Research Paper:
Intelligent Identification of Subsurface Rock Mass Fractures Based on YOLOv8 with Efficient Channel Attention (ECA)
Zhenkun Wu*1, Yu Ke*2, Yang Li*3, Hui Gao*4, Wangyong He*1
 , Songcheng Tan*4, and Longchen Duan*4,†
, Songcheng Tan*4, and Longchen Duan*4,†
*1School of Automation, China University of Geosciences
No.388 Lumo Road, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China
*2School of Future Technology, China University of Geosciences
No.388 Lumo Road, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China
*3China Solibase Engineering Co., Ltd.
Yard 3 Huihai Middle Road, Shunyi District, Beijing 101300, China
*4Faculty of Engineering, China University of Geosciences
No.388 Lumo Road, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China
†Corresponding author
Fracture identification is an important aspect of assessing rock mass stability. However, manual evaluation of borehole fracture images can be time consuming and lacks quantitative precision, particularly because of the complex shapes of fractures and the challenges in accurately annotating those images. To address these issues, this study uses the YOLOv8 model as a baseline and enhances its feature extraction capability by adding the efficient channel attention (ECA) module. In addition, the wise-intersection over union (WIoU) loss function is adopted to improve the model ability to precisely capture fracture edges. Experimental results showed that adding either the ECA module or the WIoU loss function to the baseline model effectively improved recognition performance. Among various attention modules, ECA achieved the best results. For the four metrics, namely box mAP@50, box mAP@50–95, mask mAP@50, and mask mAP@50–95, the model with only ECA demonstrated notable improvements, as did the model with only WIoU. Furthermore, the model that combined both the ECA module and WIoU loss achieved increases of 5.1% and 4.0% for box mAP@50 and box mAP@50–95, respectively, and 3.9% and 4.5% for mask mAP@50 and mask mAP@50–95, respectively. These combined improvements were greater than the sum of the individual enhancements, indicating a synergistic effect. Tests on new boreholes demonstrated that the proposed model could effectively identify fractures in borehole TV images. However, owing to differences in data distribution, certain small fractures might still be missed. Further efforts are required in future work to enhance the generalizability of the model.
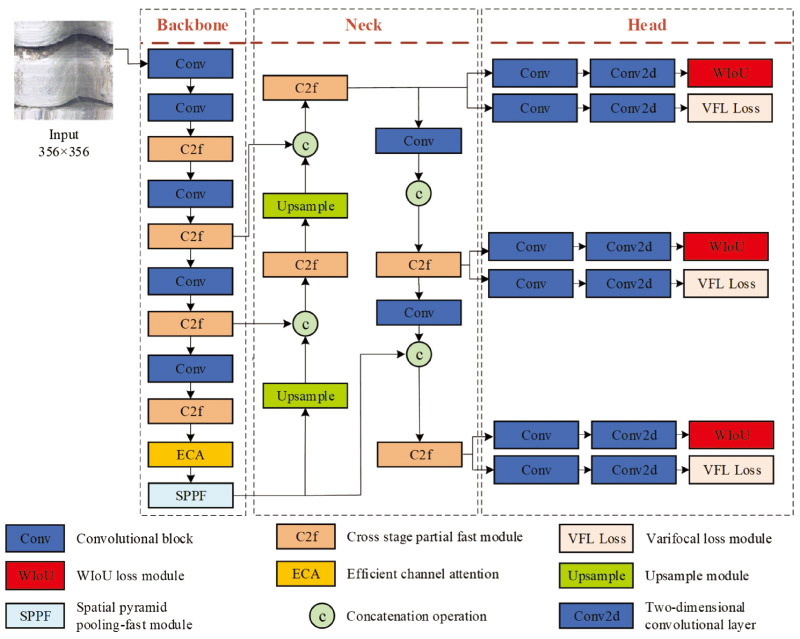
Diagram of the ECA-YOLOv8 network structure
- [1] L. Peng, W. Chao, S. Li, and B. Feng, “Research on crack detection method of airport runway based on twice-threshold segmentation,” 2015 5th Int. Conf. on Instrumentation and Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control (IMCCC), pp. 1716-1720, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/IMCCC.2015.364
- [2] D. Xu, Y. Zhao, Y. Jiang, C. Zhang, B. Sun, and X. He, “Using improved edge detection method to detect mining-induced ground fissures identified by unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing,” Remote Sensing, Vol.13, No.18, Article No.3652, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183652
- [3] H. Xu, Y. Tian, S. Lin, and S. Wang, “Research of image segmentation algorithm applied to concrete bridge cracks,” 2013 IEEE Third Int. Conf. on Information Science and Technology (ICIST), pp. 1637-1640, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIST.2013.6747851
- [4] P. del Rio-Barral, M. Soilan, S. M. Gonzalez-Collazo, and P. Arias, “Pavement crack detection and clustering via region-growing algorithm from 3D MLS point clouds,” Remote Sensing, Vol.14, No.22, Article No.5866, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225866
- [5] M. M. Hittawe, S. M. Muddamsetty, D. Sidibe, and F. Meriaudeau, “Multiple features extraction for timber defects detection and classification using SVM,” 2015 IEEE Int. Conf. on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 427-431, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2015.7350834
- [6] Y. Shi, L. Cui, Z. Qi, F. Meng, and Z. Chen, “Automatic road crack detection using random structured forests,” IEEE Trans. on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Vol.17, No.12, pp. 3434-3445, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2016.2552248
- [7] A. Cubero-Fernandez, F. J. Rodriguez-Lozano, R. Villatoro, J. Olivares, and J. M. Palomares, “Efficient pavement crack detection and classification,” J. on Image and Video Processing, Vol.2017, No.1, Article No.39, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13640-017-0187-0
- [8] M. Azarafza et al., “Application of the modified Q-slope classification system for sedimentary rock slope stability assessment in Iran,” Engineering Geology, Vol.264, No.1, Article No.105349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105349
- [9] L. A. O. Martins, F. L. C. Padua, and P. E. M. Almeida, “Automatic detection of surface defects on rolled steel using computer vision and artificial neural networks,” 36th Annual Conf. on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2010), pp. 1081-1086, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2010.5675519
- [10] O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer, and T. Brox, “U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation,” arXiv:1505.04597, 2015. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1505.04597
- [11] K. He, G. Gkioxari, P. Dollar, and R. Girshick, “Mask R-CNN,” 2017 IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2980-2988, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.322
- [12] C. V. Dung and L. D. Anh, “Autonomous concrete crack detection using deep fully convolutional neural network,” Automation in Construction, Vol.99, pp. 52-58, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2018.11.028
- [13] X. Liu, H. Wang, H. Jing, A. Shao, and L. Wang, “Research on intelligent identification of rock types based on Faster R-CNN method” IEEE Access, Vol.8, pp. 21804-21812, 2020. https://doi.org/DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968515
- [14] X. Yang, H. Li, Y. Yu, X. Luo, T. Huang, and X. Yang, “Automatic pixel-level crack detection and measurement using fully convolutional network,” Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, Vol.33, No.12, pp. 1090-1109, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/mice.12412
- [15] Z. Zhang, Q. Liu, and Y. Wang, “Road extraction by deep residual U-Net,” IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol.15, No.5, pp. 749-753, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2018.2802944
- [16] Z. Liu, Y. Cao, Y. Wang, and W. Wang, “Computer vision-based concrete crack detection using u-net fully convolutional networks,” Automation in Construction, Vol.104, No.8, pp. 129-139, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2019.04.005
- [17] Y. Yuan, N. Zhang, and C. Han, “Automated identification of fissure trace in mining roadway via deep learning,” J. of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Vol.15, No.8, pp. 2039-2052, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.12.018
- [18] S. Zhao, G. Zhang, D. Zhang, D. Tan, and H. Huang, “A hybrid attention deep learning network for refined segmentation of cracks from shield tunnel lining images,” J. of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Vol.15, No.12, pp. 3105-3117, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.02.025
- [19] L. O. Dias et al., “Automatic detection of fractures and breakouts patterns in acoustic borehole image logs using fast-region convolutional neural networks,” J. of Petroleum Science and Engineering, Vol.191, Article No.107099, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107099
- [20] S. Han et al., “Automatic borehole fracture detection and characterization with tailored Faster R-CNN and simplified Hough transform,” Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Vol.126, Article No.107024, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107024
- [21] C. Liu et al., “Intelligent recognition and identification of fracture types and parameters for borehole images based on developed convolutional neural networks and post-processing,” Engineering Fracture Mechanics, Vol.292, Article No.109624, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2023.109624
- [22] Q. Wang et al., “ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks,” 2020 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11531-11539, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155
- [23] Z. Tong, Y. Chen, Z. Xu, and R. Yu, “Wise-IoU: Bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism,” arXiv:2301.10051, 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2301.10051
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.