Research Paper:
An Ensemble Approach with Evolutionary Algorithm for Hand Posture Classification
Takenori Obo*,†
 , Eri Sato-Shimokawara*
, Eri Sato-Shimokawara*
 , Hiroki Shibata*
, Hiroki Shibata*
 , Yihsin Ho**
, Yihsin Ho**
 , and Ichiro Kobayashi**
, and Ichiro Kobayashi**

*Tokyo Metropolitan University
6-6 Asahigaoka, Hino, Tokyo 191-0065, Japan
†Corresponding author
**Takushoku University
815-1 Tatemachi, Hachioji, Tokyo 193-0985, Japan
Grasping is a fundamental action in daily life and particularly evident during mealtime situations where various grasping actions occur with tableware such as chopsticks, spoons, forks, bowls, and cups, each serving specific purposes. While tableware usage varies across regions and cultures, recognizing grasping actions is crucial for assessing performance in daily activities. In this study, we focus on assessing grasping functionality in terms of tableware usage during meals and propose a method for identifying hand movements. In recent years, there has been a surge in developing approaches for hand pose estimation and gesture recognition using deep learning. However, these approaches encounter common challenges, including the need for large-scale datasets, hyperparameter tuning, significant time and computational costs, and limited applicability to incremental learning. To address these challenges, we propose an ensemble approach employing extreme learning machines to recognize grasp postures. In addition, we apply spatiotemporal modeling to extract the relationship between grasp postures and the surrounding tools during mealtimes.
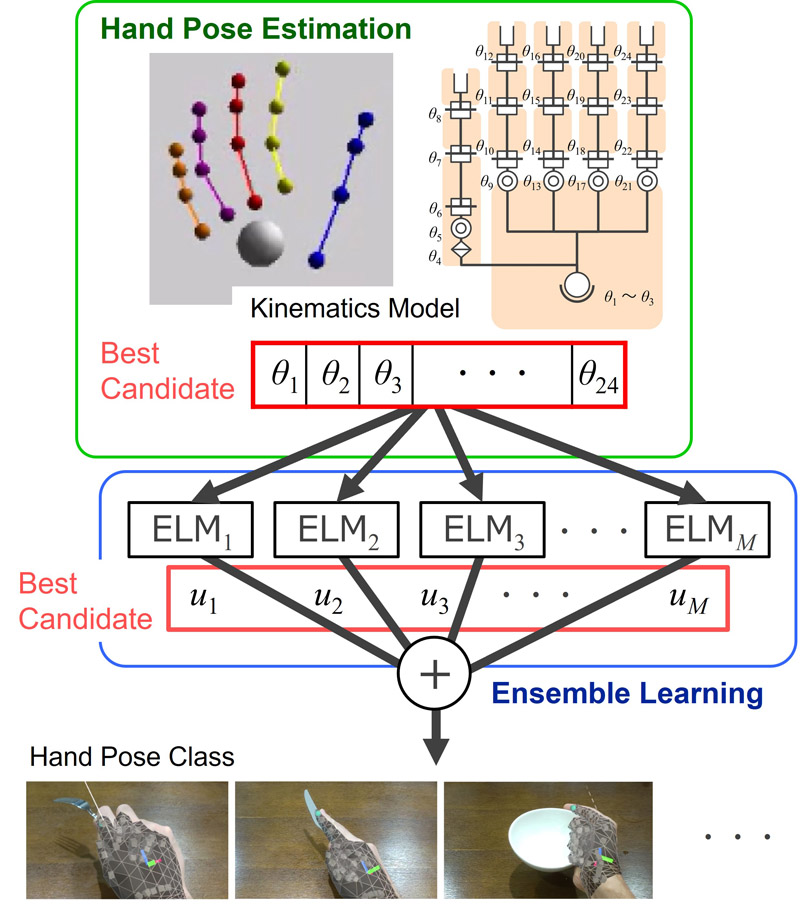
Overview of the proposed ensemble approach forhand posture classification
- [1] G. Schlesinger, “Der mechanische aufbau der künstlichen glieder,” Ersatzglieder und Arbeitshilfen – für Kriegsbeschadigte und Unfallverletzte, Springer, pp. 321-661, 1919. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-33009-8
- [2] J. R. Napier, “The prehensile movements of the human hand,” J. of Bone and Joint Surgery, Vol.38-B, No.4, pp. 902-913, 1956. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.38B4.902
- [3] N. Kamakura, M. Matsuo, H. Ishii, F. Mitsuboshi, and Y. Miura, “Patterns of static prehension in normal hands,” The American J. of Occupational Therapy, Vol.34, Issue 7, pp. 437-445, 1980. https://doi.org/10.5014/ajot.34.7.437
- [4] M. Oudah, A. Al-Naji, and J. Chahl, “Hand gesture recognition based on computer vision: a review of techniques,” J. of Imaging, Vol.6, Issue 8, Article No.73, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6080073
- [5] O. Glauser et al., “Interactive hand pose estimation using a stretch-sensing soft glove,” ACM Trans. on Graphics (ToG), Vol.38, Issue 4, Article No.41, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1145/3306346.3322957
- [6] H. Zhang, H. Qu, L. Teng, and C.-Y. Tang, “LSTM-MSA: A novel deep learning model with dual-stage attention mechanisms forearm EMG-based hand gesture recognition,” IEEE Trans. on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Vol.31, pp. 4749-4759, 2023. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3336865
- [7] Y. Dong, J. Liu, and W. Yan, “Dynamic hand gesture recognition based on signals from specialized data glove and deep learning algorithms,” IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement, Vol.70, pp. 1-14, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2021.3077967
- [8] M. Lee and J. Bae, “Deep learning based real-time recognition of dynamic ginger gestures using a data glove,” IEEE Access, Vol.8, pp. 219923-219933, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3039401
- [9] Y. Zhang et al., “Static and dynamic human arm/hand gesture capturing and recognition via multiinformation fusion of flexible strain sensors,” IEEE Sensors J., Vol.20, No.12, pp. 6450-6459, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.2965580
- [10] B. Qiang et al., “SqueezeNet and fusion network-based accurate fast fully convolutional network for hand detection and gesture recognition,” IEEE Access, Vol.9, pp. 77661-77674, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3079337
- [11] F. S. Khan, M. N. H. Mohd, D. M. Soomro, S. Bagchi, and M. D. Khan, “3D hand gestures segmentation and optimized classification using deep learning,” IEEE Access, Vol.9, pp. 131614-131624, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3114871
- [12] W. B. Dou, W. H. Chin, and N. Kubota, “Hand gesture communication using deep learning based on relevance theory,” 2020 Joint 11th Int. Conf. on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems and 21st Int. Symp. on Advanced Intelligent Systems (SCIS-ISIS), 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/SCISISIS50064.2020.9322784
- [13] B. Tekin, F. Bogo, and M. Pollefeys, “H+O: unified egocentric recognition of 3D hand-object poses and interactions,” 2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4506-4515, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00464
- [14] D. G. León et al., “Video hand gestures recognition using depth camera and lightweight CNN,” IEEE Sensors J., Vol.22, Issue 14, pp. 14610-14619, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2022.3181518
- [15] M. Al-Hammadi, G. Muhammad, W. Abdul, M. Alsulaiman, and M. S. Hossain, “Hand gesture recognition using 3D-CNN model,” IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, Vol.9, Issue 1, pp. 95-101, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCE.2019.2941464
- [16] P. Molchanov, S. Gupta, K. Kim, and J. Kautz, “Hand gesture recognition with 3D convolutional neural networks,” 2015 IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2015.7301342
- [17] S. Guo, E. Rigall, Y. Ju, and J. Dong, “3D hand pose estimation from monocular RGB with feature interaction module,” IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, Vol.32, Issue 8, pp. 5293-5306, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3142787
- [18] Y. Cai, L. Ge, J. Cai, and J. Yuan, “Weakly-supervised 3D hand pose estimation from monocular RGB images,” The 15th European Conf. on Computer Vision (ECCV 2018), pp. 678-694, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01231-1_41
- [19] B. Doosti, S. Naha, M. Mirbagheri, and D. J. Crandall, “HOPE-Net: a graph-based model for hand-object pose estimation,” 2020 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6607-6616, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00664
- [20] A. S. M. Miah, M. A. M. Hasan, and J. Shin, “Dynamic hand gesture recognition using multi-branch attention based graph and general deep learning model,” IEEE Access, Vol.11, pp. 4703-4716, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3235368
- [21] L. Ge et al., “3D hand shape and pose estimation from a single RGB image,” 2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10825-10834, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.01109
- [22] G.-B. Huang, Q.-Y. Zhu, and C.-K. Siew, “Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications,” Neurocomputing, Vol.70, Issues 1-3, pp. 489-501, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126
- [23] N.-Y. Liang, G.-B. Huang, P. Saratchandran, and N. Sundararajan, “A fast and accurate on-line sequential learning algorithm for feedforward networks,” IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, Vol.17, Issue 6, pp. 1411-1423, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2006.880583
- [24] L. Breiman, “Bagging predictors,” Machine Learning, Vol.24, pp. 123-140, 1996. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00058655
- [25] Y. Freund and R. E. Schapire, “Experiments with a new boosting algorithm,” Proc. of the 13th Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 148-156, 1996.
- [26] Y. Freund and R. E. Schapire, “A short introduction to boosting,” J. of Japanase Society for Artificial Intelligence, Vol.14, No.5, pp. 771-780, 1999.
- [27] M. M. Islam, X. Yao, S. M. S. Nirjon, M. A. Islam, and K. Murase, “Bagging and boosting negatively correlated neural networks,” IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics, Vol.38, Issue 3, pp. 771-784, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2008.922055
- [28] Y. Yang, H. Lv, and N. Chen, “A survey on ensemble learning under the era of deep learning,” Artificial Intelligence Review, Vol.56, pp. 5545-5589, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10283-5
- [29] W. Gerstner et al., “Why spikes? Hebbian learning and retrieval of time–resolved excitation patterns,” Biological Cybernetics, Vol.69, pp. 503-515, 1993. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199450
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.