Letter:
Soft Microswimmer Powered by Fluid Oscillation
Takuji Ishikawa*,**, Takeru Morita***, and Toshihiro Omori**
*Department of Biomedical Engineering, Tohoku University
6-6-01 Aoba, Aramaki, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8579, Japan
**Department of Finemechanics, Tohoku University
6-6-01 Aoba, Aramaki, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8579, Japan
***Shimadzu Corp.
1 Nishinokyo Kuwabara-cho, Nakagyo-ku, Kyoto 604-8511, Japan
In this letter, we review the results of our recent studies on a soft microswimmer powered by fluid oscillations. The microswimmer consists of an elastic membrane with a prolate spheroidal reference shape containing a rigid sphere. The swimming direction can be controlled by appropriately applying fluid oscillations. The obtained knowledge will be useful for future artificial microswimmer designs.
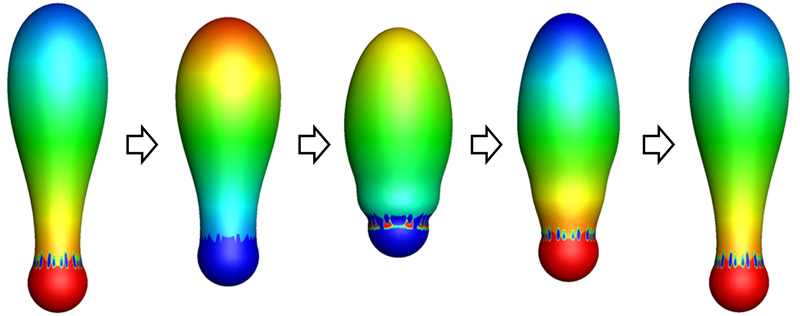
Upward propulsion of a soft microrobot
- [1] T. Morita, T. Omori, and T. Ishikawa, “Passive swimming of a microcapsule in vertical fluid oscillation,” Phys. Rev. E, Vol.98, Issue 2, 023108, 2018.
- [2] T. Morita, T. Omori, and T. Ishikawa, “Biaxial fluid oscillations can propel a microcapsule swimmer in an arbitrary direction,” Phys. Rev. E, Vol.98, Issue 6, 063102, 2018.
- [3] T. Morita, T. Omori, Y. Nakayama, S. Toyabe, and T. Ishikawa, “Harnessing random low Reynolds number flow for net migration,” Phys. Rev. E, Vol.101, Issue 6, 063101, 2020.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.