Paper:
Point Cloud Estimation During Aerial-Aquatic Transition in Monocular Camera-Based Localization and Mapping
Photchara Ratsamee*1
 , Pudit Tempattarachoke*2, Laphonchai Jirachuphun*2, Masafumi Miwa*3, and Komsoon Somprasong*4
, Pudit Tempattarachoke*2, Laphonchai Jirachuphun*2, Masafumi Miwa*3, and Komsoon Somprasong*4
*1Faculty of Robotics and Design, Osaka Institute of Technology
1-45 Chayamachi, Kita-ku, Osaka 530-8568, Japan
*2OZT Robotics Ltd.
64/22 Charoen Krung 42/1 Alley, Khwaeng Bang Rak, Bang Rak, Bangkok 10500, Thailand
*3Graduate School of Engineering, Tokushima University
2-1 Minamijosanjima-cho, Tokushima 770-8506, Japan
*4Graduate School of Engineering, Chiang Mai University
Khelang 4 Alley, Suthep, Mueang Chiang Mai District, Chiang Mai 50200, Thailand
This paper presents a multi-box interpolation method to estimate point clouds during aerial-aquatic transition. Our proposed method is developed based on an investigation of noise characteristics of aerial point clouds and aquatic point clouds. To evaluate the performance of realistic point cloud estimation, we compare the interpolation method with the Gaussian mixture method. We also investigate how single-box and multi-box approaches deal with noise in point cloud estimation. The simulation and the experimental results show that the estimated point cloud is accurate even when the aerial and aquatic point clouds contain noise. Also, the multi-box concept helps the algorithm to avoid taking unwanted noise into consideration when predicting point clouds.
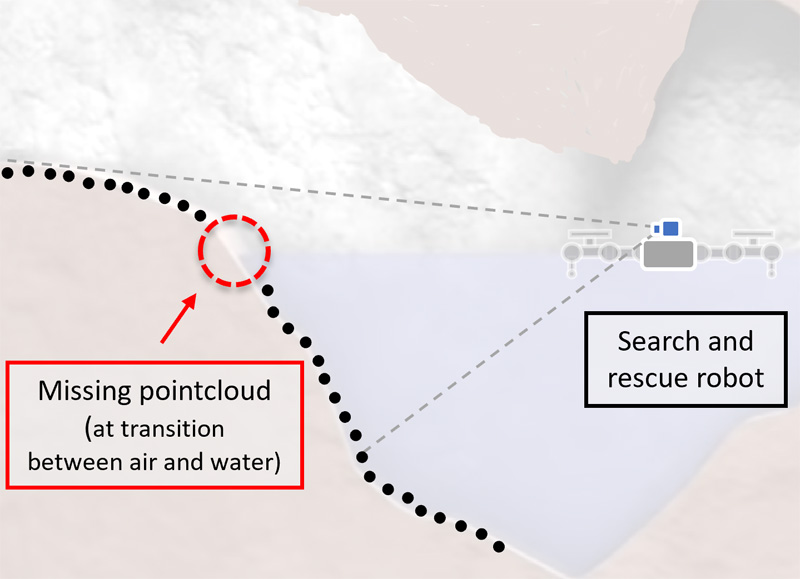
3D point cloud estimation during aerial-aquatic transition
- [1] B. Maitreesophon, “Managing and utilizing mass media as a communication tool during a crisis: A case of tham luang cave rescue operation in mae sai, chiang rai,” AJMI-ASEAN J. of Management and Innovation, Vol.5, No.2, pp. 226-236, 2018.
- [2] Y. Chen, H. Wang, E. F. Helbling, N. T. Jafferis, R. Zufferey, A. Ong, K. Ma, N. Gravish, P. Chirarattananon, M. Kovac, and R. J. Wood, “A biologically inspired, flapping-wing, hybrid aerial-aquatic microrobot,” Science Robotics, Vol.2, No.11, Article No.aao5619, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1126/scirobotics.aao5619
- [3] Y. H. Tan, R. Siddall, and M. Kovac, “Efficient aerial-aquatic locomotion with a single propulsion system,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Vol.2, No.3, pp. 1304-1311, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2017.2665689
- [4] M. M. Y. Oda, “Development of all-weather and tilt-rotor quad copter,” Int. Conf. on Intelligent Unmanned Systems (ICIUS), pp. 70-76, 2018.
- [5] M. M. T. Honta, “Underwater movable multi-copter using reverse rotation propeller,” Int. Conf. on Intelligent Unmanned Systems (ICIUS), pp. 81-87, 2018.
- [6] X. Hu, M. Wang, C. Qian, C. Huang, Y. Xia, and M. Song, “Lidar-based slam and autonomous navigation for forestry quadrotors,” 2018 IEEE CSAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conf. (CGNCC), 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/GNCC42960.2018.9018923
- [7] G. Klein and D. Murray, “Parallel tracking and mapping for small AR workspaces,” Proc. Sixth IEEE and ACM Int. Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR’07), 2007. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMAR.2007.4538852
- [8] J. Engel, T. Schöps, and D. Cremers, “LSD-SLAM: Large-scale direct monocular slam,” European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 834-849, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10605-2_54
- [9] T. Qin, P. Li, and S. Shen, “Vins-mono: A robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics, Vol.34, No.4, pp. 1004-1020, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729
- [10] A. S. Huang, A. Bachrach, P. Henry, M. Krainin, D. Maturana, D. Fox, and N. Roy, “Visual Odometry and Mapping for Autonomous Flight Using an RGB-D Camera,” pp. 235-252, Cham: Springer Int. Publishing, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-29363-9_14
- [11] S. Leutenegger, S. Lynen, M. Bosse, R. Siegwart, and P. Furgale, “Keyframe-based visual-inertial odometry using nonlinear optimization,” The Int. J. of Robotics Research, Vol.34, No.3, pp. 314-334, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1177/02783649145548
- [12] M. Dos Santos, Matheus, G. G. De Giacomo, P. L. J. Drews, and S. S. C. Botelho, “Underwater sonar and aerial images data fusion for robot localization,” 2019 19th Int. Conf. on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), pp. 578-583, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAR46387.2019.8981586
- [13] A. Manzanilla, S. Reyes, M. Garcia, D. Mercado, and R. Lozano, “Autonomous navigation for unmanned underwater vehicles: Real-time experiments using computer vision,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Vol.4, No.2, pp. 1351-1356, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2019.2895272
- [14] T. Taketomi, H. Uchiyama, and S. Ikeda, “Visual slam algorithms: A survey from 2010 to 2016,” IPSJ Trans. on Computer Vision and Applications, Vol.9, Article No.16, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41074-017-0027-2
- [15] S. Rahman, A. Q. Li, and I. Rekleitis, “An underwater slam system using sonar, visual, inertial, and depth sensor,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:1810.03200, 2018. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1810.03200
- [16] K. Richmond, C. Flesher, L. Lindzey, N. Tanner, and W. C. Stone, “Sunfish®: A human-portable exploration auv for complex 3d environments,” OCEANS 2018 MTS/IEEE Charleston, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/OCEANS.2018.8604899
- [17] R. Mur-Artal and J. Tardos, “ORB-SLAM2: An open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and rgb-d cameras,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics, Vol.33, No.5, pp. 1255-1262, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103
- [18] S. Leutenegger, S. Lynen, M. Bosse, R. Siegwart, and P. Furgale, “Keyframe-based visual-inertial odometry using nonlinear optimization,” The Int. J. of Robotics Research, Vol.34, No.3, pp. 314-334, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1177/0278364914554813
- [19] K. G. Derpanis, “Overview of the ransac algorithm,” Image Rochester NY, Vol.4, No.1, pp. 2-3, 2010.
- [20] J. Goldberger, G. E. Hinton, S. Roweis, and R. R. Salakhutdinov, “Neighbourhood components analysis,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vol.17, 2004.
- [21] Ö. Çiçek, A. Abdulkadir, S. S. Lienkamp, T. Brox, and O. Ronneberger, “3d u-net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation,” Int. Conf. on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 424-432, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.