Short Paper:
Current Control Method in Doubly Fed Induction Generator Under Low Switching Frequency
Peng Xie
School of Electrical and Information Engineering, Changsha University of Science and Technology
Changsha, Hunan 410114, China
The present current control method in doubly fed induction generator cannot realize the segmented grid-connected current control, it’s hard to effectively control the current in doubly fed induction generator. Therefore, a current control method in doubly fed induction generator under low switching frequency is proposed in this paper. Which means to build a mathematical model of the doubly fed induction generator under low switching frequency to analyze the parameters of doubly fed induction generator filter. Then the parameter values of the filter can be obtained. The current in generator can be predicted by adopting the double-sampling predict method. And the current control in generator can be improved according to dead beat control. Then the on-line identification of current parameters by least square method is needed to finish the current control method in doubly fed induction generator under low switching frequency. The experimental results show that the proposed method realized the segmented grid-connected current control in doubly fed induction generator.
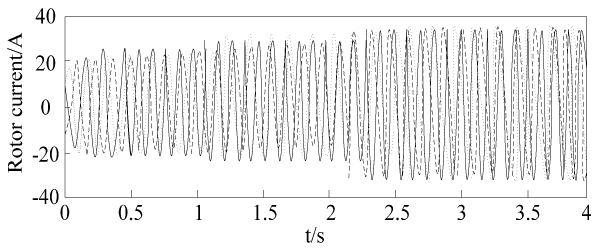
Rotor current waveform of dead beat control for current prediction
- [1] A. Calle-Prado, S. Alepuz, J. Bordonau et al., “Model Predictive Current Control of Grid-Connected Neutral-Point-Clamped Converters to Meet Low-Voltage Ride-Through Requirements,” IEEE Trans. on Industrial Electronics, Vol.62, No.3, pp. 1503-1514, 2015.
- [2] F. Wu, F. Feng, L. Luo et al., “Sampling Period Online Adjusting-Based Hysteresis Current Control Without Band With Constant Switching Frequency,” IEEE Trans. on Industrial Electronics, Vol.62, No.1, pp. 270-277, 2015.
- [3] J. M. Leavitt and H. S. Alper, “Advances and current limitations in transcript-level control of gene expression,” Current Opinion in Biotechnology, Vol.34, No.3, pp. 98-104, 2015.
- [4] C. K. Lin, J. T. Yu, Y. S. Lai et al., “Simplified model-free predictive current control for interior permanent magnet synchronous motors,” Electronics Letters, Vol.52, No.1, pp. 49-50, 2015.
- [5] Y. Gong, K. Li, S. Carver et al, “Current control of light by nonreciprocal magnetoplasmonics,” Applied Physics Letters, Vol.106, No.19, pp. 189-193, 2015.
- [6] B. Gao, L. Su, H. Yang et al., “Current control by electrode coatings formed by polymerization of dopamine at prussian blue-modified electrodes,” Analyst, Vol.141, No.6, pp. 2067-2071, 2016.
- [7] Y. K. Miao and X. J. Tian, “Research on Current Control Method of PMSM Based on Adaptive Sliding Mode,” Small & Special Electrical Machines, Vol.43, No.5, pp. 66-69, 2015.
- [8] X. G. Wang, X. Y. Wang, and T. Fu, “The Control Strategy of Disc Coreless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on the Current Chopper Control,” Procs. of the CSEE, Vol.35, No.9, pp. 2310-2317, 2015.
- [9] G. Yang, W. Tan, H. Jin et al., “Review wearable sensing system for gait recognition,” Cluster Computing, pp. 1-9, 2018.
- [10] D. Li, Q. Shen, Z. Liu, and F. Liu, “Hybrid Modulation Strategy for Two-Stage Matrix Converter and its Application in Vector Control of Doubly Fed Induction Generator,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.20, No.1, pp. 171-180, 2016.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.