Review:
Development of SCARA Robots
Kazuo Yamafuji
The University of Electro-Communications
1-5-1 Chofugaoka, Chofu, Tokyo 182-8585, Japan
The presentation on SIGMA robot for assembly by A. d’Auria at the 7th International Symposium on Industrial Robots (ISIR) held in Tokyo in October 1977 made an immense impact on engineers studying assembly automation in Japan. The 1970s witnessed the shift from the mass production of a few types to limited production of a wide variety of products in Japan, and research started for a production system with a quick response to a given type of products and change in a quantity of production. Professor Hiroshi Makino of Yamanashi University was stimulated by SIGMA and got an idea for a robot with Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arms (SCARA) and started working on the design for prototype 1 two months after the presentation. Further, he organized the SCARA Robot Consortium with Yamanashi University and thirteen domestic companies for three years, from April 1978 to March 1981, and had success in the development and spread of the SCARA robot in the assembly work. After the 1980s, the SCARA robot became one of the de facto standards of industrial robots in the world. In 2019, it is estimated that the SCARA robots will compromise 30% or more of industrial robots working all over the world. The author was one member of a research group as an associate professor, in Yamanashi University, and believes that it is extremely effective to discuss the needs for research and development of the SCARA robot and technological solutions thirty years after the establishment of JRM.
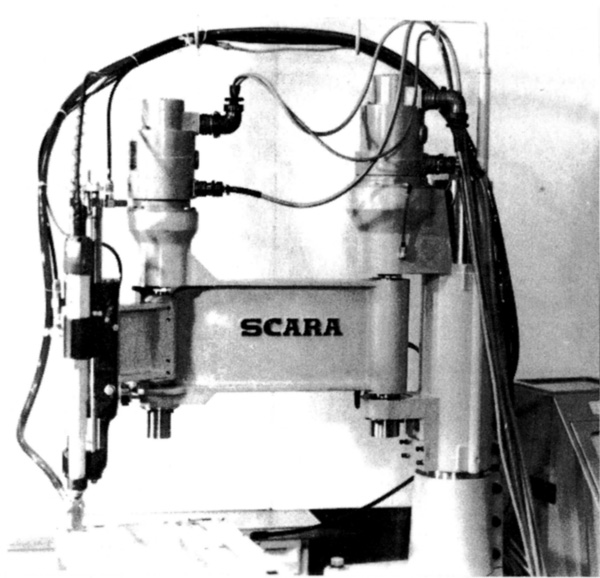
SCARA robot prototype 2 (Nitto Seiko)
- [1] A. d’Auria, “SIGMA Assembly Robot Application,” Proc. of 7th Int. Symp. on Industrial Robots, pp. 317-322, 1977.
- [2] H. Makino, “NC assembly centre,” J. of Japan Society of Precision Engineering, Vol.41, No.3, pp. 250-255, 1975 (in Japanese).
- [3] H. Makino, “Assembly process,” Automation, Vol.24, No.1, pp. 18-22, 1979 (in Japanese).
- [4] H. Makino, M. Murata, N. Furuya et al., “Research and Development of SCARA Robot,” Preprint of 47th Meeting of Special Committee for Automatic Assembly of Japan Society of Precision Engineering, p. 12, 1980 (in Japanese).
- [5] J. L. Nevins and D. E. Whitney, “What is remote center compliance and what it can do?,” Proc. of 9th Int. Symp. on Industrial Robots, 1979.
- [6] H. Makino, “Kinetics of Automated Machines,” Nikkan Kogyo Shinbunsha, 1976 (in Japanese).
- [7] H. Makino, “Universal Cam Curve and its Application,” Bulletin of Yamanashi University, Vol.28, pp. 48-58, 1977 (in Japanese).
- [8] Staff writer, NIKKEI Mechanical, p. 44, May 25, 1981 (in Japanese).
- [9] J. Hartley, “The Japanese Scene: Applications diversify,” Industrial Robot: An Int. J., Vol.9, Issue 1, pp. 56-61, 1982.
- [10] A. J. McKillop, Int. Conf. on Assembly Automation, p. 267, 1985.
- [11] H. Makino, “Development of the SCARA,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.26, No.1, pp. 5-8, 2014.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.