Paper:
Human Mimetic Forearm and Hand Design with a Radioulnar Joint and Flexible Machined Spring Finger for Human Skillful Motions
Kento Kawaharazuka, Shogo Makino, Masaya Kawamura, Shinsuke Nakashima, Yuki Asano, Kei Okada, and Masayuki Inaba
Department of Mechano-Informatics, Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656, Japan
Humans have characteristic forearm and hand structures, and most of the previously developed humanoids are not equipped with them. The human forearm has a radioulnar structure composed of two long thin bones, and the human hand has flexibility to move to fit the object and strength to support the human body. Therefore, we develop a novel miniature bone-muscle module integrating bone and muscle structures, and realize the human radioulnar structure. In addition, we develop a novel finger, which is flexible and robust, by using machined springs. We integrate them and construct a forearm and hand system which imitates human joint structures, muscle arrangements, proportion, and weight. Using this forearm and hand system, we realize several human skillful motions.
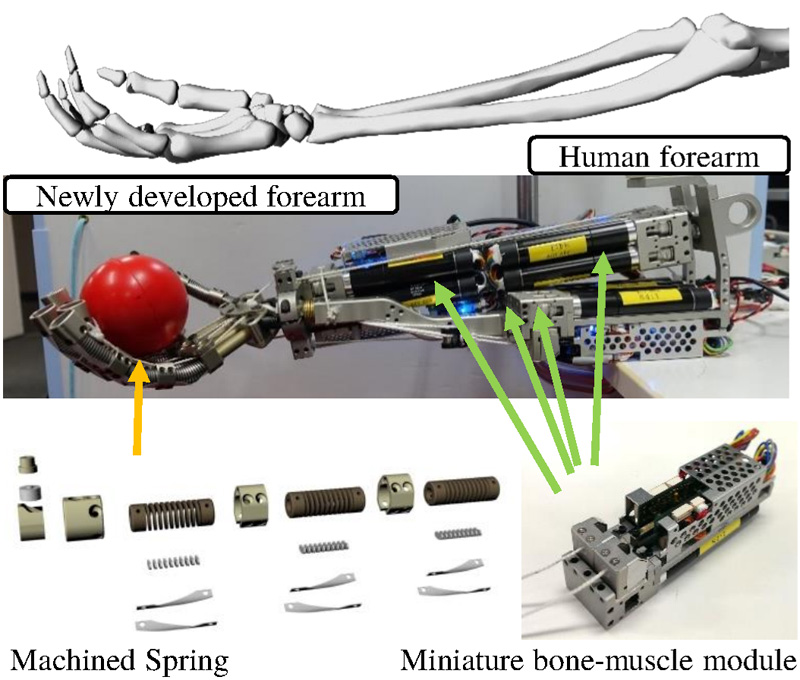
Developed forearm and hand of Kengoro
- [1] Y. Nakanishi, S. Ohta, T. Shirai, Y. Asano, T. Kozuki, Y. Kakehashi, H. Mizoguchi, T. Kurotobi, Y. Motegi, K. Sasabuchi, J. Urata, K. Okada, I. Mizuuchi, and M. Inaba, “Design Approach of Biologically-Inspired Musculoskeletal Humanoids,” Int. J. of Advanced Robotic Systems, Vol.10, No.4, pp. 216-228, 2013.
- [2] S. Wittmeier, C. Alessandro, N. Bascarevic, K. Dalamagkidis, D. Devereux, A. Diamond, M. Jäntsch, K. Jovanovic, R. Knight, H. G. Marques, P. Milosavljevic, B. Mitra, B. Svetozarevic, V. Potkonjak, R. Pfeifer, A. Knoll, and O. Holland, “Toward Anthropomimetic Robotics: Development, Simulation, and Control of a Musculoskeletal Torso,” Artificial Life, Vol.19, No.1, pp. 171-193, 2013.
- [3] M. Jäntsch, S. Wittmeier, K. Dalamagkidis, A. Panos, F. Volkart, and A. Knoll, “Anthrob – A Printed Anthropomimetic Robot,” Proc. of the 2013 IEEE-RAS Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots, pp. 342-347, 2013.
- [4] Y. Asano, T. Kozuki, S. Ookubo, M. Kawamura, S. Nakashima, T. Katayama, I. Yanokura, T. Hirose, K. Kawaharazuka, S. Makino, Y. Kakiuchi, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “Human Mimetic Musculoskeletal Humanoid Kengoro toward Real World Physically Interactive Actions,” Proc. of the 2016 IEEE-RAS Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots, pp. 876-883, 2016.
- [5] Y. Asano, H. Mizoguchi, T. Kozuki, Y. Motegi, M. Osada, J. Urata, Y. Nakanishi, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “Lower Thigh Design of Detailed Musculoskeletal Humanoid “Kenshiro”,” Proc. of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 4367-4372, 2012.
- [6] I. Mizuuchi, T. Yoshikai, Y. Nakanishi, Y. Sodeyama, T. Yamamoto, A. Miyadera, T. Niemela, M. Hayashi, J. Urata, and M. Inaba, “Development of muscle-driven flexible-spine humanoids,” Proc. of the 2005 IEEE-RAS Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots, pp. 339-344, 2005.
- [7] M. Osada, H. Mizoguchi, Y. Asano, T. Kozuki, J. Urata, Y. Nakanishi, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “Application of “Planar Muscle” with Soft Skin-Like Outer Function Suitable for Musculoskeletal Humanoid,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.24, No.6, pp. 1080-1088, 2012.
- [8] Y. Sodeyama, T. Yoshikai, T. Nishino, I. Mizuuchi, and M. Inaba, “The Designs and Motions of a Shoulder Structure with a Wide Range of Movement Using Bladebone-Collarbone Structures,” Proc. of the 2007 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 3629-3634, 2007.
- [9] H. Endo and M. Wada, “The Coupled Tendon-driven System for Musculoskeletal Elbow Joints,” J. of the Robotics Society of Japan, Vol.11, No.8, pp. 1252-1260, 1993.
- [10] S. Ikemoto, F. Kannou, and K. Hosoda, “Humanlike Shoulder Complex for Musculoskeletal Robot Arms,” Proc. of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 4892-4897, 2012.
- [11] Y. Nakanishi, T. Izawa, M. Osada, N. Ito, S. Ohta, J. Urata, and M. Inaba, “Development of Musculoskeletal Humanoid Kenzoh with Mechanical Compliance Changeable Tendons by Nonlinear Spring Unit,” Proc. of the 2011 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Biomimetics, pp. 2384-2389, 2011.
- [12] A. Kochan, “Shadow delivers first hand,” Industrial Robot: An Int. J., Vol.32, No.1, pp. 15-16, 2005.
- [13] M. Grebenstein, A. Albu-Schäffer, T. Bahls, M. Chalon, O. Eiberger, W. Friedl, R. Gruber, S. Haddadin, U. Hagn, R. Haslinger, H. Höppner, S. Jörg, M. Nickl, A. Nothhelfer, F. Petit, J. Reill, N. Seitz, T. Wimböck, S. Wolf, T. Wüsthoff, and G. Hirzinger, “The DLR Hand Arm System,” Proc. of The 2011 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3175-3182, 2011.
- [14] A. Ke, J. Huang, and J. He, “An Underactuated Prosthetic Hand with Coupled Metacarpophalangeal Joints,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.22, No.5, pp. 674-682, 2018.
- [15] A. H. Arieta, R. Katoh, H. Yokoi, and Y. Wenwei, “Development of a Multi-DOF Electromyography Prosthetic System Using the Adaptive Joint Mechanism,” Applied Bionics and Biomechanics, Vol.3, No.2, pp. 101-111, 2006.
- [16] T. E. Wiste, S. A. Dalley, T. J. Withrow, and M. Goldfarb, “Design of a multifunctional anthropomorphic prosthetic hand with extrinsic actuation,” Proc. of the 2009 IEEE Int. Conf. on Rehabilitation Robotics, pp. 675-681, 2009.
- [17] T. Mouri, K. Nakamura, H. Kawasaki, T. Abe, Y. Kobayashi, K. Mori, and M. Saito, “High Output Robot Hand with Retention Mechanism,” Proc. of the 2016 JSME Annual Conf. on Robotics and Mechatronics, 2016 (in Japanese).
- [18] J. Yang, E. P. Pitarch, K. Abdel-Malek, A. Patrick, and L. Lindkvist, “A multi-fingered hand prosthesis,” Mechanism and Machine Theory, Vol.39, No.6, pp. 555-581, 2004.
- [19] M. Hioki, S. Ebisawa, H. Sakaeda, T. Mouri, S. Nakagawa, Y. Uchida, and H. Kawasaki, “Design and control of electromyogram prosthetic hand with high grasping force,” Proc. of the 2011 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Biomimetics, pp. 1128-1133, 2011.
- [20] L. U. Odhner, L. P. Jentoft, M. R. Claffee, N. Corson, Y. Tenzer, R. R. Ma, M. Buehler, R. Kohout, R. D. Howe, and A. M. Dollar, “A compliant, underactuated hand for robust manipulation,” The Int. J. of Robotics Research, Vol.33, No.5, pp. 736-752, 2014.
- [21] K. Kawaharazuka, S. Makino, M. Kawamura, Y. Asano, Y. Kakiuchi, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “Human mimetic forearm design with radioulnar joint using miniature bone-muscle modules and its applications,” Proc. of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 4956-4962, 2017.
- [22] S. Makino, K. Kawaharazuka, M. Kawamura, Y. Asano, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “High-power, flexible, robust hand: Development of musculoskeletal hand using machined springs and realization of self-weight supporting motion with humanoid,” Proc. of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1187-1192, 2017.
- [23] K. Kawaharazuka, S. Makino, K. Tsuzuki, M. Onitsuka, Y. Nagamatsu, K. Shinjo, T. Makabe, Y. Asano, K. Okada, K. Kawasaki, and M. Inaba, “Component Modularized Design of Musculoskeletal Humanoid Platform Musashi to Investigate Learning Control Systems,” Proc. of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 7294-7301, 2019.
- [24] Y. Nakanishi, Y. Asano, T. Kozuki, H. Mizoguchi, Y. Motegi, M. Osada, T. Shirai, J. Urata, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “Design Concept of Detail Musculoskeletal Humanoid “Kenshiro” – Toward a real human body musculoskeletal simulator,” Proc. of the 2012 IEEE-RAS Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots, pp. 1-6, 2012.
- [25] Y. Asano, T. Kozuki, S. Ookubo, K. Kawasaki, T. Shirai, K. Kimura, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “A Sensor-driver Integrated Muscle Module with High-tension Measurability and Flexibility for Tendon-driven Robots,” Proc. of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 5960-5965, 2015.
- [26] J. Englsberger, A. Werner, C. Ott, B. Henze, M. A. Roa, G. Garofalo, R. Burger, A. Beyer, O. Eiberger, K. Schmid, and A. Albu-Schäffer, “Overview of the torque-controlled humanoid robot TORO,” Proc. of the 2014 IEEE-RAS Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots, pp. 916-923, 2014.
- [27] M. T. Mason and J. K. Salisbury, “Robot Hands and the Mechanics of Manipulation,” MIT Press, 1985.
- [28] M. C. Carrozza, G. Cappiello, G. Stellin, F. Zaccone, F. Vecchi, S. Micera, and P. Dario, “A Cosmetic Prosthetic Hand with Tendon Driven Under-Actuated Mechanism and Compliant Joints: Ongoing Research and Preliminary Results,” Proc. of the 2005 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2054-2059, 2005.
- [29] J. Yang, K. Abdel-Malek, and J. Potratz, “Design and prototyping of an active hand prosthetic device,” Industrial Robot: An Int. J., Vol.32, No.1, pp. 71-78, 2005.
- [30] C. Gosselin, F. Pelletier, and T. Laliberte, “An anthropomorphic underactuated robotic hand with 15 dofs and a single actuator,” Proc. of The 2008 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 749-754, 2008.
- [31] Y. Asano, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “Design principles of a human mimetic humanoid: Humanoid platform to study human intelligence and internal body system,” Science Robotics, Vol.2, No.13, eaaq0899, 2017.
- [32] I. A. Kapandji, “Physiologie Articulaire,” 6th Edition, Vol.1, Ishiyaku Pub, Inc., 2010.
- [33] D. A. Neumann, “Kinesiology of the Musculoskeletal System: Foundations for Rehabilitation,” Mosby, 2013.
- [34] H. Hirukawa, F. Kanehiro, K. Kaneko, S. Kajita, K. Fujiwara, Y. Kawai, F. Tomita, S. Hirai, K. Tanie, T. Isozumi, K. Akachi, T. Kawasaki, S. Ota, K. Yokoyama, H. Handa, Y. Fukase, J. Maeda, Y. Nakamura, S. Tachi, and H. Inoue, “Humanoid robotics platforms developed in HRP,” Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Vol.48, No.4, pp. 165-175, 2004.
- [35] R. Terasawa, S. Noda, K. Kojima, R. Koyama, F. Sugai, S. Nozawa, Y. Kakiuchi, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “Achievement of Dynamic Tennis Swing Motion by Offline Motion Planning and Online Trajectory Modification Based on Optimization with a Humanoid Robot,” Proc. of the 2016 IEEE-RAS Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots, pp. 1094-1100, 2016.
- [36] S. Ohta, K. Hongo, Y. Nakanishi, I. Mizuuchi, and M. Inaba, “Improvement of Performance for Musculoskeletal Robots by Mountable Actuator Units,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.22, No.3, pp. 391-401, 2010.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.