Research Paper:
Linear Transformer Based U-Shaped Lightweight Segmentation Network
Hongli He*
 , Changhao Sun**
, Changhao Sun**
 , Zhaoyuan Wang**
, Zhaoyuan Wang**
 , and Yongping Dan**,†
, and Yongping Dan**,†

*Rail Transit Institute, Henan College of Transportation
No.259 Tonghui Road, Zhengzhou 450061, China
**School of Integrated Circuits, Zhongyuan University of Technology
No.41 Zhongyuan Road, Zhengzhou 450007, China
†Corresponding author
The widespread development and application of embedded medical devices necessitate the corresponding research in lightweight, energy-efficient models. Although transformer-based segmentation models have shown promise in various visual tasks, inherent challenges, including the lack of inductive bias and an overreliance on extensive training data, emerge when striving for optimal model efficiency. By contrast, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), with their intrinsic inductive biases and parameter-sharing mechanisms, enable a reduction in the number of parameters and a focus on capturing local features, thereby lowering computational costs. However, reliance solely on transformers does not meet the practical demands of lightweight model efficiency. Hence, the integration of CNNs with transformers presents a promising research trajectory for constructing efficient and lightweight networks. This hybrid approach leverages the strengths of CNNs in feature extraction and the ability of transformers to model global dependencies, achieving a balance between model performance and efficiency. In this paper, we propose MobileViTv2s, a novel lightweight segmentation network that integrates CNNs with a linear transformer. The proposed network efficiently extracts local features via CNNs, whereas transformers adeptly manage complex feature relationships, thereby facilitating precise segmentation in intricate contexts such as medical imaging. The model demonstrates significant potential and applicability in the advancement of lightweight deep learning models. Experimental results revealed that the proposed model achieved up to a 14.34-fold improvement in efficiency, a 9.91-fold reduction in the number of parameters, and comparable or superior segmentation accuracy, while achieving a markedly lower Hausdorff distance.
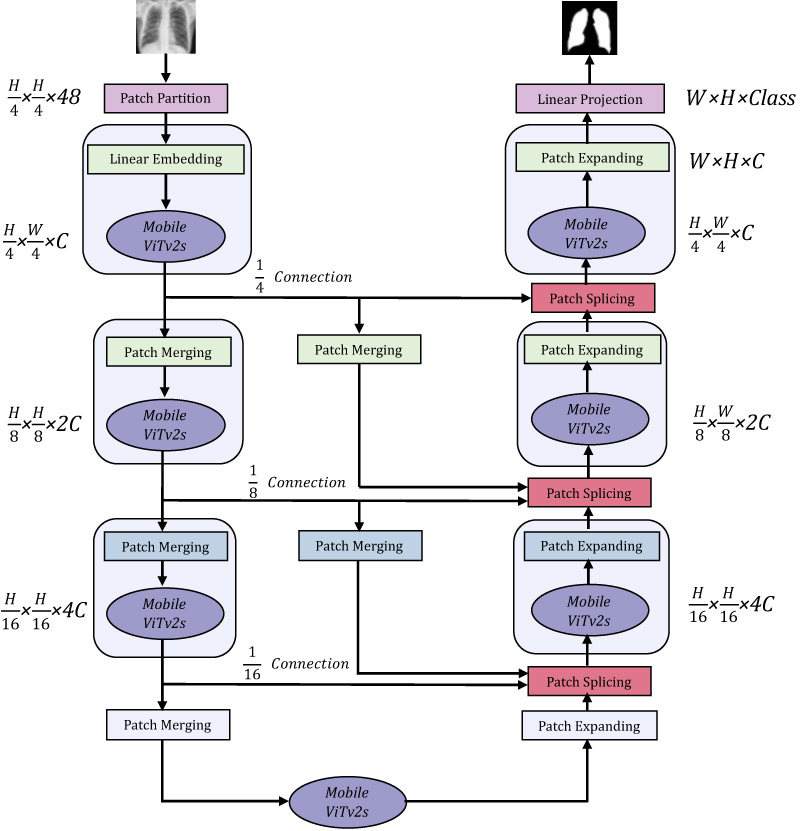
Illustration of the network architecture
- [1] G. Du, X. Cao, J. Liang, X. Chen, and Y. Zhan, “Medical image segmentation based on u-net: A review.” J. of Imaging Science & Technology, Vol.64, No.2, Article No.jist0710, 2020. https://doi.org/10.2352/J.ImagingSci.Technol.2020.64.2.020508
- [2] N. Heller, F. Isensee, K. H. Maier-Hein, X. Hou, C. Xie, F. Li, Y. Nan, G. Mu, Z. Lin, M. Han et al., “The state of the art in kidney and kidney tumor segmentation in contrast-enhanced CT imaging: Results of the kits19 challenge,” Medical Image Analysis, Vol.67, Article No.101821, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101821
- [3] J. Li, J. Chen, Y. Tang, C. Wang, B. A. Landman, and S. K. Zhou, “Transforming medical imaging with transformers? a comparative review of key properties, current progresses, and future perspectives,” Medical Image Analysis, Vol.85, Article No.102762, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2023.102762
- [4] G. Wang, W. Li, M. A. Zuluaga, R. Pratt, P. A. Patel, M. Aertsen, T. Doel, A. L. David, J. Deprest, S. Ourselin et al., “Interactive medical image segmentation using deep learning with image-specific fine tuning,” IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging, Vol.37, No.7, pp. 1562-1573, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2791721
- [5] M. H. Hesamian, W. Jia, X. He, and P. Kennedy, “Deep learning techniques for medical image segmentation: Achievements and challenges,” J. of Digital Imaging, Vol.32, pp. 582-596, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-019-00227-x
- [6] M. Li and P. Vitányi, “Two decades of applied Kolmogorov complexity: In memoriam Andrei Nikolaevich Kolmogorov 1903-87,” Proc. Structure in Complexity Theory 3rd Annual Conf., pp. 80-101, 1988. https://doi.org/10.1109/SCT.1988.5265
- [7] J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell, “Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation,” Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431-3440, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965
- [8] O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer, and T. Brox, “U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation,” 18th Int. Conf. on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2015), pp. 234-241, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
- [9] O. Oktay, J. Schlemper, L. L. Folgoc, M. Lee, M. Heinrich, K. Misawa, K. Mori, S. McDonagh, N. Y. Hammerla, B. Kainz et al., “Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas,” arXiv:1804.03999, 2018.
- [10] Z. Zhou, M. M. Rahman Siddiquee, N. Tajbakhsh, and J. Liang, “UNet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation,” 4th Int. Workshop on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis (DLMIA 2018) and 8th Int. Workshop on Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support (ML-CDS 2018), Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, pp. 3-11, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1
- [11] F. Isensee, P. F. Jaeger, S. A. Kohl, J. Petersen, and K. H. Maier-Hein, “nnU-net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation,” Nature Methods, Vol.18, No.2, pp. 203-211, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-01008-z
- [12] A. Vaswani, “Attention is all you need,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), 2017.
- [13] A. Dosovitskiy, “An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale,” arXiv:2010.11929, 2020.
- [14] J. Chen, Y. Lu, Q. Yu, X. Luo, E. Adeli, Y. Wang, L. Lu, A. L. Yuille, and Y. Zhou, “TransUNet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation,” arXiv:2102.04306, 2021.
- [15] T.-H. Pham, X. Li, and K.-D. Nguyen, “seUNet-trans: A simple yet effective UNet-transformer model for medical image segmentation,” IEEE Access, Vol.12, pp. 122139-122154, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3451304
- [16] F. Shamshad, S. Khan, S. W. Zamir, M. H. Khan, M. Hayat, F. S. Khan, and H. Fu, “Transformers in medical imaging: A survey,” Medical Image Analysis, Vol.88, Article No.102802, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2023.102802
- [17] A. Lin, B. Chen, J. Xu, Z. Zhang, G. Lu, and D. Zhang, “DS-TransUNet: Dual swin transformer u-net for medical image segmentation,” IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement, Vol.71, pp. 1-15, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2022.3178991
- [18] G. Sun, Y. Pan, W. Kong, Z. Xu, J. Ma, T. Racharak, L.-M. Nguyen, and J. Xin, “ DA-TransUNet: Integrating spatial and channel dual attention with transformer u-net for medical image segmentation,” Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, Vol.12, Article No.1398237, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2024.1398237
- [19] S. Pan, X. Liu, N. Xie, and Y. Chong, “EG-TransUNet: a transformer-based u-net with enhanced and guided models for biomedical image segmentation,” BMC Bioinformatics, Vol.24, No.1, Article No.85, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-023-05196-1
- [20] B. Niu, Q. Feng, B. Chen, C. Ou, Y. Liu, and J. Yang, “HSI-TransUNet: A transformer based semantic segmentation model for crop mapping from UAV hyperspectral imagery,” Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, Vol.201, Article No.107297, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2022.107297
- [21] D. Han, X. Pan, Y. Han, S. Song, and G. Huang, “Flatten transformer: Vision transformer using focused linear attention,” Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 5961-5971, 2023.
- [22] J. Chen, J. Mei, X. Li, Y. Lu, Q. Yu, Q. Wei, X. Luo, Y. Xie, E. Adeli, Y. Wang et al., “TransUNet: Rethinking the U-Net architecture design for medical image segmentation through the lens of transformers,” Medical Image Analysis, Vol.97, Article No.103280, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2024.103280
- [23] V. Torre and T. A. Poggio, “On edge detection,” IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, No.2, pp. 147-163, 1986. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.1986.4767769
- [24] U. Mallik, M. Clapp, E. Choi, G. Cauwenberghs, and R. Etienne-Cummings, “Temporal change threshold detection imager,” 2005 IEEE Int. Digest of Technical Papers. Solid-State Circuits Conf., pp. 362-603, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSCC.2005.1494019
- [25] G. Li, D. Jin, Q. Yu, and M. Qi, “IB-TransUNet: Combining information bottleneck and transformer for medical image segmentation,” J. of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, Vol.35, No.3, pp. 249-258, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2023.02.012
- [26] Z. Zhu, M. Sun, G. Qi, Y. Li, X. Gao, and Y. Liu, “Sparse dynamic volume TransUNet with multi-level edge fusion for brain tumor segmentation,” Computers in Biology and Medicine, Article No.108284, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108284
- [27] S. Mehta and M. Rastegari, “MobileViT: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer,” arXiv:2110.02178, 2021.
- [28] S. Mehta and M. Rastegari, “Separable self-attention for mobile vision transformers,” arXiv:2206.02680, 2022.
- [29] W. Wang, E. Xie, X. Li, D.-P. Fan, K. Song, D. Liang, T. Lu, P. Luo, and L. Shao, “Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions,” Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 568-578, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00061
- [30] K. Han, A. Xiao, E. Wu, J. Guo, C. Xu, and Y. Wang, “Transformer in transformer,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vol.34, pp. 15908-15919, 2021.
- [31] X. Zhu, W. Su, L. Lu, B. Li, X. Wang, and J. Dai, “Deformable DETR: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection,” arXiv:2010.04159, 2020.
- [32] H. Wu, B. Xiao, N. Codella, M. Liu, X. Dai, L. Yuan, and L. Zhang, “CvT: Introducing convolutions to vision transformers,” Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 22-31, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00009
- [33] S. P. Morozov, A. E. Andreychenko, N. Pavlov, A. Vladzymyrskyy, N. Ledikhova, V. Gombolevskiy, I. A. Blokhin, P. Gelezhe, A. Gonchar, and V. Y. Chernina, “Mosmeddata: Chest CT scans with covid-19 related findings dataset,” arXiv:2005.06465, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.20.20100362
- [34] J. Ma, Y. Wang, X. An, C. Ge, Z. Yu, J. Chen, Q. Zhu, G. Dong, J. He, Z. He et al., “Toward data-efficient learning: A benchmark for covid-19 CT lung and infection segmentation,” Medical Physics, Vol.48, No.3, pp. 1197-1210, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.14676
- [35] S. Jaeger, A. Karargyris, S. Candemir, L. Folio, J. Siegelman, F. Callaghan, Z. Xue, K. Palaniappan, R. K. Singh, S. Antani et al., “Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs,” IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging, Vol.33, No.2, pp. 233-245, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2013.2284099
- [36] S. Candemir, S. Jaeger, K. Palaniappan, J. P. Musco, R. K. Singh, Z. Xue, A. Karargyris, S. Antani, G. Thoma, and C. J. McDonald, “Lung segmentation in chest radiographs using anatomical atlases with nonrigid registration,” IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging, Vol.33, No.2, pp. 577-590, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2013.2290491
- [37] X. Xiao, S. Lian, Z. Luo, and S. Li, “Weighted Res-UNet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation,” 2018 9th Int. Conf. on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), pp. 327-331, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITME.2018.00080
- [38] X. Huang, Z. Deng, D. Li, and X. Yuan, “MISSFormer: An effective medical image segmentation transformer,” arXiv:2109.07162, 2021.
- [39] M. Heidari, A. Kazerouni, M. Soltany, R. Azad, E. K. Aghdam, J. Cohen-Adad, and D. Merhof, “HiFormer: Hierarchical multi-scale representations using transformers for medical image segmentation,” Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conf. on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 6202-6212, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00614
- [40] H. Cao, Y. Wang, J. Chen, D. Jiang, X. Zhang, Q. Tian, and M. Wang, “Swin-Unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation,” European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 205-218, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25066-8_9
- [41] L.-C. Chen, “Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation,” arXiv:1706.05587, 2017.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.