Paper:
Efficient Corpus Creation Method for NLU Using Interview with Probing Questions
Kazuaki Shima*, Takeshi Homma**, Masataka Motohashi*, Rintaro Ikeshita**, Hiroaki Kokubo**, Yasunari Obuchi***, and Jinhua She***,†
*Clarion Co., Ltd.
7-2 Shintoshin, Chuo-ku, Saitama, Saitama 330-0081, Japan
**Research & Development Group, Hitachi, Ltd.
1-280 Higashi-koigakubo, Kokubunji, Tokyo 185-8601, Japan
***Tokyo University of Technology
1404-1 Katakura, Hachioji, Tokyo 192-0982, Japan
†Corresponding Author
This paper presents an efficient method to build a corpus to train natural language understanding (NLU) modules. Conventional corpus creation methods involve a common cycle: a subject is given a specific situation where the subject operates a device by voice, and then the subject speaks one utterance to execute the task. In these methods, many subjects are required in order to build a large-scale corpus, which causes a problem of increasing lead time and financial cost. To solve this problem, we propose to incorporate a “probing question” into the cycle. Specifically, after a subject speaks one utterance, the subject is asked to think of alternative utterances to execute the same task. In this way, we obtain many utterances from a small number of subjects. An evaluation of the proposed method applied to interview-based corpus creation shows that the proposed method reduces the number of subjects by 41% while maintaining morphological diversity in a corpus and morphological coverage for user utterances spoken to commercial devices. It also shows that the proposed method reduces the total time for interviewing subjects by 36% compared with the conventional method. We conclude that the proposed method can be used to build a useful corpus while reducing lead time and financial cost.
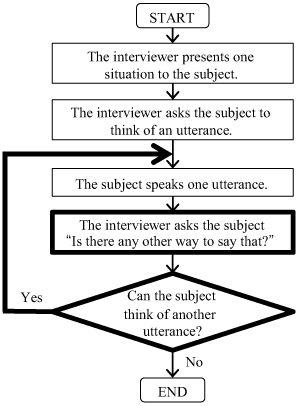
Corpus creation method with probing
- [1] G. Tur, D. Hakkani-Tür, and L. Heck, “What is left to be understood in ATIS?,” Proc. of the 2010 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop, pp. 19-24, 2010.
- [2] R. Sarikaya, G. E. Hinton, and A. Deoras, “Application of Deep Belief Networks for Natural Language Understanding,” IEEE/ACM Trans. on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, Vol.22, No.4, pp. 778-784, 2014.
- [3] Z. Yan and Y. Wu, “A Neural N-Gram Network for Text Classification,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.22, No.3, pp. 380-386, 2018.
- [4] Y.-B. Kim, D. Kim, A. Kumar, and R. Sarikaya, “Efficient Large-Scale Neural Domain Classification with Personalized Attention,” Proc. of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vol.1, pp. 2214-2224, 2018.
- [5] G. Kurata, O. Ichikawa, and M. Nishimura, “Speech Input Method in Automobiles Reflecting Analysis on How Users Speak,” IEICE Trans. on Information and Systems (Japanese Edition), Vol.J93-D, No.10, pp. 2107-2117, 2010 (in Japanese).
- [6] T. Homma, K. Shima, and T. Matsumoto, “Robust utterance classification using multiple classifiers in the presence of speech recognition errors,” Proc. of the 2016 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop, pp. 369-375, 2016.
- [7] T. Homma, Y. Obuchi, K. Shima, R. Ikeshita, H. Kokubo, and T. Matsumoto, “In-Vehicle Voice Interface with Improved Utterance Classification Accuracy Using Off-the-Shelf Cloud Speech Recognizer,” IEICE Trans. on Information and Systems, Vol.E101-D, No.12, pp. 3123-3137, 2018.
- [8] C. T. Hemphill, J. J. Godfrey, and G. R. Doddington, “The ATIS spoken language systems pilot corpus,” HLT’90 Proc. of the Workshop on Speech and Natural Language Workshop, pp. 96-101, 1990.
- [9] L. Hirschman, “Multi-site data collection for a spoken language corpus,” HLT’91 Proc. of the Workshop on Speech and Natural Language Workshop, pp. 7-14, 1992.
- [10] J. Goto, K. Komine, M. Miyazaki, Y.-B. Kim, and N. Uratani, “A Spoken Dialogue Interface for TV Operations Based on Data Collected by Using WOZ Method,” IEICE Trans. on Information and Systems, Vol.E87-D, No.6, pp. 1397-1404, 2004.
- [11] M. Tateishi, K. Asami, I. Akahori, S. Judy, Y. Obuchi, T. Mitamura, E. Nyberg, and N. Hataoka, “A Spoken Dialog Corpus for Car Telematics Services,” H. Abut, J. H. L. Hansen, and K. Takeda (Eds.), “DSP for In-Vehicle and Mobile Systems,” pp. 47-64, Springer, 2005.
- [12] K. Shima, T. Homma, R. Ikeshita, H. Kokubo, Y. Obuchi, and J. She, “Interview-style-based Method of Collecting Spontaneous Speech Corpus for Car Navigation Systems,” IEICE Trans. on Information and Systems (Japanese Edition), Vol.J101-D, No.2, pp. 446-455, 2018 (in Japanese).
- [13] Y. Wang, J. Berant, and P. Liang, “Building a Semantic Parser Overnight,” Proc. of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th Int. Joint Conf. on Natural Language Processing, Vol.1, pp. 1332-1342, 2015.
- [14] G. Campagna, R. Ramesh, S. Xu, M. Fischer, and M. S. Lam, “Almond: The Architecture of an Open, Crowdsourced, Privacy-Preserving, Programmable Virtual Assistant,” Proc. of the 26th Int. Conf. on World Wide Web (WWW’17), pp. 341-350, 2017.
- [15] A. Coucke, A. Saade, A. Ball, T. Bluche, A. Caulier, D. Leroy, C. Doumouro, T. Gisselbrecht, F. Caltagirone, T. Lavril, M. Primet, and J. Dureau, “Snips Voice Platform: an embedded Spoken Language Understanding system for private-by-design voice interfaces,” arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1805.10190, 2018.
- [16] K. Shima, T. Homma, M. Motohashi, R. Ikeshita, H. Kokubo, Y. Obuchi, and J. She, “Efficient Corpus Creation with Reduced Number of Subjects for Natural Language Understanding,” Proc. ot the 8th Int. Symp. on Computational Intelligence and Industrial Applications and the 12th China Japan Int. Workshop on Information Technology and Control Applications (ISCIIA & ITCA 2018), No.3M1-3-5, 2018.
- [17] K. J. Roulston, “Probes and probing,” L. M. Given (Ed.), “The SAGE Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods,” pp. 681-683, SAGE Publishing, 2008.
- [18] MeCab, http://taku910.github.io/mecab/ [accessed February 10, 2019]
- [19] Clarion Co., Ltd., “Intelligent VOICE,” http://www.clarion.com/jp/ja/products-personal/service/IntelligentVoice/index.html [accessed February 10, 2019]
- [20] Clarion Co., Ltd., http://www.clarion.com/top.html [accessed February 10, 2019]
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.