Paper:
Quasi-Static Imaging System for Swimming Fish by High-Speed Elliptic and Optical Tracking
Tomohiro Sueishi*, Shoji Yachida**, Takuya Ogawa**, Murtuza Petladwala**
 , and Masatoshi Ishikawa*
, and Masatoshi Ishikawa*

*Tokyo University of Science
6-3-1 Niijuku, Katsushika-ku, Tokyo 125-8585, Japan
**NEC Corporation
1753 Shimonumabe, Nakahara-ku, Kawasaki, Kanagawa 211-8666, Japan
A continuous, non-contact, and non-fixed observation of a specific point of a free-swimming fish body is effective for monitoring the health of fish (e.g., measuring the heartbeat). However, real-time high-resolution imaging is difficult because of the wide range of fish movements, including translation and rotation. In addition, the inter-individual crossing of multiple fish hinders a stable continuous observation of an individual for an extended period. We propose a system that enables the high-speed tracking of a sparse school of fish using elliptical self-windowing to address inter-individual crossing. The system also enables quasi-static imaging near the head of free-swimming fish using high-speed optical tracking and correlation-integrated elliptical self-windowing. Evaluation experiments showed that ellipse self-windowing is faster than 1 ms, including occlusion recovery in offline videos. We also demonstrated the sufficient sharpness of the high-speed optical tracking videos. The calculation of the normalization parameter for the video was fast (within 2 ms), had sufficiently low vibration, and was robust against inter-individual crossing.
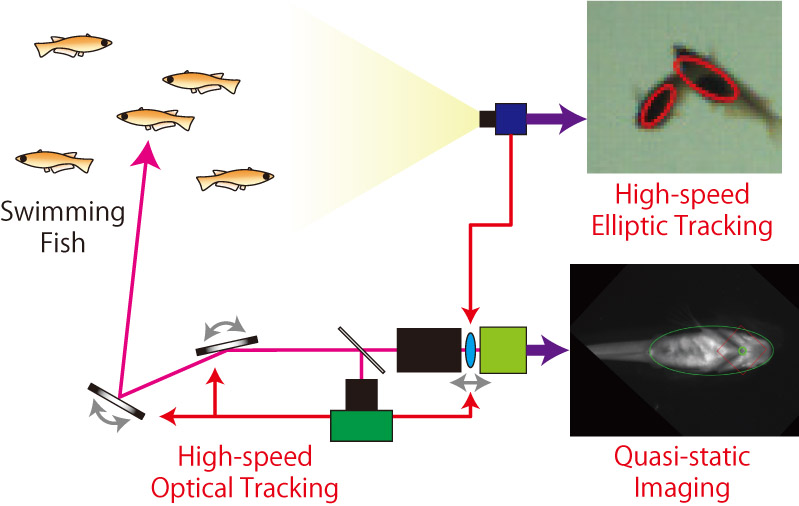
Concept of the proposed system
- [1] M. G. Bondad-Reantaso, R. P. Subasinghe, J. R. Arthur, K. Ogawa, S. Chinabut, R. Adlard, Z. Tan, and M. Shariff, “Disease and health management in Asian aquaculture,” Veterinary Parasitology, Vol.132, Nos.3-4, pp. 249-272, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.07.005
- [2] B. Zion, “The use of computer vision technologies in aquaculture—A review,” Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, Vol.88, pp. 125-132, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2012.07.010
- [3] M. R. Shortis, M. Ravanbakskh, F. Shaifat, E. S. Harvey, A. Mian, J. W. Seager, P. F. Culverhouse, D. E. Cline, and D. R. Edgington, “A review of techniques for the identification and measurement of fish in underwater stereo-video image sequences,” Proceedings, Vol.8791, Videometrics, Range Imaging, and Applications XII; and Automated Visual Inspection (SPIE Optical Metrology 2013), Article No.87910G, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2020941
- [4] K. Okumura, K. Yokoyama, H. Oku, and M. Ishikawa, “1 ms auto pan-tilt – Video shooting technology for objects in motion based on saccade mirror with background subtraction,” Advanced Robotics, Vol.29, No.7, pp. 457-468, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1080/01691864.2015.1011299
- [5] T. Sueishi, T. Ogawa, S. Yachida, and M. Ishikawa, “Continuous high-resolution observation system using high-speed gaze and focus control with wide-angle triangulation,” Proceedings, Vol.11250, High-Speed Biomedical Imaging and Spectroscopy V (SPIE BiOS, 2020), Article No.1125012, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2544313
- [6] T. Watanabe-Asaka, M. Niihori, M. Terada, S. Oda, K. Iwasaki, M. Sudoh, S. Yamada, H. Ohshima, and C. Mukai, “Technology with high-speed movies to analyze the movement of internal organs in medaka,” Trans. of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, Aerospace Technology Japan, Vol.10, No.ists28, pp. Pp_1-Pp_4, 2012. https://doi.org/10.2322/tastj.10.Pp_1
- [7] M. Kinoshita, K. Murata, K. Naruse, and M. Tanaka, “Medaka: Biology, Management, and Experimental Protocols,” John Wiley & Sons, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780813818849
- [8] D. S. Bolme, J. R. Beveridge, B. A. Draper, and Y. M. Lui, “Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters,” 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2544-2550, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2010.5539960
- [9] J. Xu, Y. Liu, S. Cui, and X. Miao, “Behavioral responses of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to acute fluctuations in dissolved oxygen levels as monitored by computer vision,” Aquacultural Engineering, Vol.35, No.3, pp. 207-217, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaeng.2006.02.004
- [10] T. H. Pinkiewicz, G. J. Purser, and R. N. Williams, “A computer vision system to analyse the swimming behaviour of farmed fish in commercial aquaculture facilities: A case study using cage-held Atlantic salmon,” Aquacultural Engineering, Vol.45, No.1, pp. 20-27, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaeng.2011.05.002
- [11] E. De Luca, G. M. Zaccaria, M. Hadhoud, G. Rizzo, R. Ponzini, U. Morbiducci, and M. M. Santoro, “ZebraBeat: A flexible platform for the analysis of the cardiac rate in zebrafish embryos,” Scientific Reports, Vol.4, No.1, Article No.4898, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04898
- [12] M. Yoshida, R. Hirano, and T. Shima, “Photocardiography: a novel method for monitoring cardiac activity in fish,” Zoological Science, Vol.26, No.5, pp. 356-361, 2009. https://doi.org/10.2108/zsj.26.356
- [13] M. Riyanto and T. Arimoto, “Heart rate and muscle performance during forced swimming of jack mackerel Trachurus japonicus at different temperatures,” Fisheries Science, Vol.81, pp. 1083-1090, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-015-0932-1
- [14] N. Hafner, J. C. Drazen, and V. M. Lubecke, “Fish heart rate monitoring by body-contact Doppler radar,” IEEE Sensors J., Vol.13, No.1, pp. 408-414, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2012.2210400
- [15] A. Pérez-Escudero, J. Vicente-Page, R. C. Hinz, S. Arganda, and G. G. De Polavieja, “idTracker: tracking individuals in a group by automatic identification of unmarked animals,” Nature Methods, Vol.11, No.7, pp. 743-748, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2994
- [16] T. Fukunaga, S. Kubota, S. Oda, and W. Iwasaki, “GroupTracker: Video tracking system for multiple animals under severe occlusion,” Computational Biology and Chemistry, Vol.57, pp. 39-45, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2015.02.006
- [17] O. Yamanaka and R. Takeuchi, “UMATracker: An intuitive image-based tracking platform,” J. of Experimental Biology, Vol.221, No.16, Article No.jeb182469, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.182469
- [18] E. Fontaine, D. Lentink, S. Kranenbarg, U. K. Müller, J. L. Van Leeuwen, A. H. Barr, and J. W. Burdick, “Automated visual tracking for studying the ontogeny of zebrafish swimming,” J. of Experimental Biology, Vol.211, No.8, pp. 1305-1316, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.010272
- [19] I. Ishii, Y. Nakabo, and M. Ishikawa, “Target tracking algorithm for 1 ms visual feedback system using massively parallel processing,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, Vol.3, pp. 2309-2314, 1996. https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.1996.506508
- [20] T. Sueishi, T. Ogawa, S. Yachida, Y. Watanabe, and M. Ishikawa, “High-resolution observation method for freely swimming medaka using high-speed optical tracking with ellipse self-window,” 40th Int. Conf. of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Article No.FrPoS-32.41, 2018.
- [21] M. Petladwala, T. Sueishi, S. Yachida, and M. Ishikawa, “High-speed occlusion recovery method for multiple fish visual tracking,” 42nd Int. Conf. of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Article No.MoAT14.12, 2020.
- [22] T. Senoo, A. Konno, Y. Wang, M. Hirano, N. Kishi, and M. Ishikawa, “Tracking of overlapped vehicles with spatio-temporal shared filter for high-speed stereo vision,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.34, No.5, pp. 1033-1042, 2022. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2022.p1033
- [23] M. Wang, G.-Y. Yang, J.-K. Lin, S.-H. Zhang, A. Shamir, S.-P. Lu, and S.-M. Hu, “Deep online video stabilization with multi-grid warping transformation learning,” IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, Vol.28, No.5, pp. 2283-2292, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2884280
- [24] A. Lim, B. Ramesh, Y. Yang, C. Xiang, Z. Gao, and F. Lin, “Real-time optical flow-based video stabilization for unmanned aerial vehicles,” J. of Real-Time Image Processing, Vol.16, pp. 1975-1985, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-017-0699-y
- [25] K.-S. Hwang and M.-D. Tsai, “On-line collision-avoidance trajectory planning of two planar robots based on geometric modeling,” J. of Information Science and Engineering, Vol.15, No.1, pp. 131-152, 1999. https://doi.org/10.6688/JISE.1999.15.1.6
- [26] J. Shi and Tomasi, “Good features to track,” 1994 Proc. of IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 593-600, 1994. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.1994.323794
- [27] B. D. Lucas and T. Kanade, “An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision,” Proc. of 7th Int. Joint Conf. on Artificial intelligence, Vol.2, pp. 674-679, 1981.
- [28] A. Savitzky and M. J. E. Golay, “Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures,” Analytical Chemistry, Vol.36, No.8, pp. 1627-1639, 1964. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60214a047
- [29] H. Habe, Y. Takeuchi, K. Terayama, and M. Sakagami, “Pose estimation of swimming fish using NACA airfoil model for collective behavior analysis,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.33, No.3, pp. 547-555, 2021. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2021.p0547
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.