Research Paper:
Proposal of a Course-Classification Support System Using Deep Learning and its Evaluation When Combined with Reinforcement Learning
Kazuteru Miyazaki†
 , Shu Yamaguchi
, Shu Yamaguchi
 , Rie Mori, Yumiko Yoshikawa, Takanori Saito, and Toshiya Suzuki
, Rie Mori, Yumiko Yoshikawa, Takanori Saito, and Toshiya Suzuki
National Institution for Academic Degrees and Quality Enhancement of Higher Education
1-29-1 Gakuennishimachi, Kodaira-shi, Tokyo 185-8587, Japan
†Corresponding author
The National Institution for Academic Degrees and Quality Enhancement of Higher Education (NIAD-QE) awards academic degrees based on credit accumulation. These credits must be classified according to predetermined criteria for the selected disciplinary fields. This study was conducted by subcommittees within the Committee for Validation and Examination of Degrees, the members of which should be well-versed in the syllabus of each course to ensure appropriate classification. The number of applicants has been increasing annually, and thus, a course-classification system supported by information technology is strongly desired. We proposed a course-classification support system (CCS) and an active CCS system for awarding degrees in NIAD-QE. In contrast, in this study, we construct a CCS using deep learning, which has been significantly developed in recent years. We also propose a method “CLCNNwithXoL” combined with the reinforcement learning method. We evaluate its effectiveness using the data submitted.
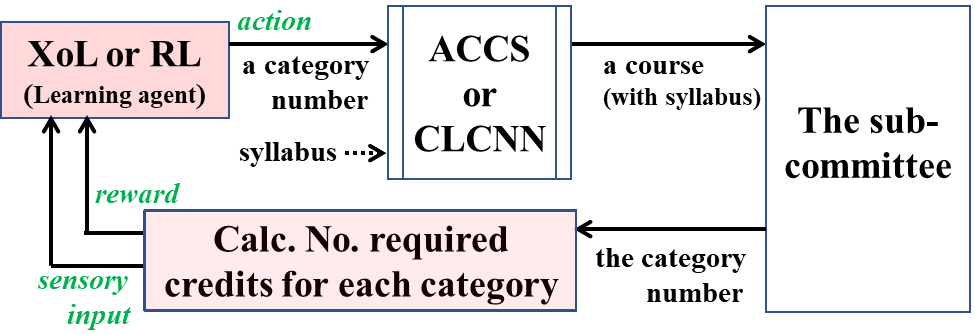
Overall process of course examination
- [1] National Institution for Academic Degrees and Quality Enhancement of Higher Education. http://www.niad.ac.jp [Accessed June 16, 2023]
- [2] “Alternative Routes to a Bachelor’s Degree,” (in Japanese). https://www.niad.ac.jp/n_gakui/media-download/5948/7a397ed4625204b6/ [Accessed June 16, 2023]
- [3] K. Miyazaki, M. Ida, F. Yoshikane, T. Nozawa, and H. Kita, “Development of a Course Classification Support System for the Awarding of Degrees Using Syllabus Data,” Trans. of Information Processing Society of Japan, Vol.46, No.3, pp. 782-791, 2015 (in Japanese).
- [4] K. Miyazaki, M. Ida, F. Yoshikane, T. Nozawa, and H. Kita, “Proposal and Evaluation of the Active Course Classification Support System for Degree Awarding-Control of the Number of Candidate Courses in Classification,” Japan Society for Fuzzy Theory and Intelligent Informatics, Vol.17, No.5, pp. 558-568, 2005 (in Japanese).
- [5] R. Mori, “System of Assessment of Learning Outcomes in Regents College: Evaluation of Learning and Credit,” Research in Academic Degrees, Vol.10, pp. 107-129, 1999 (in Japanese).
- [6] R. Mori, “The Credit Transfer System and the Validation Service at the Open University,” Research in Academic Degrees, Vol.17, pp. 183-198, 2003 (in Japanese).
- [7] S. Puirseil, “Quality Assurance in Irish Higher Education - The Higher Education and Training Awards Council,” Research in Academic Degrees, Vol.15, pp. 124-140, 2001 (in Japanese).
- [8] A. Tachi, “A Study on Thomas Edison State College, the External Degree College Established by the State of New Jersey,” Research in Academic Degrees, Vol.10, pp. 73-89, 1999 (in Japanese).
- [9] H. Yumoto, I. Mori, and H. Nakagawa, “Term Extraction Based on Occurrence and Concatenation Frequency,” Natural Language Processing, Vol.10, No.1, pp. 27-45, 2003 (in Japanese).
- [10] Q. V. Le, M. Ranzato, R. Monga, M. Devin, K. Chen, G. S. Corrado, J. Dean, and A. Y. Ng, “Building High-Level Features Using Large Scale Unsupervised Learning,” Proc. of the 29th Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 507-514, 2012.
- [11] V. Mnih, K. Kavukcuoglu, D. Silver, A. Graves, I. Antonoglou, D. Wierstra, and M. Riedmiller, “Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning,” arXiv:1312.5602, 2013. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1312.5602
- [12] K. Miyazaki, “Exploitation-Oriented Learning with Deep Learning Introducing Profit Sharing to a Deep Q-Network,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.21, No.5, pp. 849-855, 2017. https://doi.org/10.20965/jaciii.2017.p0849
- [13] T. Mikolov, K. Chen, G. Corrado, and J. Dean, “Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space,” arXiv:1301.3781, 2013. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1301.3781
- [14] X. Zhang, J. Zhao, and Y. LeCun, “Character Level Convolutional Networks for Text Classification,” arXiv:1509.01626, 2015. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1509.01626
- [15] Retty (in Japanese). https://retty.me [Accessed June 16, 2023]
- [16] A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, J. Uszkoreit, L. Jones, A. N. Gomez, L. Kaiser, and I. Polosukhin, “Attention Is All You Need,” arXiv:1706.03762, 2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762
- [17] K. Miyazaki and S. Kobayashi, “Exploitation-Oriented Learning PS-r#,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.13, No.6, pp. 624-630, 2009. https://doi.org/10.20965/jaciii.2009.p0624
- [18] K. Miyazaki and M. Ida, “Proposal and Evaluation of the Active Course Classification Support System with Exploitation-oriented Learning,” The 9th European Workshop on Reinforcement Learning (EWRL-9), pp. 333-344, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29946-9_32
- [19] K. Miyazaki and M. Ida, “Proposal of the Active Course Classification Support System with Positive and Negative Examples and Combining with Exploitation-oriented Learning,” Research on Academic Degrees and University Evaluation, No.15, 2014 (in Japanese).
- [20] L. Chrisman, “Reinforcement Learning with Perceptual Aliasing: The Perceptual Distinctions Approach,” Proc. of the 10th National Conf. on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 183-188, 1992.
- [21] K. Miyazaki, M. Yamamura, and S. Kobayashi, “A Theory of Profit Sharing in Reinforcement Learning,” Trans. of the Japanese Society for Artificial Intelligence, Vol.9, No.4, pp. 580-587, 1994 (in Japanese).
- [22] K. Miyazaki, S. Arai, and S. Kobayashi, “Learning Deterministic Policies in Partially Observable Markov Decision Processes,” Trans. of the Japanese Society for Artificial Intelligence, Vol.14, No.1, pp. 148-156, 1999 (in Japanese).
- [23] C. J. H. Watkins and P. Dayan, “Technical Note: Q-Learning,” Machine Learning, Vol.8, pp. 55-68, 1992. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022676722315
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.