Research Paper:
System for Analyzing User Interest Based on Eye Gaze Responses to Enhance Empathy with Users
Jinseok Woo†
 and Jiaren Hu
and Jiaren Hu
Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Engineering, Tokyo University of Technology
1404-1 Katakuracho, Hachioji, Tokyo 192-0982, Japan
†Corresponding author
Recently, robotic systems that offer practical services in everyday life, such as smart home systems, have been developed. The latest trend moves beyond user-controlled internal systems through traditional methods, such as remote controls, to systems that autonomously understand user contexts and evolve to provide a more comfortable living environment. Therefore, this research aims to advance this field by exploring the potential of a system capable of understanding human conditions and behavior, and by proposing or executing actions that align with an individual’s intended actions. To investigate a system capable of achieving this goal, we focused on analyzing the gazes of users and developed an eyeglass-type wearable device. The primary objective of this study was to track a specific user’s gaze, identify the object of focus, and analyze the user’s level of attention and interest in that object. Therefore, for the sensory configuration of the system, an analysis was performed using data collected from camera sensors for eye tracking and sensors for measuring environmental information. Based on the analysis results, we evaluated whether the system could accurately interpret and anticipate the actions that user intended to perform.
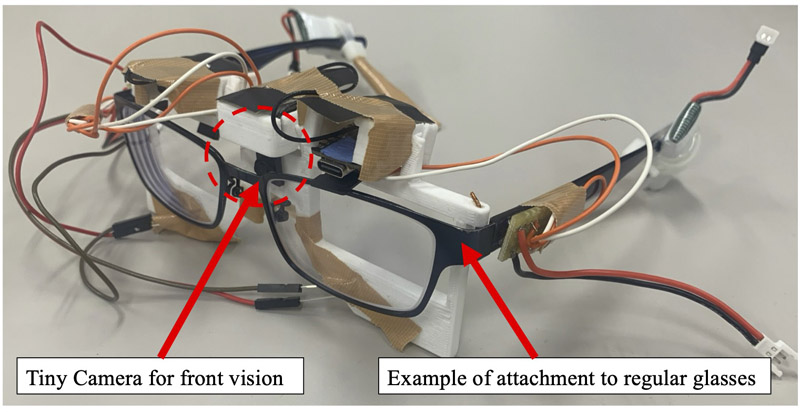
Wearable device for gaze measurement
- [1] C. Ming, S. Kadry, and A. A. Dasel, “Automating smart internet of things devices in modern homes using context-based fuzzy logic,” Computational Intelligence, Vol.40, No.1, Article No.e12370, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1111/coin.12370
- [2] A. Almusaed, I. Yitmen, and A. Almssad, “Enhancing smart home design with ai models: A case study of living spaces implementation review,” Energies, Vol.16, No.6, Article No.2636, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16062636
- [3] M. K. I. Shafi, M. R. Sultan, S. M. M. Rahman, and M. M. Hoque, “Iot based smart home: A machine learning approach,” 2021 24th Int. Conf. on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCIT54785.2021.9689786
- [4] Y. Mittal, P. Toshniwal, S. Sharma, D. Singhal, R. Gupta, and V. K. Mittal, “A voice-controlled multi-functional smart home automation system,” 2015 Annual IEEE India Conf. (INDICON), 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/INDICON.2015.7443538
- [5] D. Marikyan, S. Papagiannidis, and E. Alamanos, “A systematic review of the smart home literature: A user perspective,” Technological Forecasting and Social Change, Vol. 138, pp. 139-154, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.08.015
- [6] M. Tomasello, “Origins of Human Communication,” MIT Press, 2010.
- [7] R. Jahanmahin, S. Masoud, J. Rickli, and A. Djuric, “Human-robot interactions in manufacturing: A survey of human behavior modeling,” Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, Vol.78, Article No.102404, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2022.102404
- [8] Y. Sone, J. Woo, and Y. Ohyama, “Designing an interactive robot interface for a user-friendly information support system,” ISIS2023 The 24th Int. Symp. on Advanced Intelligent Systems, pp. 485-491, 2023.
- [9] J. Hu, J. Woo, and Y. Ohyama, “Development of a measurement system based on level of interest for providing human-friendly services,” The 11th Int. Symp. on Computational Intelligence and Industrial Applications (ISCIIA 2024) & the 15th China-Japan Int. Workshop on Information Technology and Control Applications (ITCA2024) (ISCIIA&ITCA2024), 2024.
- [10] Y. Amirat, D. Daney, S. Mohammed, A. Spalanzani, A. Chibani, and O. Simonin, “Assistance and service robotics in a human environment,” Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Vol.75, Part A, pp. 1-3, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2015.11.002
- [11] J. Woo, T. Sato, and Y. Ohyama, “Development of a human-centric system using an iot-based socially embedded robot partner,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.35, No.3, pp. 859-866, 2023. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2023.p0859
- [12] C. Ohneberg, N. Stöbich, A. Warmbein, I. Rathgeber, A. C. Mehler-Klamt, U. Fischer, and I. Eberl, “Assistive robotic systems in nursing care: a scoping review,” BMC Nursing, Vol.22, No.1, Article No.72, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-023-01230-y
- [13] D. Buil-Gil, S. Kemp, S. Kuenzel, L. Coventry, S. Zakhary, D. Tilley, and J. Nicholson, “The digital harms of smart home devices: A systematic literature review,” Computers in Human Behavior, Vol.145, Article No.107770, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2023.107770
- [14] S. Alghamdi and S. Furnell, “Assessing security and privacy insights for smart home users,” Proc. of the 9th Int. Conf. on Information Systems Security and Privacy – Volume 1: ICISSP, pp. 592-599, 2023. https://doi.org/10.5220/0011741800003405
- [15] Y. Li, P. Xu, D. Lagun, and V. Navalpakkam, “Towards measuring and inferring user interest from gaze,” Proc. of the 26th Int. Conf. on World Wide Web Companion, pp. 525-533, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1145/3041021.3054182
- [16] J. Redmon, S. Divvala, R. Girshick, and A. Farhadi, “You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection,” 2016 IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 779-788, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.91
- [17] S. Imambi, K. Prakash, and G. Kanagachidambaresan, “PyTorch,” Springer International Publishing, 2021, pp. 87-104. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57077-4_10
- [18] S. Croom, H. Zhou, and C. Firestone, “Seeing and understanding epistemic actions,” Proc. of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 120, No.49, Article No.e2303162120, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2303162120
- [19] R. Faragher and R. Harle, “Location fingerprinting with bluetooth low energy beacons,” IEEE J. on Selected Areas in Communications, Vol.33, No.11, pp. 2418-2428, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2015.2430281
- [20] P. S. Farahsari, A. Farahzadi, J. Rezazadeh, and A. Bagheri, “A survey on indoor positioning systems for iot-based applications,” IEEE Internet of Things J., Vol.9, No.10, pp. 7680-7699, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2022.3149048
- [21] Y. Zhang, J. Liu, and W. Shen, “A review of ensemble learning algorithms used in remote sensing applications,” Applied Sciences, Vol.12, No.17, Article No.8654, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178654
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.