Research Paper:
Single Human Parsing Based on Visual Attention and Feature Enhancement
Zhi Ma*
 , Lei Zhao**
, Lei Zhao**
 , and Longsheng Wei*,**
, and Longsheng Wei*,**

*Zhejiang Engineering Research Center of Intelligent Urban Infrastructure, Hangzhou City University
48 Huzhan Street, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310015, China
**School of Automation, China University of Geosciences
388 Lumo Road, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China
Human parsing is one of the basic tasks in the field of computer vision. It aims at assigning pixel-level semantic labels to each human body part. Single human parsing requires further associating semantic parts with each instance. Aiming at the problem that it is difficult to distinguish the body parts with similar local features, this paper proposes a single human parsing method based on the visual attention mechanism. The proposed algorithm integrates advanced semantic features, global context information, and edge information to obtain accurate results of single human parsing resolution. The proposed algorithm is validated on standard look into part (LIP) dataset, and the results prove the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
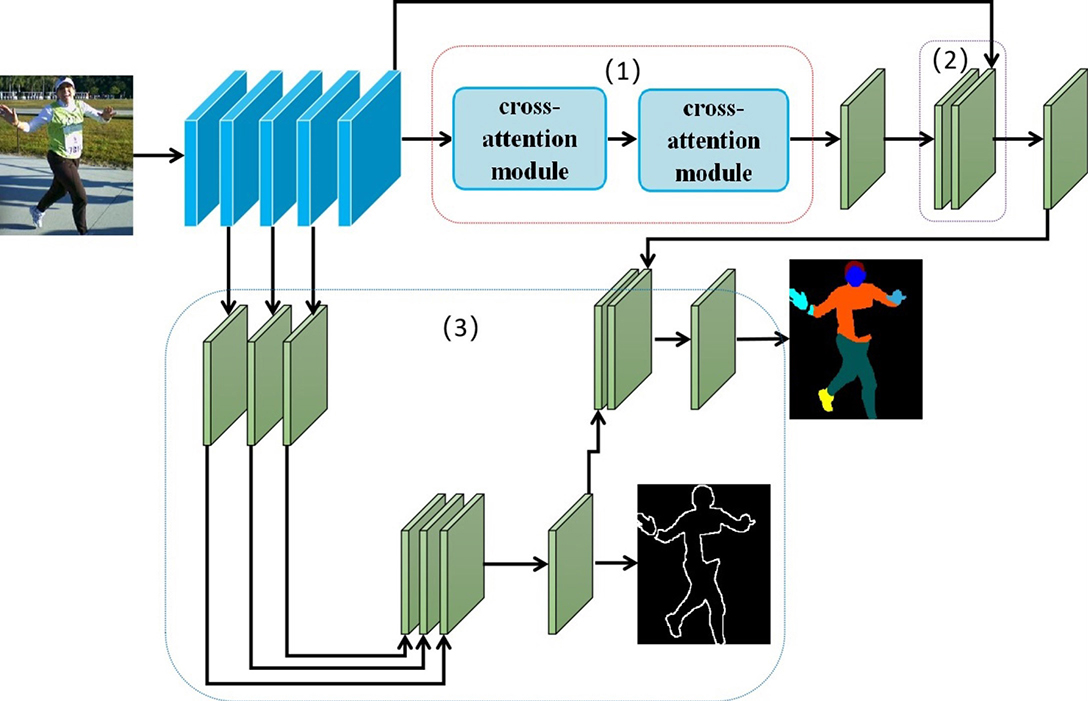
Single human parsing network
- [1] Q. Li, A. Arnab, and P. Torr, “Holistic, instance-level human parsing,” Proc. of the British Machine Vision Conf. (BMVC 2017), pp. 25.1-25.13, 2017. https://doi.org/10.5244/C.31.25
- [2] K. Gong et al., “Instance-level human parsing via part grouping network,” Proc. of the 15th European Conf. on Computer Vision (ECCV 2018), Part 4, pp. 805-822, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0_47
- [3] X. Wang et al., “Non-local neural networks,” 2018 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7794-7803, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00813
- [4] X. Liang et al., “Human parsing with contextualized convolutional neural network,” 2015 IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1386-1394, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.163
- [5] G. Lin et al., “RefineNet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation,” 2017 IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5168-5177, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.549
- [6] L. Yang et al., “Parsing R-CNN for instance-level human analysis,” 2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 364-373, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00045
- [7] T.-Y. Lin et al., “Feature pyramid networks for object detection,” 2017 IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 936-944, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.106
- [8] F. Xia et al., “Pose-guided human parsing by an AND/OR graph using pose-context features,” Proc. of the 30th AAAI Conf. on Artificial Intelligence, Vol.30, No.1, pp. 3632-3640, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v30i1.10460
- [9] J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell, “Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation,” 2015 IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3431-3440, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965
- [10] K. Gong et al., “Look into person: Self-supervised structure-sensitive learning and a new benchmark for human parsing,” 2017 IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6757-6765, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.715
- [11] H.-S. Fang et al., “Weakly and semi supervised human body part parsing via pose-guided knowledge transfer,” 2018 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 70-78, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00015
- [12] J. Zhao et al., “Understanding humans in crowded scenes: Deep nested adversarial learning and a new benchmark for multi-human parsing,” Proc. of the 26th ACM Int. Conf. on Multimedia (MM’18), pp. 792-800, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1145/3240508.3240509
- [13] K. Gong et al., “Graphonomy: Universal human parsing via graph transfer learning,” 2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7442-7451, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00763
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.