Research Paper:
Low Illumination Image Enhancement Method Based on White Balance Correction for Conveying Foreign Objects Detection
Mingming Zuo*, Daxin Zheng**, Siyuan Wu**, Ning Jiang**, and Mengchao Zhang**,†

*Shandong Zhaojin Group Company Limited
No.118 Wenquan Road, Zhaoyuan, Yantai 265400, China
**Shandong University of Science and Technology
No.579 Qianwangang Road, Huangdao District, Qingdao 266590, China
†Corresponding author
The presence of foreign objects in conveyor systems significantly contributes to conveyor belt damage and hinders efficient production in enterprises such as mines and ports. To address the reliability challenges posed by low illumination conditions on foreign object detection algorithms, this paper introduces an image adaptive enhancement algorithm based on white balance correction. By developing an end-to-end neural network that simulates the camera’s white balance and gamma correction processes, we achieve an inverse solution to the camera imaging process. Additionally, network training facilitates the updating of weights for the simulated imaging parameters, thereby establishing a correlation between low-illumination images and their enhanced counterparts. Objective image quality evaluation metrics, including PSNR (peak signal-to-noise ratio) and SSIM (structure similarity index measure) demonstrate that the proposed image enhancement algorithm significantly improves image quality and enriches target detail features, with greater improvements observed at lower image brightness levels. When integrated into the YOLOv5 foreign object detection algorithm, experimental results reveal that the enhanced detection algorithm performs better under low illumination conditions, achieving higher detection accuracy on the CUMT-Belt public dataset and substantially reducing the chances of missed detection. This method offers valuable technical support for the intelligent development of belt conveyors and target detection in other low illumination scenarios.
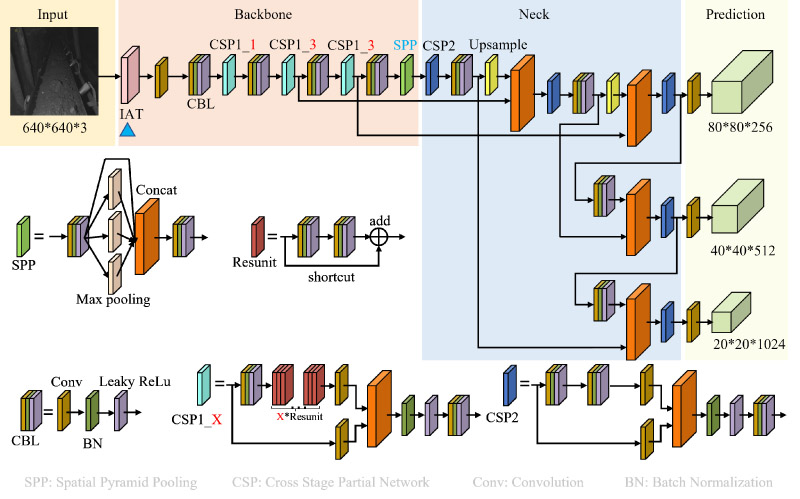
Improved object detection network with ITA
- [1] J. Zhang and D. Tao, “Empowering Things with Intelligence: A Survey of the Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities in Artificial Intelligence of Things,” IEEE Internet of Things J., Vol.8, Issue 10, pp. 7789-7817, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3039359
- [2] B. Ji, Y. Wang, K. Song et al., “A Survey of Computational Intelligence for 6G: Key Technologies, Applications and Trends,” IEEE Trans. on Industrial Informatics, Vol.17, Issue 10, pp. 7145-7154, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2021.3052531
- [3] P. Dąbek, P. Krot, J. Wodeckiet al., “Measurement of idlers rotation speed in belt conveyors based on image data analysis for diagnostic purposes,” Measurement, Vol.202, Article No.111869, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111869
- [4] J. Szrek, J. Wodecki, R. Błażej, and R. Zimroz, “An Inspection Robot for Belt Conveyor Maintenance in Underground Mine – Infrared Thermography for Overheated Idlers Detection,” Applied Sciences, Vol.10, Issue 14, Article No.4984, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144984
- [5] P. Bortnowski, H. Gondek, R. Król et al., “Detection of Blockages of the Belt Conveyor Transfer Point Using an RGB Camera and CNN Autoencoder,” Energies, Vol.16, Issue 4, Article No.1666, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041666
- [6] M. Zhang, Y. Cao, K. Jiang et al., “Proactive measures to prevent conveyor belt failures: Deep learning-based faster foreign object detection,” Engineering Failure Analysis, Vol.141, Article No.106653, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106653
- [7] L. Dai, X. Zhang, P. Gardoni et al., “A new machine vision detection method for identifying and screening out various large foreign objects on coal belt conveyor lines,” Complex & Intelligent Systems, Vol.9, No.5, pp. 5221-5234, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-023-01011-9
- [8] G. Saran, A. Ganguly, V. Tripathi et al., “Multi-Modal Imaging-Based Foreign Particle Detection System on Coal Conveyor Belt,” Trans. of the Indian Institute of Metals, Vol.75, No.9, pp. 2231-2240, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02492-3
- [9] C. K. Xiao, B. Sun, Y. L. Wang, and L. D. Qiu, “Foreign Object Detection of Sintering Transport Belt Based on CNN,” IFAC-PapersOnLine, Vol.54, Issue 21, pp. 25-30, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.12.005
- [10] R. Girshick, “Fast R-CNN,” Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1440-1448, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169
- [11] N. T. Moon, S. A. Siddiqua, S. Parvin et al., “Leveraging Robust CNN Architectures for Real-Time Object Recognition from Conveyor Belt,” 2023 IEEE Symp. on Industrial Electronics & Applications (ISIEA), 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISIEA58478.2023.10212380
- [12] Y. Wang, Y. Wang, and L. Dang, “Video detection of foreign objects on the surface of belt conveyor underground coal mine based on improved SSD,” J. of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, Vol.14, pp. 5507-5516, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02495-w
- [13] D. Varna and V. Abromavičius, “A System for a Real-Time Electronic Component Detection and Classification on a Conveyor Belt,” Applied Sciences, Vol.12, Issue 11, Article No.5608, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115608
- [14] Q. Liu, J. Bi, J. Zhang et al., “B-FPN SSD: An SSD algorithm based on a bidirectional feature fusion pyramid,” The Visual Computer, Vol.39, No.12, pp. 6265-6277, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02727-4
- [15] W. Liu, D. Anguelov, D. Erhan et al., “SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector,” B. Leibe et al. (Eds.), “Computer Vision – ECCV 2016,” 14th European Conf., Part I, pp. 21-37, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
- [16] R. Yao, P. Qi, D. Hua et al., “A Foreign Object Detection Method for Belt Conveyors Based on an Improved YOLOX Model,” Technologies, Vol.11, Issue 5, Article No.114, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11050114
- [17] J. Liu, H. Qiao, L. Yang, and J. Guo, “Improved Lightweight YOLOv4 Foreign Object Detection Method for Conveyor Belts Combined with CBAM,” Applied Sciences, Vol.13, Issue 14, Article No.8465, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148465
- [18] D. Miao, Y. Wang, L. Yang, and S. Wei, “Foreign Object Detection Method of Conveyor Belt Based on Improved Nanodet,” IEEE Access, Vol.11, pp. 23046-23052, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3253624
- [19] B. Luo, Z. Kou, C. Han, and J. Wu, “A “Hardware-Friendly” Foreign Object Identification Method for Belt Conveyors Based on Improved YOLOv8,” Applied Sciences, Vol.13, Issue 20, Article No.11464, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011464
- [20] Y. Kang, “FOD-DETR: Improved DETR based foreign object detection for coal mine conveyor,” 3rd Int. Conf. on Electronic Information Engineering and Data Processing (EIEDP 2024), pp. 1579-1584, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.3032920
- [21] S. N. Matos, O. F. Coletti, R. Zimmer et al., “Machine Learning Techniques for Improving Multiclass Anomaly Detection on Conveyor Belts,” 2024 IEEE Int. Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conf. (I2MTC), 2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/I2MTC60896.2024.10561167
- [22] G. Li, X. Li, Y. Wang et al., “DTG-SSOD: Dense teacher guidance for semi-supervised object detection,” Proc. of the 36th Int. Conf. on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’22), Article No.643, 2022.
- [23] Q. Zhou, C. Yu, Z. Wang et al., “Instant-Teaching: An End-to-End Semi-Supervised Object Detection Framework,” 2021 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4081-4090, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00407
- [24] E. Xie, J. Ding, W. Wang et al., “DetCo: Unsupervised Contrastive Learning for Object Detection,” 2021 IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 8372-8381, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00828
- [25] T. Brooks, B. Mildenhall, T. Xue et al., “Unprocessing Images for Learned Raw Denoising,” 2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11028-11037, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.01129
- [26] C. Guo, C. Li, J. Guo et al., “Zero-Reference Deep Curve Estimation for Low-Light Image Enhancement,” 2020 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1777-1786, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00185
- [27] Y. Jiang, X. Gong, D. Liu et al., “EnlightenGAN: Deep Light Enhancement Without Paired Supervision,” IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, Vol.30, pp. 2340-2349, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3051462
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.