Paper:
Long-Term Lidar Observations of Volcanic Ash from Sakurajima
Atsushi Shimizu*,†
 , Haruhisa Nakamichi**
, Haruhisa Nakamichi**
 , and Masato Iguchi***
, and Masato Iguchi***

*National Institute for Environmental Studies
16-2 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8506, Japan
†Corresponding author
**Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University
Kagoshima, Japan
***Kagoshima City
Kagoshima, Japan
Lidar observations of volcanic ash in Sakurajima, Japan, were conducted during 2016–2024 to determine the volcanic impact on the atmosphere. The range from the lidar observatory to the vent was divided into four zones, and the characteristics of the extinction coefficient were then analyzed. The discrimination threshold between cloud and volcanic ash was suggested, and volcanic activity reports by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) were employed to explain the long-term variation of the extinction coefficient coupled with the high depolarization ratio measured by lidar. The correlation between the number of eruptions mentioned in the JMA report and the monthly mean extinction coefficient was low. This result suggests other smaller-scale eruptions affect atmospheric conditions around the volcano.
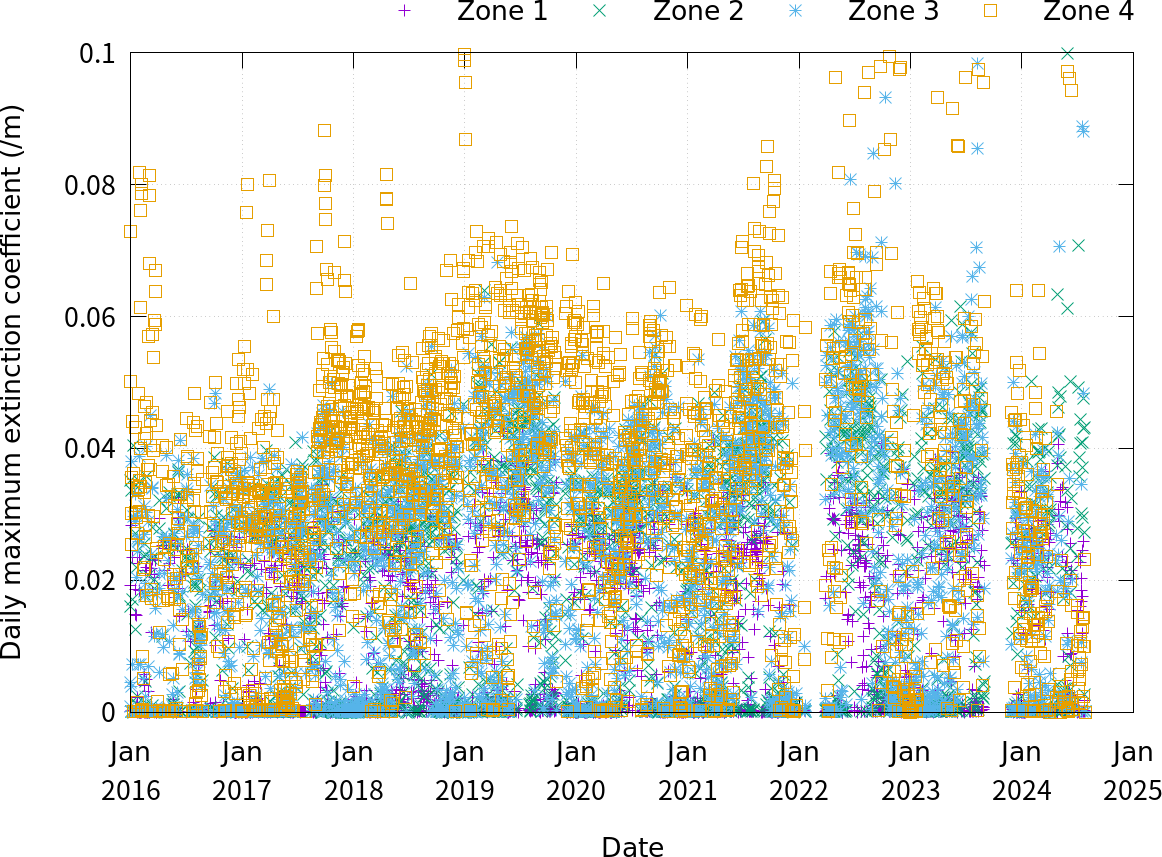
Daily maximum extinction coefficient in four zones.
- [1] J. Heintzenberg, “Fine particles in the global troposphere A review,” Tellus B: Chem. Phys. Meteorol., Vol.41B, No.2, pp. 149-160, 1989. https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v41i2.15064
- [2] International Agency for Research on Cancer, “Air pollution and cancer,” 2013.
- [3] T. Nakamura, Y. Nishiwaki, K. Hashimoto, A. Takeuchi, T. Kitajima, K. Komori, K. Tashiro, H. Hasunuma, K. Ueda, A. Shimizu, H. Odajima, H. Moriuchi, and M. Hashizume, “Association between Asian dust exposure and respiratory function in children with bronchial asthma in Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan,” Environ. Health Prev. Med., Vol.25, No.1, Article No.8, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12199-020-00846-9
- [4] T. Y. Tanaka and M. Chiba, “Global simulation of dust aerosol with a chemical transport model, MASINGAR,” J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn., Ser. II, Vol.83A, pp. 255-278, 2005. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.83A.255
- [5] N. Sugimoto, I. Matsui, Z. Liu, A. Shimizu, K. Asai, K. Yoneyama, and M. Katsumata, “Latitudinal distribution of aerosols and clouds in the western Pacific observed with a lidar on board the research vessel Mirai,” Geophys. Res. Lett., Vol.28, No.22, pp. 4187-4190, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001GL013510
- [6] A. C. Rust and K. V. Cashman, “Permeability controls on expansion and size distributions of pyroclasts,” J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth, Vol.116, No.B11, Article No.B11202, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JB008494
- [7] M. Maki, M. Iguchi, T. Maesaka, T. Miwa, T. Tanada, T. Kozono, T. Momotani, A. Yamaji, and I. Kakimoto, “Preliminary results of weather radar observations of Sakurajima volcanic smoke,” J. Disaster Res., Vol.11, No.1, pp. 15-30, 2016. https://doi.org/10.20965/jdr.2016.p0015
- [8] N. Sugimoto, I. Uno, M. Nishikawa, A. Shimizu, I. Matsui, X. Dong, Y. Chen, and H. Quan, “Record heavy Asian dust in Beijing in 2002: Observations and model analysis of recent events,” Geophys. Res. Lett., Vol.30, No.12, Article No.1640, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GL016349
- [9] A. Shimizu, N. Sugimoto, I. Matsui, K. Arao, I. Uno, T. Murayama, N. Kagawa, K. Aoki, A. Uchiyama, and A. Yamazaki, “Continuous observations of Asian dust and other aerosols by polarization lidars in China and Japan during ACE-Asia,” J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres, Vol.109, Article No.D19S17, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD003253
- [10] T. Nakamura, M. Hashizume, K. Ueda, A. Shimizu, A. Takeuchi, T. Kubo, K. Hashimoto, H. Moriuchi, H. Odajima, T. Kitajima, K. Tashiro, K. Tomimasu, and Y. Nishiwaki, “Asian dust and pediatric emergency department visits due to bronchial asthma and respiratory diseases in Nagasaki, Japan,” J. Epidemiol., Vol.26, No.11, pp. 593-601, 2016. https://doi.org/10.2188/jea.JE20150309
- [11] A. Ansmann, M. Tesche, S. Groß, V. Freudenthaler, P. Seifert, A. Hiebsch, J. Schmidt, U. Wandinger, I. Mattis, D. Müller, and M. Wiegner, “The 16 april 2010 major volcanic ash plume over central europe: Earlinet lidar and aeronet photometer observations at Leipzig and Munich, Germany,” Geophys. Res. Lett., Vol.37, No.13, Article No.L13810, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL043809
- [12] A. Shimizu, M. Iguchi, and H. Nakamichi, “Seasonal variations of volcanic ash and aerosol emissions around Sakurajima detected by two lidars,” Atmosphere, Vol.12, No.3, Article No.326, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030326
- [13] H. Nakamichi, “Lidar observations of eruptive products of the Sakurajima Volcano,” J. Las. Radar Soc. Jpn., Vol.4, No.1, pp. 48-56, 2023 (in Japanese).
- [14] A. Shimizu, T. Nishizawa, Y. Jin, S.-W. Kim, Z. Wang, D. Batdorj, and N. Sugimoto, “Evolution of a lidar network for tropospheric aerosol detection in East Asia,” Opt. Eng., Vol.56, No.3, Article No.03129, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.OE.56.3.031219
- [15] F. G. Fernald, “Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments,” Appl. Opt., Vol.23, No.5, pp. 652-653, 1984. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.23.000652
- [16] A. Shimizu, N. Sugimoto, I. Matsui, I. Mori, M. Nishikawa, and M. Kido, “Relationship between lidar-derived dust extinction coefficients and mass concentrations in Japan,” SOLA, Vol.7A, pp. 1-4, 2011. https://doi.org/10.2151/sola.7A-001
- [17] Committee on Space Research; NASA National Space Science Data Center, “COSPAR International Reference Atmosphere (CIRA-86): Global Climatology of Atmospheric Parameters,” 2006.
- [18] K. Sassen and R. L. Petrilla, “Lidar depolarization from multiple scattering in marine stratus clouds,” Appl. Opt., Vol.25, No.9, pp. 1450-1459, 1986. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.25.001450
- [19] “Volcanic activity reports by JMA Kagoshima Observatory (in Japanese).” https://www.jma-net.go.jp/kagoshima/vol/kazan_top.html [Accessed January 6, 2025]
- [20] E. Del Bello, J. Taddeucci, J. Merrison, K. Rasmussen, D. Andronico, T. Ricci, P. Scarlato, and J. Iversen, “Field-based measurements of volcanic ash resuspension by wind,” Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., Vol.554, Article No.116684, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2020.116684
- [21] S. Itahashi and I. Uno, “Dramatic improvement of aerosol pollution status over the East Asian ocean: From the establishment of japanese environmental quality standard for PM2.5 in 2009 to its achievement in 2021,” Environ. Res. Lett., Vol.19, No.4, Article No.044065, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ad37ce
- [22] A. P. Poulidis, A. Shimizu, H. Nakamichi, and M. Iguchi, “A computational methodology for the calibration of tephra transport nowcasting at Sakurajima Volcano, Japan,” Atmosphere, Vol.12, No.1, Article No.104, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010104
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.