Research Paper:
Interactive Image Caption Generation Reflecting User Intent from Trace Using a Diffusion Language Model
Satoko Hirano and Ichiro Kobayashi

Ochanomizu University
2-1-1 Otsuka, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 112-8610, Japan
This study proposes an image captioning method designed to incorporate user-specific explanatory intentions into the generated text, as signaled by the user’s trace on the image. We extract areas of interest from dense sections of the trace, determine the order of explanations by tracking changes in the pen-tip coordinates, and assess the degree of interest in each area by analyzing the time spent on them. Additionally, a diffusion language model is utilized to generate sentences in a non-autoregressive manner, allowing control over sentence length based on the temporal data of the trace. In the actual caption generation task, the proposed method achieved higher string similarity than conventional methods, including autoregressive models, and successfully captured user intent from the trace and faithfully reflected it in the generated text.
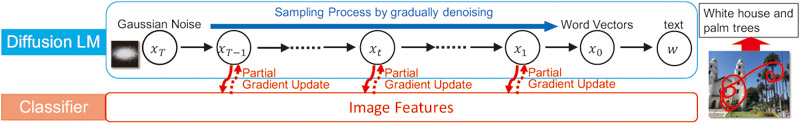
Overview of the proposed method
- [1] D. Driess, F. Xia, M. S. M. Sajjadi, C. Lynch, A. Chowdhery, B. Ichter, A. Wahid, J. Tompson, Q. Vuong, T. Yu, W. Huang, Y. Chebotar, P. Sermanet, D. Duckworth, S. Levine, V. Vanhoucke, K. Hausman, M. Toussaint, K. Greff, A. Zeng, I. Mordatch, and P. Florence, “Palm-e: An embodied multimodal language model,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2303.03378, 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.03378
- [2] A. Radford, J. W. Kim, C. Hallacy, A. Ramesh, G. Goh, S. Agarwal, G. Sastry, A. Askell, P. Mishkin, J. Clark, G. Krueger, and I. Sutskever, “Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2103.00020, 2021. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2103.00020
- [3] J. Li, D. Li, C. Xiong, and S. Hoi, “BLIP: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified vision-language understanding and generation,” Proc. of the 39th Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 12888-12900, 2022.
- [4] J. Li, D. Li, S. Savarese, and S. Hoi, “BLIP-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models,” Proc. of the 40th Int. Conf. on Machine Learning (ICML’23), pp. 19730-19742, 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2301.12597
- [5] A. Bhattacharyya, M. Palmer, and C. Heckman, “ReCAP: Semantic role enhanced caption generation,” Proc. of the 2024 Joint Int. Conf. on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024), pp. 13633-13649, 2024.
- [6] K. Basioti, M. A. Abdelsalam, F. Fancellu, V. Pavlovic, and A. Fazly, “Cic-bart-ssa: Controllable image captioning with structured semantic augmentation,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2407.11393, 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.11393
- [7] S. Mao, C. Zhang, H. Su, H. Song, I. Shalyminov, and W. Cai, “Controllable contextualized image captioning: Directing the visual narrative through user-defined highlights,” Proc. of the 18th European Conf. on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72973-7_27
- [8] X. Wang, M. Diao, B. Li, H. Zhang, K. Liang, and Z. Ma, “From simple to professional: A combinatorial controllable image captioning agent,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2412.11025, 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2412.11025
- [9] Y. Zhao, Y. Liu, Z. Guo, W. Wu, C. Gong, F. Wan, and Q. Ye, “Controlcap: Controllable region-level captioning,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2401.17910, 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2401.17910
- [10] A. Ramesh, P. Dhariwal, A. Nichol, C. Chu, and M. Chen, “Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with clip latents,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2204.06125, 2022. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2204.06125
- [11] R. Rombach, A. Blattmann, D. Lorenz, P. Esser, and B. Ommer, “High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2112.10752, 2021. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2112.10752
- [12] X. L. Li, J. Thickstun, I. Gulrajani, P. Liang, and T. Hashimoto, “Diffusion-lm improves controllable text generation,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2205.14217, 2022. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2205.14217
- [13] J. Ho and T. Salimans, “Classifier-free diffusion guidance,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2207.12598, 2022. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2207.12598
- [14] A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, J. Uszkoreit, L. Jones, A. N. Gomez, L. u. Kaiser, and I. Polosukhin, “Attention is all you need,” Prof. of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Vol.30, 2017.
- [15] O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer, and T. Brox, “U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation,” Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2015), pp. 234-241, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
- [16] H. Zhang, X. Liu, and J. Zhang, “DiffuSum: Generation enhanced extractive summarization with diffusion,” Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2023), pp. 13089-13100, 2023. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2023.findings-acl.828.
- [17] S. Gong, M. Li, J. Feng, Z. Wu, and L. Kong, “DiffuSeq: Sequence to sequence text generation with diffusion models,” Proc. of Int. Conf. on Learning Representations (ICLR 2023), 2023.
- [18] H. Yuan, Z. Yuan, C. Tan, F. Huang, and S. Huang, “Seqdiffuseq: Text diffusion with encoder-decoder transformers,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2212.10325, 2022. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2212.10325
- [19] P. Dhariwal and A. Nichol, “Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2105.05233, 2021. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2105.05233
- [20] X. Han, S. Kumar, and Y. Tsvetkov, “SSD-LM: Semi-autoregressive simplex-based diffusion language model for text generation and modular control,” Proc. of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Vol.1: Long Papers), pp. 11575-11596, 2023. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2023.acl-long.647.
- [21] Z. Horvitz, A. Patel, C. Callison-Burch, Z. Yu, and K. McKeown, “Paraguide: Guided diffusion paraphrasers for plug-and-play textual style transfer,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2308.15459, 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2308.15459
- [22] T. Wu, Z. Fan, X. Liu, Y. Gong, Y. Shen, J. Jiao, H.-T. Zheng, J. Li, Z. Wei, J. Guo, N. Duan, and W. Chen, “Ar-diffusion: Auto-regressive diffusion model for text generation,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2305.09515, 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.09515
- [23] J. Ho, A. Jain, and P. Abbeel, “Denoising diffusion probabilistic models,” Prof. of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’20), Vol.33, pp. 6840-6851, 2020.
- [24] J. Sohl-Dickstein, E. Weiss, N. Maheswaranathan, and S. Ganguli, “Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics,” Proc. of the 32nd Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 2256-2265, 2015.
- [25] J. Pont-Tuset, J. Uijlings, S. Changpinyo, R. Soricut, and V. Ferrari, “Connecting vision and language with localized narratives,” European Conf. on Computer Vision (ECCV 2020), pp. 647-664, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58558-7_38
- [26] J. Hessel, A. Holtzman, M. Forbes, R. Le Bras, and Y. Choi, “CLIPScore: A reference-free evaluation metric for image captioning,” Proc. of the 2021 Conf. on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 7514-7528, 2021. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.emnlp-main.595
- [27] A. Karpathy and L. Fei-Fei, “Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions,” 2015 IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3128-3137, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298932
- [28] I. Loshchilov and F. Hutter, “Decoupled weight decay regularization,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:1711.05101, 2019. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1711.05101
- [29] K. Papineni, S. Roukos, T. Ward, and W.-J. Zhu, “Bleu: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation,” Proc. of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 311-318, 2002. https://doi.org/10.3115/1073083.1073135
- [30] C.-Y. Lin, “ROUGE: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries,” Text Summarization Branches Out (WAS 2004), pp. 74-81, 2004.
- [31] T. Zhang, V. Kishore, F. Wu, K. Q. Weinberger, and Y. Artzi, “Bertscore: Evaluating text generation with bert,” Int. Conf. on Learning Representations (ICLR 2020), 2020.
- [32] C. Deng, N. Ding, M. Tan, and Q. Wu, “Length-controllable image captioning,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2007.09580, 2020. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2007.09580
- [33] J. Wang, Z. Yang, X. Hu, L. Li, K. Lin, Z. Gan, Z. Liu, C. Liu, and L. Wang, “Git: A generative image-to-text transformer for vision and language,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2205.14100, 2022. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2205.14100
- [34] S. Watanabe and I. Kobayashi, “Image captioning that reflects the intent of the explainer based on tracing with a pen,” Proc. of the 36th Annual Conf. of the Japanese Society for Artificial Intelligence (JSAI2022), Article No.3Yin2-23, 2022 (in Japanese). https://doi.org/10.11517/pjsai.JSAI2022.0_3Yin223
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.