Research Paper:
The Color Harmony Estimation Model Construction Based on Two Layers of MLE and BPNN in the Color Matching Field
Fang Peng†
Department of Art and Design, Luohe Vocational Technology College
No.123 Daxue Road, Luohe, Henan 462000, China
†Corresponding author
In the field of art, color matching is widely used in various art designs, such as images, posters, clothing, and interior home design. Among them, harmonious color matching is the decisive factor in whether a design is popular or not. To solve the problem of estimating color harmony, this study analyzes from the perspective of color pairs and uses the two-layer maximum likelihood estimation method to make preliminary predictions of color harmony by statistically modeling paired color preferences in existing datasets. After obtaining the preliminary estimation of color harmony, multiple linear regression is selected for denoising processing. Subsequently, the preliminary prediction results were refined using a backpropagation neural network, extracting various color features in different color spaces, and ultimately obtaining accurate harmony estimates. The results indicate that, compared with existing methods, the proposed method can simulate the aesthetic cognition of different users towards different color themes. Under the same statistical method, the model can maintain good harmony estimation and experimental results. This method can promote the development of related research fields, such as quickly evaluating the color harmony of an image, and one click color changing in scenes such as clothing, home, 3D models, etc. according to different user needs.
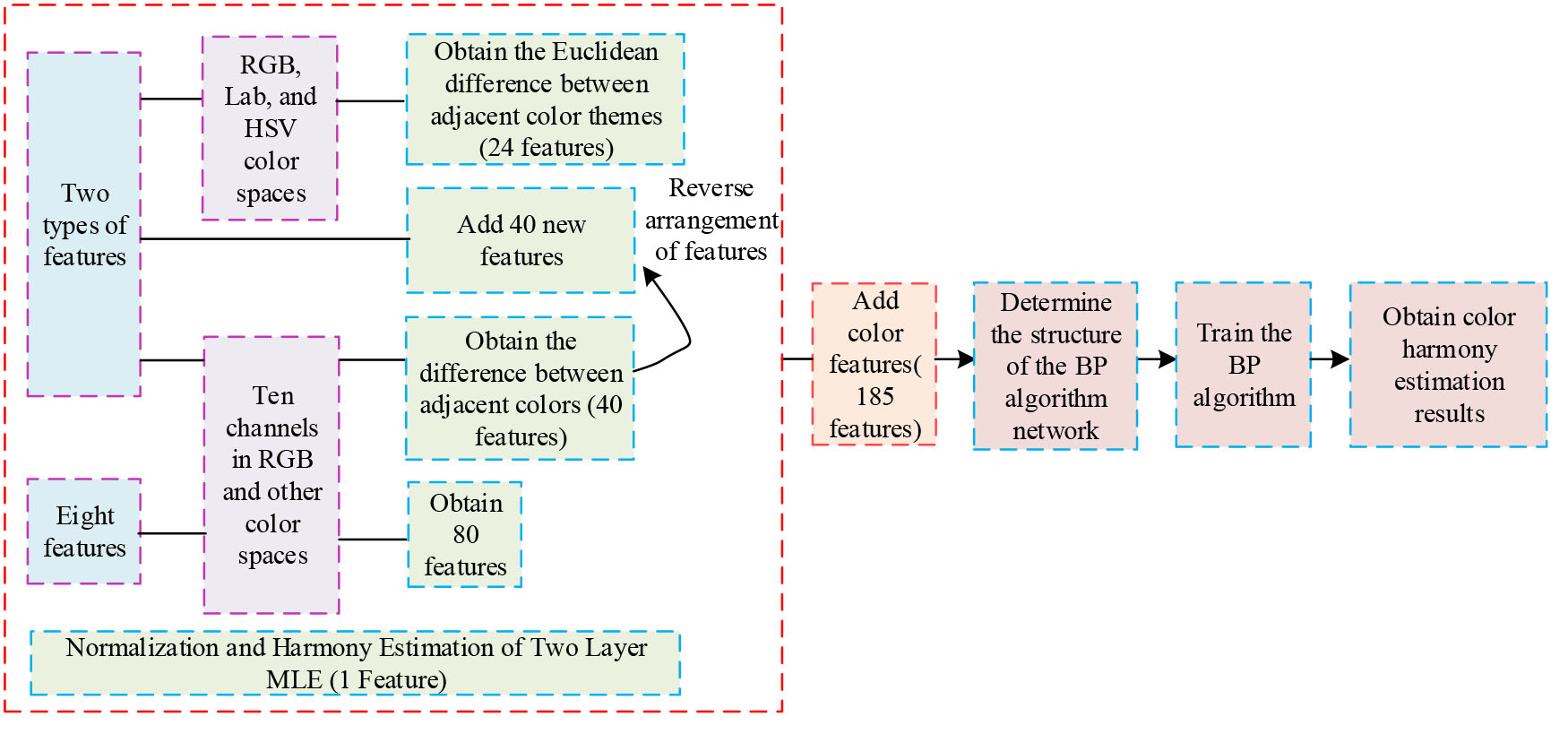
Color harmony estimation based on BPNN
- [1] S. Chaouch, A. Moussa, I. B. Marzoug, and N. Ladhari, “Application of genetic algorithm to color recipe formulation using reactive and direct dyestuffs mixtures,” Color Research and Application, Vol.45, No.5, pp. 869-910, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.22533
- [2] L. Yang et al., “The optimization of color-prediction models for colored cotton fiber yarns,” Textile Research J., Vol.89, Nos.19-20, pp. 4007-4014, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517519826892
- [3] G. Zhang, R. Pan, J. Zhou, L. Wang, and W. Gao, “Spectrophotometric color matching for pre-colored fiber blends based on a hybrid of least squares and grid search method,” Textile Research J., Vol.92, Nos.15-16, pp. 2569-2579, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517521989788
- [4] X. Sun, Y. Xue, Q. Xu, J. Shen, and Z. Xu, “Research on colored yarns for a full color phase mixing model and the Stearns–Noechel color prediction approach,” Textile Research J., Vol.93, Nos.1-2, pp. 206-220, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/00405175221115887
- [5] F. Glöckler, D. Reitzle, A.-M. Gierke, and A. Kienle, “Radiative transfer equation-based color prediction and color adjustment strategies,” J. of the Optical Society of America, Vol.40, No.3, pp. 549-559, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.477183
- [6] S. Einakian and T. S. Newman, “An examination of color theories in map-based information visualization,” J. of Computer Languages, Vol.51, pp. 143-153, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cola.2018.12.003
- [7] P. Shamoi, A. Inoue, and H. Kawanaka, “Modeling aesthetic preferences: Color coordination and fuzzy sets,” Fuzzy Sets and Systems, Vol.395, pp. 217-234, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2019.02.014
- [8] H. Wang and R. Hu, “Perception and harmony guided color assignment optimization for multi-charts,” J. of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, Vol.33, No.6, pp. 815-825, 2021 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1089.2021.18639
- [9] Y. Lin, W. Zeng, Y. Ye, and H. Qu, “Saliency-aware color harmony models for outdoor signboard,” Computers & Graphics, Vol.105, pp. 25-35, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cag.2022.04.012
- [10] S. Won and Y. J. Lee, “The effect of the number of signboard colors on color harmony and legibility,” Archives of Design Research, Vol.33, No.4, pp. 159-173, 2020 (in Korean). https://doi.org/10.15187/adr.2020.11.33.4.159
- [11] J. He, D. Chen, and S. Yu, “Research on color design and evaluation method of cultural creative products based on color harmony theory,” J. of Northwestern Polytechnical University, Vol.38, No.4, pp. 766-773, 2020 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.1051/jnwpu/20203840766
- [12] X. Ling et al., “Research on remaining service life prediction of platform screen doors system based on genetic algorithm to optimise BP neural network,” Enterprise Information Systems, Vol.16, Nos.8-9, Article No.1864478, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/17517575.2020.1864478
- [13] P. Cheng, D. Chen, and J. Wang, “Research on underwear pressure prediction based on improved GA-BP algorithm,” Int. J. of Clothing Science and Technology, Vol.33, No.4, pp. 619-642, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCST-05-2020-0078
- [14] H. Li and S. Yuan, “Corrosion prediction of marine engineering materials based on genetic algorithm and BP neural network,” Marine Sciences, Vol.44, No.10, pp. 33-38, 2020 (in Chinese).
- [15] R. Xiao et al., “The prediction of liquid holdup in horizontal pipe with BP neural network,” Energy Science & Engineering, Vol.8, No.6, pp. 2159-2168, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.655
- [16] M. H. Asad and A. Bais, “Weed detection in canola fields using maximum likelihood classification and deep convolutional neural network,” Information Processing in Agriculture, Vol.7, No.4, pp. 535-545, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2019.12.002
- [17] M. Li and X. Liu, “Maximum likelihood least squares based iterative estimation for a class of bilinear systems using the data filtering technique,” Int. J. of Control, Automation and Systems, Vol.18, No.6, pp. 1581-1592, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-019-0191-5
- [18] S. Gonçalves, U. Hounyo, A. J. Patton, and K. Sheppard, “Bootstrapping two-stage quasi-maximum likelihood estimators of time series models,” J. of Business & Economic Statistics, Vol.41, No.3, pp. 683-694, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/07350015.2022.2058949
- [19] F. Smarandache, “Plithogeny, plithogenic set, logic, probability and statistics: A short review,” J. of Computational and Cognitive Engineering, Vol.1, No.2, pp. 47-50, 2022. https://doi.org/10.47852/bonviewJCCE2202191
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.