Paper:
Dataset Creation for Semantic Segmentation Using Colored Point Clouds Considering Shadows on Traversable Area
Marin Wada*, Yuriko Ueda*, Junya Morioka*, Miho Adachi*
 , and Ryusuke Miyamoto**
, and Ryusuke Miyamoto**

*Department of Computer Science, Graduate School of Science and Technology, Meiji University
1-1-1 Higashimita, Tama-ku, Kawasaki, Kanagawa 214-8571, Japan
**Department of Computer Science, School of Science and Technology, Meiji University
1-1-1 Higashimita, Tama-ku, Kawasaki, Kanagawa 214-8571, Japan
Semantic segmentation, which provides pixel-wise class labels for an input image, is expected to improve the movement performance of autonomous robots significantly. However, it is difficult to train a good classifier for target applications; public large-scale datasets are often unsuitable. Actually, a classifier trained using Cityscapes is not enough accurate for the Tsukuba Challenge. To generate an appropriate dataset for the target environment, we attempt to construct a semi-automatic method using a colored point cloud obtained with a 3D scanner. Although some degree of accuracy is achieved, it is not practical. Hence, we propose a novel method that creates images with shadows by rendering them in the 3D space to improve the classification accuracy of actual images with shadows, for which existing methods do not output appropriate results. Experimental results using datasets captured around the Tsukuba City Hall demonstrate that the proposed method was superior when appropriate constraints were applied for shadow generation; the mIoU was improved from 0.358 to 0.491 when testing images were obtained at different locations.
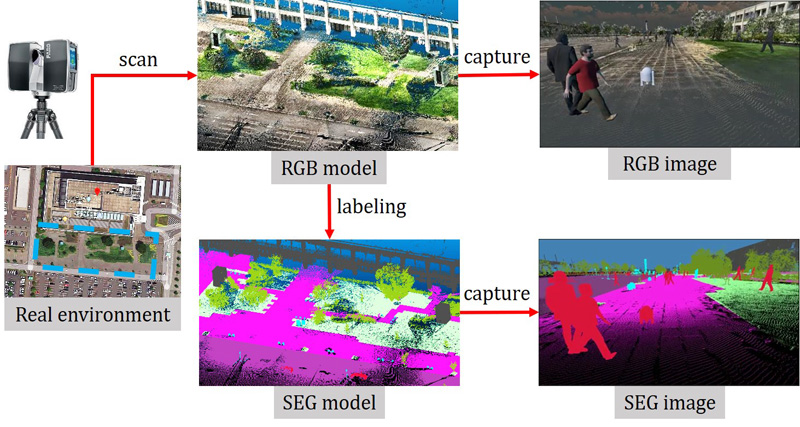
How to generate datasets from a 3D model
- [1] R. Miyamoto, M. Adachi, H. Ishida, T. Watanabe, K. Matsutani, H. Komatsuzaki, S. Sakata, R. Yokota, and S. Kobayashi, “Visual Navigation Based on Semantic Segmentation Using Only a Monocular Camera as an External Sensor,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.32, No.6, pp. 1137-1153, 2020. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2020.p1137
- [2] R. Miyamoto, Y. Nakamura, M. Adachi, T. Nakajima, H. Ishida, K. Kojima, R. Aoki, T. Oki, and S. Kobayashi, “Vision-Based Road-Following Using Results of Semantic Segmentation for Autonomous Navigation,” Proc. of ICCE-Berlin, pp. 194-199, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCE-Berlin47944.2019.8966198
- [3] M. Adachi, K. Honda, and R. Miyamoto, “Turning at Intersections Using Virtual LiDAR Signals Obtained from a Segmentation Result,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.35, No.2, pp. 347-361, 2022. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2023.p0347
- [4] J. Xu, Z. Xiong, and S. P. Bhattacharyya, “PIDNet: A Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Network Inspired by PID Controllers,” Proc. of IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 19529-19539, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01871
- [5] D. Mehta, A. Skliar, H. Ben Yahia, S. Borse, F. Porikli, A. Habibian, and T. Blankevoort, “Simple and Efficient Architectures for Semantic Segmentation,” Proc. of IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. Workshop, pp. 2627-2635, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW56347.2022.00296
- [6] R. Ranftl, A. Bochkovskiy, and V. Koltun, “Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction,” Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 12179-12188, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01196
- [7] M. Cordts, M. Omran, S. Ramos, T. Rehfeld, M. Enzweiler, R. Benenson, U. Franke, S. Roth, and B. Schiele, “The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding,” Proc. of IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 3213-3223, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.350
- [8] A. Geiger, P. Lenz, C. Stiller, and R. Urtasun, “Vision meets Robotics: The KITTI Dataset,” Int. J. of Robotics Research, Vol.32, No.11, pp. 1231-1237, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1177/0278364913491297
- [9] B. Zhou, H. Zhao, X. Puig, T. Xiao, S. Fidler, A. Barriuso, and A. Torralba, “Semantic understanding of scenes through the ade20k dataset,” Int. J. of Computer Vision, Vol.127, No.3, pp. 302-321, 2019. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1007/s11263-018-1140-0
- [10] T.-Y. Lin, M. Maire, S. Belongie, J. Hays, P. Perona, D. Ramanan, P. Dollár, and C. L. Zitnick, “Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context,” Proc. of European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 740-755, 2014. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
- [11] R. Miyamoto, M. Adachi, Y. Nakamura, T. Nakajima, H. Ishida, and S. Kobayashi, “Accuracy Improvement of Semantic Segmentation Using Appropriate Datasets for Robot Navigation,” Proc. CoDIT, pp. 1610-1615, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CoDIT.2019.8820616
- [12] S. R. Richter, V. Vineet, S. Roth, and V. Koltun, “Playing for Data: Ground Truth from Computer Games,” Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol.9906, Proc. of European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 102-118, 2016. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_7
- [13] G. Ros, L. Sellart, J. Materzynska, D. Vazquez, and A. M. Lopez, “The SYNTHIA Dataset: A Large Collection of Synthetic Images for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes,” Proc. of IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 3234-3243, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.352
- [14] X. Huang and S. Belongie, “Arbitrary Style Transfer in Real-time with Adaptive Instance Normalization,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., pp. 1501-1510, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.167
- [15] M. Wada, Y. Ueda, M. Adachi, and R. Miyamoto, “Dataset Genreratoin for Semantic Segmentation from 3D Scanned Data Considering Domain Gap,” Proc. CoDIT, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/CoDIT58514.2023.10284381
- [16] A. Nicolaou, V. Christlein, E. Riba, J. Shi, G. Vogeler, and M. Seuret, “TorMentor: Deterministic dynamic-path, data augmentations with fractals,” Proc. of IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. Workshop, pp. 2706-2710, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW56347.2022.00305
- [17] E. Riba, D. Mishkin, D. Ponsa, E. Rublee, and G. Bradski, “Kornia: an Open Source Differentiable Computer Vision Library for PyTorch,” Proc. of IEEE Winter Conf. Appl. Comput. Vis., pp. 3663-3672, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV45572.2020.9093363
- [18] A. Fournier, D. Fussell, and L. Carpenter, “Computer Rendering of Stochastic Models,” Commun. ACM, Vol.25, No.6, pp. 371-384, 1982. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1145/358523.358553
- [19] Y. Jin, A. Sharma, and R. T. Tan, “DC-ShadowNet: Single-Image Hard and Soft Shadow Removal Using Unsupervised Domain-Classifier Guided Network,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., pp. 5027-5036, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00498
- [20] Z. Chen, L. Zhu, L. Wan, S. Wang, W. Feng, and P.-A. Heng, “A Multi-task Mean Teacher for Semi-supervised Shadow Detection,” Proc. of IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00565
- [21] Q. Hu, B. Yang, L. Xie, S. Rosa, Y. Guo, Z. Wang, N. Trigoni, and A. Markham, “RandLA-Net: Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Point Clouds,” Proc. of IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01112
- [22] Y. Zhang, Z. Zhou, P. David, X. Yue, Z. Xi, B. Gong, and H. Foroosh, “PolarNet: An Improved Grid Representation for Online LiDAR Point Clouds Semantic Segmentation,” Proc. of IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00962
- [23] Z. Zhang, B. Yang, B. Wang, and B. Li, “GrowSP: Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds,” Proc. of IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 17619-17629, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01690
- [24] M. Kim and H. Byun, “Learning Texture Invariant Representation for Domain Adaptation of Semantic Segmentation,” Proc. of IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 12972-12981, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01299
- [25] D. Y. Park and K. H. Lee, “Arbitrary Style Transfer With Style-Attentional Networks,” Proc. of IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 5873-5881, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00603
- [26] D.-Y. Chen, “ArtFusion: Controllable Arbitrary Style Transfer using Dual Conditional Latent Diffusion Models,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2306.09330, 2023. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2306.09330
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.