Letter:
Experimental Verification of Fermentation Acceleration Effect by Peristaltic Pump —Facilitation of Fermentation of Lactic Acid Bacteria by Fibrous and Porous Fermentation Substrates—
Yuki Enomoto*, Masataka Uchino**, Kaho Nomura**, and Taro Nakamura*

*Chuo University
1-13-27 Kasuga, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 112-8551, Japan
**Tokyo University of Agriculture
1-1-1 Sakuragaoka, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo 156-8502, Japan
This study presents a novel method of fermentation promotion using a peristaltic pump for large-scale fermentation. This pump physically crushes, mixes, and diffuses fermentation substrates to mimic fermentation in the human gut. The proposed device effectively mixes fermentation substrates according to their properties and promotes fermentation. Preliminary studies were conducted on fermentation experiments using this device with fibrous and porous substrates.
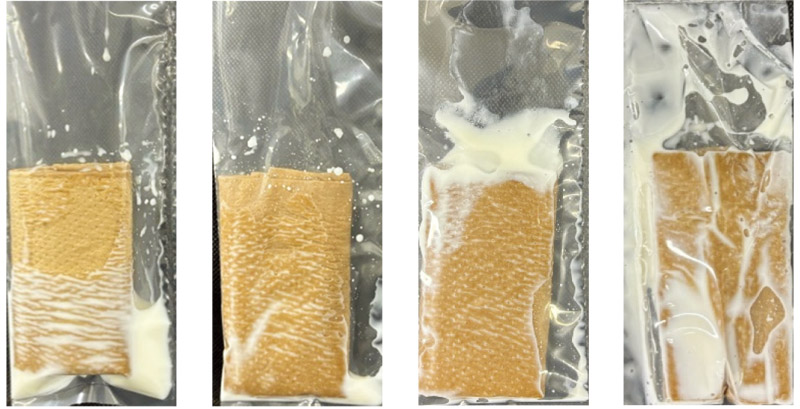
Peristaltic pumps are used to promote fermentation
- [1] J. A. Narvhus and R. K. Abrahamsen, “Traditional and modern Nordic fermented milk products: a review,” Int. Dairy J., Vol.142, Article No.105641, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2023.105641
- [2] J. Wang, Y. Chen, J. Tao, A. Kumar, Z. Liu, B. Yan, H. Su, and G. Chen, “Ni/MOFs-derived α-MoO3 catalyst for renewable hydrogen production and treatment of biogas slurry by aqueous-phase reforming,” Fuel Processing Technology, Vol.245, Article No.107738, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2023.107738
- [3] D. N. Afifah, S. N. Pratiwi, A. N. Al-Baarri, and D. N. Sugianto, “Health Benefits Indonesian Fermented Food of Tempeh Gembus Upon National Readiness for Sustainable Development Goals Achievement,” A. N. Al-Baarri and D. N. Afifah (Eds.), “Food Sustainability, Environmental Awareness, and Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies for Developing Countries,” pp. 41-61, IGI Global, 2023. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-6684-5629-3.ch003
- [4] H. Wang, Y. Zhou, S. Xu, B. Zhang, T. Cernava, Z. Ma, and Y. Chen, “Enhancement of herbicolin a production by integrated fermentation optimization and strain engineering in Pantoea agglomerans ZJU23,” Microbial Cell Factories, Vol.22, Article No.50, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-023-02051-z
- [5] W. Yang, F. Yang, C. Feng, S. Zhao, X. Zhang, and Y. Wang, “Fermentation properties and bacterial community composition of mixed silage of mulberry leaves and smooth bromegrass with and without lactobacillus plantarum inoculation,” Fermentation, Vol.9, No.3, Article No.279, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9030279
- [6] R. P. Hobson, “Studies on the nutrition of blow-fly larvae: II. role of the intestinal flora in digestion,” J. Exp. Biol., Vol.9, No.2, pp. 128-138, 1932. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.9.2.128
- [7] T. Ishikawa, T. Sato, G. Mohit, Y. Imai, and T. Yamaguchi, “Transport phenomena of microbial flora in the small intestine with peristalsis,” J. of Theoretical Biology, Vol.279, No.1, pp. 63-73, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.03.026
- [8] S. Yoshihama, R. Ban, T. Nakamura, A. Iwasaki, and H. Habu, “Mixing of solid propellant by peristaltic pump based on bowel peristalsis,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS2015), pp. 3862-3868, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2015.7353920
- [9] K. Ashigaki, A. Iwasaki et al., “Considering mixing process of rocket solid propellant using mixing transport device simulating peristaltic movement of intestinal tract,” 2018 7th IEEE Int. Conf. on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), pp. 1291-1296, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/BIOROB.2018.8487789
- [10] T. Nakamura, “Peristaltic mixing pump based on bowel peristalsis using pneumatic artificial rubber muscles and prospects for practical applications,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.34, No.2, pp. 276-278, 2022. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2022.p0276
- [11] Y. Enomoto, M. Uchino, K. Nomura, R. Sawahashi, and T. Nakamura, “Experimental verification of the effect of peristaltic mixing pumps on fermentation acceleration: Initial investigation of the acceleration of lactic acid fermentation by a high viscosity fermentation substrate,” 2024 IEEE/SICE Int. Symp. on System Integration (SII), pp. 1381-1386, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/SII58957.2024.10417527
- [12] Y. Enomoto, M. Uchino, K. Nomura, and T. Nakamura, “Experimental verification of fermentation acceleration by peristaltic pump: –Initial investigation of fermentation acceleration of lactic acid bacteria by fermentation substrate made of gel material–*,” 2024 IEEE Int. Conf. on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), pp. 303-308, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/AIM55361.2024.10637128
- [13] R. Harada, S. Uchida, A. Suzuki, and Y. Sato, “Structure and function of human body (2nd Ed.),” Ishiyaku Publishers, 2008 (in Japanese).
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.