Paper:
Visual Emotion Recognition Through Multimodal Cyclic-Label Dequantized Gaussian Process Latent Variable Model
Naoki Saito*
 , Keisuke Maeda**
, Keisuke Maeda**
 , Takahiro Ogawa**
, Takahiro Ogawa**
 , Satoshi Asamizu***, and Miki Haseyama**
, Satoshi Asamizu***, and Miki Haseyama**

*Office of Institutional Research, Hokkaido University
Kita 8, Nishi 5, Kita-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido 060-0808, Japan
**Faculty of Information Science and Technology, Hokkaido University
Kita 14, Nishi 9, Kita-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido 060-0814, Japan
***National Institute of Technology, Kushiro College
2-32-1 Otanoshike-Nishi, Kushiro 084-0916, Japan
A multimodal cyclic-label dequantized Gaussian process latent variable model (mCDGP) for visual emotion recognition is presented in this paper. Although the emotion is followed by various emotion models that describe cyclic interactions between them, they should be represented as precise labels respecting the emotions’ continuity. Traditional feature integration approaches, however, are incapable of reflecting circular structures to the common latent space. To address this issue, mCDGP uses the common latent space and the cyclic-label dequantization by maximizing the probability function utilizing the cyclic-label feature as one of the observed features. The likelihood maximization problem provides limits to preserve the emotions’ circular structures. Then mCDGP increases the number of dimensions of the common latent space by translating the rough label to the detailed one by label dequantization, with a focus on emotion continuity. Furthermore, label dequantization improves the ability to express label features by retaining circular structures, making accurate visual emotion recognition possible. The main contribution of this paper is the implementation of feature integration through the use of cyclic-label dequantization.
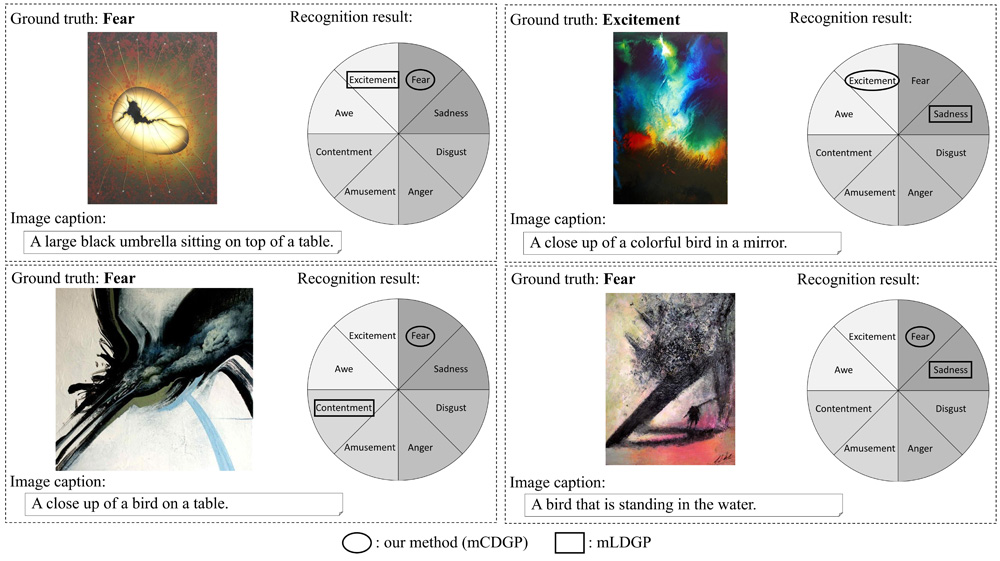
Emotion recognition results via mCDGP
- [1] P. J. Lang, “A bio-informational theory of emotional imagery,” Psychophysiology, Vol.16, No.6, pp. 495-512, 1979. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.1979.tb01511.x
- [2] D. Joshi, R. Datta, E. Fedorovskaya, Q.-T. Luong, J. Z. Wang, J. Li, and J. Luo, “Aesthetics and emotions in images,” IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, Vol.28, No.5, pp. 94-115, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2011.941851
- [3] G. Chandrasekaran, N. Antoanela, G. Andrei, C. Monica, and J. Hemanth, “Visual sentiment analysis using deep learning models with social media data,” Applied Sciences, Vol.12, No.3, Article No.1030, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031030
- [4] J. Zhang, X. Liu, M. Chen, Q. Ye, and Z. Wang, “Image sentiment classification via multi-level sentiment region correlation analysis,” Neurocomputing, Vol.469, pp. 221-233, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.10.062
- [5] J. Inthiam, A. Mowshowitz, and E. Hayashi, “Mood Perception Model for Social Robot Based on Facial and Bodily Expression Using a Hidden Markov Model,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.31, No.4, pp. 629-638, 2019. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2019.p0629
- [6] S. Lee, C. Ryu, and E. Park, “OSANet: Object Semantic Attention Network for Visual Sentiment Analysis,” IEEE Trans. on Multimedia, pp. 1-12, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3217414
- [7] H. Zhang, Y. Liu, D. Xu, K. He, G. Peng, Y. Yue, and R. Liu, “Learning multi-level representations for image emotion recognition in the deep convolutional network,” Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Graphics and Image Processing, Vol.12083, pp. 636-646, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2623414
- [8] H. Hotelling, “Relations between two sets of variates,” Biometrika, Vol.28, No.3, pp. 321-377, 1936. https://doi.org/10.2307/2333955
- [9] Y.-T. Lan, W. Liu, and B.-L. Lu, “Multimodal emotion recognition using deep generalized canonical correlation analysis with an attention mechanism,” Proc. of the Int. Joint Conf. on Neural Networks, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN48605.2020.9207625
- [10] L. Chen, K. Wang, M. Li, M. Wu, W. Pedrycz, and K. Hirota, “K-means clustering-based kernel canonical correlation analysis for multimodal emotion recognition in human-robot interaction,” IEEE Trans. on Industrial Electronics, Vol.70, No.1, pp. 1016-1024, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2022.3150097
- [11] C. Guanghui and Z. Xiaoping, “Multi-modal emotion recognition by fusing correlation features of speech-visual,” IEEE Signal Processing Letters, Vol.28, pp. 533-537, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2021.3055755
- [12] S. Nemati, “Canonical correlation analysis for data fusion in multimodal emotion recognition,” Proc. of Int. Symposium on Telecommunications, pp. 676-681, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISTEL.2018.8661140
- [13] G. Andrew, R. Arora, J. Bilmes, and K. Livescu, “Deep canonical correlation analysis,” Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 1247-1255, 2013.
- [14] N. M. Correa, T. Eichele, T. Adalı, Y.-O. Li, and V. D. Calhoun, “Multi-set canonical correlation analysis for the fusion of concurrent single trial ERP and functional MRI,” Neuroimage, Vol.50, No.4, pp. 1438-1445, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.062
- [15] G. Lee, A. Singanamalli, H. Wang, M. D. Feldman, S. R. Master, N. N. C. Shih, E. Spangler, T. Rebbeck, J. E. Tomaszewski, and A. Madabhushi, “Supervised multi-view canonical correlation analysis (sMVCCA): Integrating histologic and proteomic features for predicting recurrent prostate cancer,” IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging, Vol.34, No.1, pp. 284-297, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2355175
- [16] G. Song, S. Wang, Q. Huang, and Q. Tian, “Multimodal similarity gaussian process latent variable model,” IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, Vol.26, No.9, pp. 4168-4181, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2713045
- [17] A. Shon, K. Grochow, A. Hertzmann, and R. P. Rao, “Learning shared latent structure for image synthesis and robotic imitation,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 18, 2005.
- [18] J. Li, G. Lu, B. Zhang, J. You, and D. Zhang, “Shared Linear Encoder-Based Multikernel Gaussian Process Latent Variable Model for Visual Classification,” IEEE Trans. on Cybernetics, Vol.51, No.2, pp. 534-547, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2915789
- [19] S. Eleftheriadis, O. Rudovic, and M. Pantic, “Discriminative shared gaussian processes for multiview and view-invariant facial expression recognition,” IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, Vol.24, No.1, pp. 189-204, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2014.2375634
- [20] M. Matsumoto, K. Maeda, N. Saito, T. Ogawa, and M. Haseyama, “Multi-modal label dequantized Gaussian process latent variable model for ordinal label estimation,” Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 3985-3989, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9415090
- [21] R. Plutchik, “A general psychoevolutionary theory of emotion,” Theories of Emotion, pp. 3-33, 1980. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-558701-3.50007-7
- [22] M. Matsumoto, N. Saito, K. Maeda, T. Ogawa, and M. Haseyama, “Supervised fractional-order embedding multiview canonical correlation analysis via ordinal label dequantization for image interest estimation,” IEEE Access, Vol.9, pp. 21810-21822, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3055868
- [23] N. D. Lawrence and J. Quinonero-Candela, “Local distance preservation in the gp-lvm through back constraints,” Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 513-520, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1145/1143844.1143909
- [24] J. Machajdik and A. Hanbury, “Affective image classification using features inspired by psychology and art theory,” Proc. of the ACM Int. Conf. on Multimedia, pp. 83-92, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1145/1873951.1873965
- [25] J. A. Mikels, B. L. Fredrickson, G. R. Larkin, C. M. Lindberg, S. J. Maglio, and P. A. Reuter-Lorenz, “Emotional category data on images from the international affective picture system,” Behavior Research Methods, Vol.37, No.4, pp. 626-630, 2005. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03192732
- [26] M. Tan and Q. Le, “Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks,” Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 6105-6114, 2019. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1905.11946
- [27] J. Deng, W. Dong, R. Socher, L.-J. Li, K. Li, and L. Fei-Fei, “ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database,” Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248-255, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848
- [28] K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun, “Deep residual learning for image recognition,” Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770-778, 2016. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1512.03385
- [29] K. Xu, J. Ba, R. Kiros, K. Cho, A. Courville, R. Salakhudinov, R. Zemel, and Y. Bengio, “Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention,” Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 2048-2057, 2015. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1502.03044
- [30] T.-Y. Lin, M. Maire, S. Belongie, J. Hays, P. Perona, D. Ramanan, P. Dollár, and C. L. Zitnick, “Microsoft coco: Common objects in context,” Proc. of the European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 740-755, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
- [31] T. Sun, S. Chen, J. Yang, and P. Shi, “A novel method of combined feature extraction for recognition,” Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Data Mining, pp. 1043-1048, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2008.28
- [32] Y. Peng, D. Zhang, and J. Zhang, “A new canonical correlation analysis algorithm with local discrimination,” Neural Processing Letters, Vol.31, No.1, pp. 1-15, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-009-9123-3
- [33] X. Zhang, N. Guan, Z. Luo, and L. Lan, “Discriminative locality preserving canonical correlation analysis,” Proc. of the Chinese Conf. on Pattern Recognition, pp. 341-349, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33506-8_43
- [34] Y. Ito, T. Ogawa, and M. Haseyama, “SFEMCCA: Supervised fractional-order embedding multiview canonical correlation analysis for video preference estimation,” Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 3086-3090, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8461799
- [35] T. Tieleman and G. Hinton, “Lecture 6.5-rmsprop, coursera: Neural networks for machine learning,” University of Toronto, Technical Report, Vol.6, 2012.
- [36] G. Song, S. Wang, Q. Huang, and Q. Tian, “Harmonized multimodal learning with gaussian process latent variable models,” IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.43, No.3, pp. 858-872, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2942028
- [37] S. Moon, J. Hwang, and H. Lee, “SDGCCA: Supervised deep generalized canonical correlation analysis for multi-omics integration,” J. of Computational Biology, Vol.29, No.8, pp. 892-907, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2021.0598
- [38] R. Panda, J. Zhang, H. Li, J.-Y. Lee, X. Lu, and A. K. Roy-Chowdhury, “Contemplating visual emotions: Understanding and overcoming dataset bias,” Proc. of the European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 579-595, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01216-8_36
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.