Paper:
Multiview Object Pose Estimation Using Viewpoint Weight Based on Shared Object Representation
Kazuya Yabashi and Tsuyoshi Tasaki

Meijo University
1-501 Shiogamaguchi, Tempaku-ku, Nagoya, Aichi 468-8502, Japan
Product display robots are considered for industrial arm robot applications. Object pose estimation is necessary to automate product displays. However, the shapes of some objects in retail stores are simple, and robots often use RGB images from a single viewpoint. Consequently, the pose estimation accuracy is low depending on the viewpoint. Therefore, this paper proposes a multiview pose estimation method that fuses features using weights for each viewpoint. To calculate the weights, we focus on a shared object representation that expresses object poses through classification. The classification score for each class increased when pose estimation became easier. Thus, we developed a method that weighs features from each viewpoint using classification scores as confidence, and estimates the object pose. We compared the pose estimation results with those of the conventional method, which derives the most plausible pose from multiple estimation results. When the permissible angle error was set to 30°, the success rate of our method was 68.0%, which was 8.2 points higher than that of the conventional method.
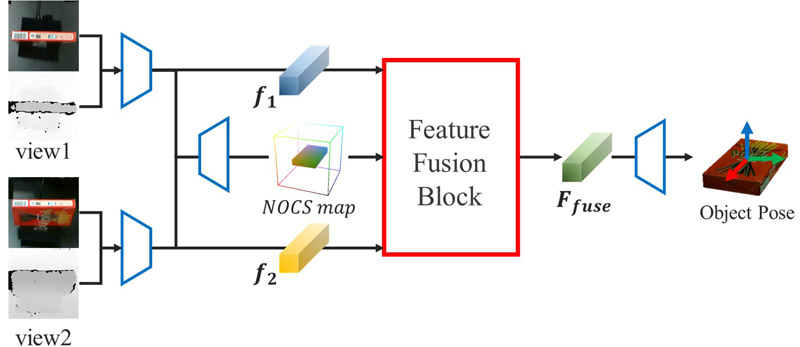
Feature fusion for multiview object pose estimation
- [1] H. Okada, T. Inamura, and K. Wada, “What competitions were conducted in the service categories of the world robot summit?,” Advanced Robotics, Vol.33, No.17, pp. 900-910, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/01691864.2019.1663608
- [2] Y. Xiang, T. Schmidt, V. Narayanan, and D. Fox, “PoseCNN: A convolutional neural network for 6D object pose estimation in cluttered scenes,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:1711.00199, 2018. https://doi.org/10.15607/RSS.2018.XIV.019
- [3] Y. Di, F. Manhardt, G. Wang, X. Ji, N. Navab, and F. Tombari, “SO-Pose: Exploiting self-occlusion for direct 6D pose estimation,” 2021 IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 12396-12405, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01217
- [4] Y. Su, M. Saleh, T. Fetzer, J. Rambach, N. Navab, B. Busam, D. Stricker, and F. Tombari, “ZebraPose: Coarse to fine surface encoding for 6dof object pose estimation,” 2022 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6728-6738, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00662
- [5] Z. Li and I. Stamos, “Depth-based 6dof object pose estimation using swin transformer,” 2023 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 1185-1191, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS55552.2023.10342215
- [6] F. Hagelskjær and A. G. Buch, “Pointvotenet: Accurate object detection and 6 dof pose estimation in point clouds,” 2020 IEEE Int. Conf. on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2641-2645, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP40778.2020.9191119
- [7] X. Liu, G. Wang, Y. Li, and X. Ji, “CATRE: Iterative point clouds alignment for category-level object pose refinement,” 2022 European Conf. on Computer Vision (ECCV 2022), pp. 499-516, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20086-1_29
- [8] Y. He, W. Sun, H. Huang, J. Liu, H. Fan, and J. Sun, “PVN3D: A deep point-wise 3D keypoints voting network for 6dof pose estimation,” 2020 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11629-11638, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01165
- [9] Y. He, H. Huang, H. Fan, Q. Chen, and J. Sun, “FFB6D: A full flow bidirectional fusion network for 6D pose estimation,” 2021 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3002-3012, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00302
- [10] C. Wang, D. Xu, Y. Zhu, R. Martín-Martín, C. Lu, L. Fei-Fei, and S. Savarese, “DenseFusion: 6D object pose estimation by iterative dense fusion,” 2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3338-3347, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00346
- [11] J. Lin, L. Liu, D. Lu, and K. Jia, “SAM-6D: Segment anything model meets zero-shot 6D object pose estimation,” 2024 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 27906-27916, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.02636
- [12] K. Fujita and T. Tasaki, “PYNet: Poseclass and yaw angle output network for object pose estimation,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.35, No.1, pp. 8-17, 2023. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2023.p0008
- [13] Y. Labbé, J. Carpentier, M. Aubry, and J. Sivic, “CosyPose: Consistent multi-view multi-object 6D pose estimation,” 2020 European Conf. on Computer Vision (ECCV 2020), pp. 574-591, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58520-4_34
- [14] F. Duffhauss, T. Demmler, and G. Neumann, “MV6D: Multi-view 6D pose estimation on RGB-D frames using a deep point-wise voting network,” 2022 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 3568-3575, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9982268
- [15] F. Duffhauss, S. Koch, H. Ziesche, N. A. Vien, and G. Neumann, “SyMFM6D: Symmetry-aware multi-directional fusion for multi-view 6D object pose estimation,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Vol.8, No.9, pp. 5315-5322, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2023.3293317
- [16] H. Wang, S. Sridhar, J. Huang, J. Valentin, S. Song, and L. J. Guibas, “Normalized object coordinate space for category-level 6D object pose and size estimation,” 2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2637-2646, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00275
- [17] B. Calli, A. Singh, A. Walsman, S. Srinivasa, P. Abbeel, and A. M. Dollar, “The YCB object and model set: Towards common benchmarks for manipulation research,” 2015 Int. Conf. on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), pp. 510-517, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAR.2015.7251504
- [18] S. Tyree, J. Tremblay, T. To, J. Cheng, T. Mosier, J. Smith, and S. Birchfield, “6-dof pose estimation of household objects for robotic manipulation: An accessible dataset and benchmark,” 2022 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 13081-13088, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9981838
- [19] S. Peng, X. Zhou, Y. Liu, H. Lin, Q. Huang, and H. Bao, “PVNet: Pixel-wise voting network for 6dof object pose estimation,” IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.44, No.6, pp. 3212-3223, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3047388
- [20] A. Collet, D. Berenson, S. S. Srinivasa, and D. Ferguson, “Object recognition and full pose registration from a single image for robotic manipulation,” 2009 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 48-55, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2009.5152739
- [21] M. A. Fischler and R. C. Bolles, “Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography,” M. A. Fischler and O. Firschein (Eds.), “Readings in Computer Vision,” Elsevier B.V., pp. 726-740, 1987. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-051581-6.50070-2
- [22] C. R. Qi, L. Yi, H. Su, and L. J. Guibas, “Pointnet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space,” Proc. of the 31st Int. Conf. on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 5105-5114, 2017.
- [23] Q. Hu, B. Yang, L. Xie, S. Rosa, Y. Guo, Z. Wang, N. Trigoni, and A. Markham, “RandLA-Net: Efficient semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds,” 2020 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11105-11114, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01112
- [24] J. Lin, Z. Wei, Y. Zhang, and K. Jia, “VI-Net: Boosting category-level 6D object pose estimation via learning decoupled rotations on the spherical representations,” 2023 IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 13955-13965, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.01287
- [25] B. Wan, Y. Shi, and K. Xu, “SOCS: Semantically-aware object coordinate space for category-level 6D object pose estimation under large shape variations,” 2023 IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 14019-14028, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.01293
- [26] G. Li, Y. Li, Z. Ye, Q. Zhang, T. Kong, Z. Cui, and G. Zhang, “Generative category-level shape and pose estimation with semantic primitives,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2210.01112, 2022. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2210.01112
- [27] H. Wang, W. Li, J. Kim, and Q. Wang, “Attention-guided RGB-D fusion network for category-level 6D object pose estimation,” 2022 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 10651-10658, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9981242
- [28] B. Triggs, P. F. McLauchlan, R. I. Hartley, and A. W. Fitzgibbon, “Bundle adjustment – A modern synthesis,” Int. Workshop on Vision Algorithms (IWVA 1999), pp. 298-372, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44480-7_21
- [29] A. Dosovitskiy et al., “An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2010.11929, 2020. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2010.11929
- [30] K. Han, Y. Wang, J. Guo, Y. Tang, and E. Wu, “Vision GNN: An image is worth graph of nodes,” Proc. of the 36th Int. Conf. on Neural Information Processing System, Vol.35, pp. 8291-8303, 2022.
- [31] B. Mildenhall, P. P. Srinivasan, M. Tancik, J. T. Barron, R. Ramamoorthi, and R. Ng, “NeRF: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis,” Communications of the ACM, Vol.65, No.1, pp. 99-106, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1145/3503250
- [32] B. Kerbl, G. Kopanas, T. Leimkühler, and G. Drettakis, “3D gaussian splatting for real-time radiance field rendering,” ACM Trans. Graph., Vol.42, No.4, Article No.139, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1145/3592433
- [33] J. Yang, H. Li, and Y. Jia, “Go-ICP: Solving 3D registration efficiently and globally optimally,” 2013 IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1457-1464, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.184
- [34] S. Pan, L. Jin, H. Hu, M. Popović, and M. Bennewitz, “How many views are needed to reconstruct an unknown object using NeRF?,” 2024 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 12470-12476, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA57147.2024.10610617
- [35] M. Tan and Q. Le, “EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks,” Proc. of the 36th Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 6105-6114, 2019.
- [36] A. Kirillov, E. Mintun, N. Ravi, H. Mao, C. Rolland, L. Gustafson, T. Xiao, S. Whitehead, A. C. Berg, W.-Y. Lo, P. Dollár, and R. Girshick, “Segment Anything,” 2023 IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 3992-4003, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00371
- [37] J. Redmon, S. Divvala, R. Girshick, and A. Farhadi, “You Only Look Once: Unified, real-time object detection,” 2016 IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 779-788, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.91
- [38] K. Simonyan and A. Zisserman, “Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition,” 3rd Int. Conf. on Learning Representations (ICLR 2015), 2015.
- [39] M. Denninger, D. Winkelbauer, M. Sundermeyer, W. Boerdijk, M. Knauer, K. H. Strobl, M. Humt, and R. Triebel, “BlenderProc2: A procedural pipeline for photorealistic rendering,” J. of Open Source Software, Vol.8, No.82, Article No.4901, 2023. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.04901
- [40] T. Mizuno, K. Yabashi, and T. Tasaki, “Object pose estimation by camera arm control based on the next viewpoint estimation,” 2024 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 9481-9486, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS58592.2024.10801633
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.