Paper:
Asymptotic Realization of Desired Control Performance by Body Adaptation of Passive Dynamic Walker
Daisuke Ura, Yasuhiro Sugimoto, Yuichiro Sueoka, and Koichi Osuka
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Osaka University
M4-105, 2-1 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan
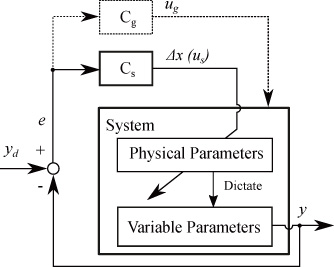
Schematic of the proposed design method
- [1] T. McGeer, “Passive dynamic walking,” The Int. J. of Robotics Research, Vol.9, No.2, 1990.
- [2] Y. Sugimoto and K. Osuka, “Hierarchical implicit feedback structure in passive dynamic walking,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.20, No.4, pp. 559-566, 2008.
- [3] Y. Sugimoto and K. Osuka, “Stability analysis of passive dynamic walking – an approach via interpretation of poincare map’s structure,” Trans. of the Institute of Systems, Vol.18, No.7, pp. 255-260, 2005.
- [4] T. Kinugasa, T. Ito, H. Kitamura, K. Ando, and S. Fujimoto, K. Yoshida, and M. Iribe, “3d dynamic biped walker with flat feet and ankle springs: Passive gait analysis and extension to active walking,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.27, No.4, pp. 444-452, 2015.
- [5] J.-S. Moon, D. M. Stipanović, and M. W. Spong, “Gait generation and stabilization for nearly passive dynamic walking using auto-distributed impulses,” Asian J. of Control, Vol.18, No.4, pp. 1-16, Aug. 2015.
- [6] T. Chyou, G. F. Liddell, and M. G. Paulin, “An upper-body can improve the stability and efficiency of passive dynamic walking,” J. of Theoretical Biology, 2011.
- [7] M. Gomes and A. Ruina, “Walking model with no energy cost,” Physical Review E, Vol.83, No.3, Mar. 2011.
- [8] S. Collins, A. Ruina, R. Tedrake, and M. Wisse, “Efficient bipedal robots based on passive dynamic walkers,” Science, Vol.307, pp. 1082-1085, 2005.
- [9] I. Handuzić and K. B. Reed, “Validation of a passive dynamic walker model for human gait analysis,” 35th Annual Int. Conf. of the IEEE EMBS, 2013.
- [10] F. Asano, T. Saka, and Y. Harata, “3-dof passive dynamic walking of compass-like biped robot with semicircular feet generated on slippery downhill,” Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2016.
- [11] Y. Harata, F. Asano, K. Taji, and Y. Uno, “Efficient parametric excitation walking with delayed feedback control,” Nonlinear Dynamics, Vol.67, No.2, pp. 1327-1335, Jun. 2011.
- [12] I. R. Manchester, U. Mettin, F. Iida, and R. Tedrake, “Stable dynamic walking over uneven terrain,” The Int. J. of Robotics Research, Vol.30, No.3, pp. 265-279, Jan. 2011.
- [13] T. Nanayakkara, K. Byl, H. Liu, X. Song, and T. Villabona, “Dominant sources of variability in passive walking,” Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2012.
- [14] Y. Huang, Q. Wang, B. Chen, G. Xie, and L. Wang, “Modeling and gait selection of passivity-based seven-link bipeds with dynamic series of walking phases,” Robotica, Vol.30, pp. 39-51, 2012.
- [15] D. J. Braun, J. E. Mitchell, and M. Goldfarb, “Actuated dynamic walking in a seven-link biped robot,” Trans. on Mechatronics, Vol.17, No.1, pp. 147-156, Feb. 2012.
- [16] Y. Hanazawa and M. Yamakita, “High-efficient biped walking based on flat-footed passive dynamic walking with mechanical impedance at ankles,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.24, No.3, pp. 498-506, 2012.
- [17] X. Luo, L. Zhu, and L. Xia, “Principle and method of speed control for dynamic walking biped robots,” Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Vol.66, pp. 129-144, Apr. 2015.
- [18] N. H. Shah and M. A. Yeolekar, “Influence of slope angle on the walking of passive dynamic biped robot,” Applied Mathematics, Vol.06, pp. 456-465, 2015.
- [19] Q. Li, J. Guo, and X.-S. Yang, “Bifurcation and chaos in the simple passive dynamic walking model with upper body,” Chaos, Vol.24, No.3, p. 033114, Sep. 2014.
- [20] D. Owaki, M. Koyama, S. Yamaguchi, S. Kubo, and A. Ishiguro, “A 2-d passive-dynamic-running biped with elastic elements,” Trans. on Robotics, Vol.27, No.1, pp. 156-162, Feb. 2011.
- [21] Z. Gan and C. D. Remy, “A passive dynamic quadruped that moves in a large variety of gaits,” Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2014), 2014.
- [22] M. Iribe, D. Hayashi, D. Ura, T. Kinugasa, and K. Osuka, “Development of the passive dynamic walk robot which has symmetrized structure,” Proc. of the 2014 JSME Conf. on Robotics and Mechatronics, 2A1-H06, 2014.
- [23] M. Iribe and K. Osuka, “A design of the passive dynamic walking robot by applying its dynamic properties,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.19, No.4, pp. 402-408, 2007.
- [24] D. Ura, M. Iribe, K. Osuka, and T. Kinugasa, “Legged walking robot design applying a behavior of passive dynamic walking – joint d.o.f alignment design applying the adaptive function –,” Trans. of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers, Vol.51, No.5, pp. 329-335, 2015.
- [25] X. Zang, L. Wang, Y.-X. Liu, and S. Iqbal, “Research on 3d walking of oscillator-based passive biped robot,” Int. Conf. on Mechanics and Control Engineering (MCE 2015), 2015.
- [26] T. Aoyama, K. Sekiyama, Z. Lu, Y. Hasegawa, and T. Fukuda, “3-d biped walking using double support phase and swing leg retraction based on the assumption of point-contact,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.24, No.5, pp. 866-875, 2012.
- [27] 先生E T. Kinugasa, T. Haji, M. Iribe, T. Kobayashi, S. Fujimoto, and K. Yoshida, “3-d passive dynamic walker made of cardboard for robot education – design strategy, experiment and manual training –,” J. of the Robotics Society of Japan, Vol.31, No.2, pp. 154-160, 2013.
- [28] Y. Ikemata, A. Sano, and H. Fujimoto, “A stability mechanism of the fixed point in passive walking,” J. of the Robotics Society of Japan, Vol.23, No.7, pp. 839-846, 2005.
- [29] I. Obayashi, S. Aoi, K. Tsuchiya, and H. Kokubu, “Formation mechanism of a basin of attraction for passive dynamic walking induced by intrinsic hyperbolicity,” Proc. of the Royal Society A, The Royal Society Publishing, 2016.
- [30] Y. Hu, G. Yan, and Z. Lin, “Feedback control of planar biped robot with regulable step length and walking speed,” Trans. on Robotics, Vol.27, No.1, pp. 162-169, Feb. 2011.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.