Research Paper:
Research on Efficient Asymmetric Attention Module for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Networks in Urban Scenes
Xu Su*
 , Lihong Li*,**,†
, Lihong Li*,**,†
 , Jiejie Xiao*
, Jiejie Xiao*
 , and Pengtao Wang*
, and Pengtao Wang*

*School of Information and Electrical Engineering, Hebei University of Engineering
No.19 Taiji Road, Handan, Hebei 056038, China
**Hebei Key Laboratory of Security & Protection Information Sensing and Processing
No.19 Taiji Road, Handan, Hebei 056038, China
†Corresponding author
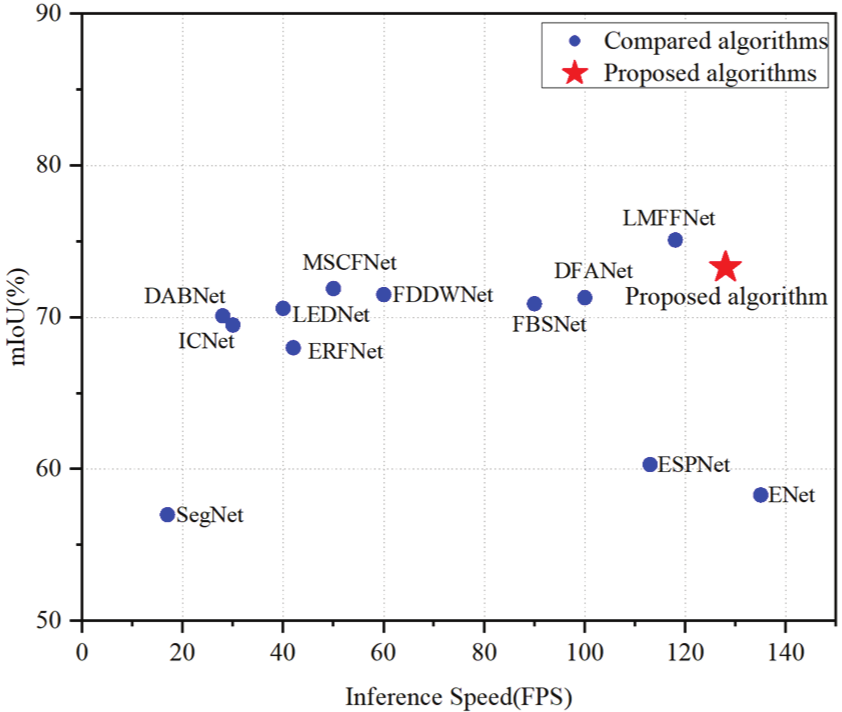
Currently, numerous high-precision models have been proposed for semantic segmentation, but the model parameters are large and the segmentation speed is slow. Real-time semantic segmentation for urban scenes necessitates a balance between accuracy, inference speed, and model size. In this paper, we present an efficient solution to this challenge, efficient asymmetric attention module net (EAAMNet) for the semantic segmentation of urban scenes, which adopts an asymmetric encoder–decoder structure. The encoder part of the network utilizes an efficient asymmetric attention module to form the network backbone. In the decoding part, we propose a lightweight multi-feature fusion decoder that can maintain good segmentation accuracy with a small number of parameters. Our extensive evaluations demonstrate that EAAMNet achieves a favorable equilibrium between segmentation efficiency, model parameters, and segmentation accuracy, rendering it highly suitable for real-time semantic segmentation in urban scenes. Remarkably, EAAMNet attains a 73.31% mIoU at 128 fps on Cityscapes and a 69.32% mIoU at 141 fps on CamVid without any pre-training. Compared to state-of-the-art models, our approach not only matches their model parameters but also enhances accuracy and increases speed.
EAAMNet for real-time semantic segmentation
- [1] J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell, “Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation,” Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431-3440, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965
- [2] H. Zhao, J. Shi, X. Qi, X. Wang, and J. Jia, “Pyramid Scene Parsing Network,” Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2881-2890, 2017.
- [3] O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer, and T. Brox, “U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation,” 18th Int. Conf. on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2015), pp. 234-241, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
- [4] L.-C. Chen, G. Papandreou, I. Kokkinos, K. Murphy, and A. L. Yuille, “Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets and Fully Connected CRFs,” arXiv:1412.7062, 2014. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1412.7062
- [5] L.-C. Chen, G. Papandreou, I. Kokkinos, K. Murphy, and A. L. Yuille, “Deeplab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs,” IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.40, No.4, pp. 834-848, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
- [6] L.-C. Chen, G. Papandreou, F. Schroff, and H. Adam, “Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation,” arXiv:1706.05587, 2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.05587
- [7] L.-C. Chen, Y. Zhu, G. Papandreou, F. Schroff, and H. Adam, “Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation,” Proc. of the European Conf. on Computer Vision (ECCV2018), pp. 801-818, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49
- [8] A. Paszke, A. Chaurasia, S. Kim, and E. Culurciello, “ENet: A Deep Neural Network Architecture for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” arXiv:1606.02147, 2016. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1606.02147
- [9] W. Han, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhang, J. Yu, C.-C. Chiu, J. Qin, A. Gulati, R. Pang, and Y. Wu, “ContextNet: Improving Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Speech Recognition with Global Context,” arXiv:2005.03191, 2020. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2005.03191
- [10] T. Emara, H. E. A. E. Munim, and H. M. Abbas, “LiteSeg: A Novel Lightweight ConvNet for Semantic Segmentation,” 2019 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/DICTA47822.2019.8945975
- [11] H. Zhao, X. Qi, X. Shen, J. Shi, and J. Jia, “ICNet for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation on High-Resolution Images,” Proc. of the European Conf. on Computer Vision (ECCV2018), pp. 405-420, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_25
- [12] F. Chollet, “Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions,” 2017 IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1800-1807, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.195
- [13] A. G. Howard, M. Zhu, B. Chen, D. Kalenichenko, W. Wang, T. Weyand, M. Andreetto, and H. Adam, “MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications,” arXiv:1704.04861, 2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1704.04861
- [14] G. Li and J. Kim, “DABNet: Depth-Wise Asymmetric Bottleneck for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” 30th British Machine Vision Conf. 2019 (BMVC), 2019.
- [15] Y. Wang, Q. Zhou, J. Liu, J. Xiong, G. Gao, X. Wu, and L. J. Latecki, “LEDnet: A Lightweight Encoder-Decoder Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” 2019 IEEE Int. Conf. on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1860-1864, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2019.8803154
- [16] M. Yang, K. Yu, C. Zhang, Z. Li, and K. Yang, “DenseASPP for Semantic Segmentation in Street Scenes,” 2018 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3684-3692, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00388
- [17] M. Lu, Z. Chen, Q. M. J. Wu, N. Wang, X. Rong, and X. Yan, “FRNet: Factorized and Regular Blocks Network for Semantic Segmentation in Road Scene,” IEEE Trans. on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Vol.23, No.4, pp. 3522-3530, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.3037727
- [18] M. A. M. Elhassan, C. Huang, C. Yang, and T. L. Munea, “DSANet: Dilated Spatial Attention for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation in Urban Street Scenes,” Expert Systems with Applications, Vol.183, Article No.115090, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115090
- [19] C. Yu, J. Wang, C. Peng, C. Gao, G. Yu, and N. Sang, “BiSeNet: Bilateral Segmentation Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” Proc. of the European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 325-341, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_20
- [20] S. Mehta, M. Rastegari, A. Caspi, L. Shapiro, and H. Hajishirzi, “ESPNet: Efficient Spatial Pyramid of Dilated Convolutions for Semantic Segmentation,” Proc. of the European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 552-568, 2018.
- [21] E. Romera, J. M. Álvarez, L. M. Bergasa, and R. Arroyo, “ERFNet: Efficient Residual Factorized ConvNet for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” IEEE Trans. on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Vol.19, No.1, pp. 263-272, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2017.2750080
- [22] Q. Yi, G. Dai, M. Shi, Z. Huang, and A. Luo, “ELANet: Effective Lightweight Attention-Guided Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” Neural Processing Letters, Vol.55, pp. 6425-6442, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-023-11145-z
- [23] J. Liu, Q. Zhou, Y. Qiang, B. Kang, X. Wu, and B. Zheng, “FDDWNet: A Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” Proc. of the 2020 IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP2020), pp. 2373-2377, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9053838
- [24] J. Liu, F. Zhang, Z. Zhou, and J. Wang, “BFMNet: Bilateral Feature Fusion Network with Multi-Scale Context Aggregation for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” Neurocomputing, Vol.521, pp. 27-40, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.11.084
- [25] M. Zhuang, X. Zhong, D. Gu, L. Feng, X. Zhong, and H. Hu, “LRDNet: A Lightweight and Efficient Network with Refined Dual Attention Decorder for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” Neurocomputing, Vol.459, pp. 349-360, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.07.019
- [26] J. Hu, L. Shen, and G. Sun, “Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks,” Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132-7141, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745
- [27] S. Woo, J. Park, J.-Y. Lee, and I. S. Kweon, “CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module,” Proc. of the European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 3-19, 2018.
- [28] J. Fu, J. Liu, H. Tian, Y. Li, Y. Bao, Z. Fang, and H. Lu, “Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation,” 2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3146-3154, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00326
- [29] Z. Huang, X. Wang, L. Huang, C. Huang, Y. Wei, and W. Liu, “CCNet: Criss-Cross Attention for Semantic Segmentation,” 2019 IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 603-612, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00069
- [30] Q. Wang, X. Wang, L. Huang, C. Huang, Y. Wei, and W. Liu, “ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks,” Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11534-11542, 2020.
- [31] Y. Yuan, L. Huang, J. Guo, C. Zhang, X. Chen, and J. Wang, “OCNet: Object Context Network for Scene Parsing,” arXiv:1809.00916, 2018. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1809.00916
- [32] X. Hao, X. Hao, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, and C. Wu, “Real-Time Semantic Segmentation with Weighted Factorized-Depthwise Convolution,” Image and Vision Computing, Vol.114, Article No.104269, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2021.104269
- [33] V. Badrinarayanan, A. Kendall, and R. Cipolla, “SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation,” IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.39, No.12, pp. 2481-2495, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
- [34] X. Zhang, X. Zhou, M. Lin, and J. Sun, “ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices,” Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6848-6856, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00716
- [35] Q.-L. Zhang and Y.-B. Yang, “SA-Net: Shuffle Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks,” Proc. of the 2021 IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP2021), pp. 2235-2239, 2021.
- [36] H. Wang, X. Jiang, H. Ren, Y. Hu, and S. Bai, “SwiftNet: Real-Time Video Object Segmentation,” Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1296-1305, 2021.
- [37] H. Li, P. Xiong, H. Fan, and J. Sun, “DFANet: Deep Feature Aggregation for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9522-9531, 2019.
- [38] C. Yu, C. Gao, J. Wang, G. Yu, C. Shen, and N. Sang, “BiSeNet V2: Bilateral Network with Guided Aggregation for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” Int. J. of Computer Vision, Vol.129, pp. 3051-3068, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-021-01515-2
- [39] R. P. K. Poudel, S. Liwicki, and R. Cipolla, “Fast-SCNN: Fast Semantic Segmentation Network,” arXiv:1902.04502, 2019. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1902.04502
- [40] G. Gao, G. Xu, J. Li, Y. Yu, H. Lu, and J. Yang, “FBSNet: A Fast Bilateral Symmetrical Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” IEEE Trans. on Multimedia, Vol.25, pp. 3273-3283, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3157995
- [41] G. Gao, G. Xu, Y. Yu, J. Xie, J. Yang, and D. Yue, “MSCFNet: A Lightweight Network with Multi-Scale Context Fusion for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” IEEE Trans. on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Vol.23, No.12, pp. 25489-25499, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2021.3098355
- [42] Q. Tang, Y. Chen, M. Zhao, S. Min, and W. Jiang, “DAABnet: Depth-Wise Asymmetric Attention Bottleneck for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” Preprint, 2023.
- [43] Y. Dai, J. Wang, J. Li, and J. Li, “PDBNet: Parallel Dual Branch Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,” Int. J. of Control, Automation and Systems, Vol.20, No.8, pp. 2702-2711, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-021-0430-4
- [44] T. Singha, D.-S. Pham, and A. Krishna, “SDBNet: Lightweight Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Using Short-Term Dense Bottleneck,” Proc. of the 2022 Int. Conf. on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/DICTA56598.2022.10034634
- [45] M. Shi, J. Shen, Q. Yi, J. Weng, Z. Huang, A. Luo, and Y. Zhou, “LMFFN: A Well-Balanced Lightweight Network for Fast and Accurate Semantic Segmentation,” IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, Vol.34, No.6, pp. 3205-3219, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3176493
- [46] A. Kherraki, M. Maqbool, and R. E. Ouazzani, “Efficient Lightweight Residual Network for Real-Time Road Semantic Segmentation,” IAES Int. J. of Artificial Intelligence, Vol.12, No.1, pp. 394-401, 2023. http://doi.org/10.11591/ijai.v12.i1.pp394-401
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.