Paper:
Comparison of Risk Aversity for Two Utility Functions on ℝ2
Yuji Yoshida
Faculty of Economics and Business Administration, University of Kitakyushu
4-2-1 Kitagata, Kokuraminami, Kitakyushu 802-8577, Japan
Utility functions on two-dimensional regions are demonstrated for decision makers’ risk averse behavior by weighted quasi-arithmetic means. For two utility functions on two-dimensional regions, a concept is introduced that decision making with one utility is more risk averse than decision making with the other utility. A necessary condition and sufficient conditions for the concept are demonstrated by their utility functions.
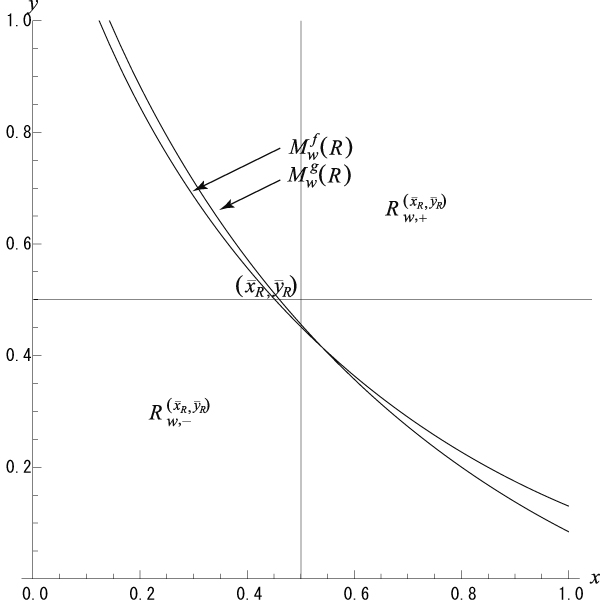
Mfw(R) and Mgw(R) in Example 1
- [1] J. Aczél, “On weighted mean values,” Bulletin of the American Math. Society, Vol.54, pp. 392-400, 1948.
- [2] A. N. Kolmogoroff, “Sur la notion de la moyenne,” Acad. Naz. Lincei Mem. Cl. Sci. Fis. Mat. Natur. Sez., Vol.12, pp. 388-391, 1930.
- [3] K. Nagumo, “Über eine Klasse der Mittelwerte,” Japanese J. of Mathematics, Vol.6, pp. 71-79, 1930.
- [4] P. C. Fishburn, “Utility Theory for Decision Making,” John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1970.
- [5] Y. Yoshida, “Aggregated mean ratios of an interval induced from aggregation operations,” Int. Conf. on Modeling Decisions for Artificial Intelligence (MDAI2008), Vol.5285, pp. 26-37, 2008.
- [6] Y. Yoshida, “Weighted quasi-arithmetic means and a risk index for stochastic environments,” Int. J. of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems, Vol.16, suppl., pp. 1-16, 2011.
- [7] H. Bustince, T. Calvo, B. De Baets, J. Fodor, R. Mesiar, J. Montero, D. Paternain, and A. Pradera, “A class of aggregation functions encompassing two-dimensional OWA operators,” Information Sciences, Vol.180, pp. 1977-1989, 2010.
- [8] C. Labreuche and M. Grabisch, “The Choquet integral for the aggregation of interval scales in multicriteria decision making,” Fuzzy Sets and Systems, Vol.137, pp. 11-26, 2003.
- [9] V. Torra and L. Godo, “On defuzzification with continuous WOWA operators,” Aggregation Operators, pp. 159-176, 2002.
- [10] Y. Yoshida, “Weighted quasi-arithmetic means on two-dimensional regions and their applications,” Int. Conf. on Modeling Decisions for Artificial Intelligence (MDAI2015) LNAI, Vol.9321, pp. 42-53, 2015.
- [11] Y. Yoshida, “Comparison of risk averse utility functions on two-dimensional regions,” Int. Conf. on Modeling Decisions for Artificial Intelligence (MDAI2017), Vol.10571, pp. 15-25, 2017.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.