouzaki, “Identification of muscle synergies associated with gait transition in humans,” Frontiers in human neuroscience, Vol.9, 2015.
- [15] T. Fujikawa, T. Oshima, M. Kumamoto, and N. Yokoi, “Functional Coordination Control of Pairs of Antagonistic Muscles,” Trans. of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, Series C, Vol.63, No.607, pp. 769-776, 1997.
- [16] K. C. D. Fu, Y. Nakamura, T. Yamamoto, and H. Ishiguro, “Analysis of Motor Synergies Utilization for Optimal Movement Generation for a Human-like Robotic Arm,” Int. J. of Automation and Computing, Vol.10, No.6, pp. 515-524, Dec. 2013.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.