Development Report:
Remote Ultrasound Diagnostic System (RUDS)
Norihiro Koizumi*, Takehiko Tsurumi*, Takahiro Kato*,
Shin’ichi Warisawa*, Mitsuru Nagoshi**, Hiroyuki Hashizume***,
and Mamoru Mitsuishi*
*School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656, Japan
**Nagoshi Orthopaedics, 229-2 Niwase, Okayama, Okayama 701-153, Japan
***Kasaoka Daiichi Hospital, 1945 Yokoshima, Kasaoka, Okayama 714-0043, Japan
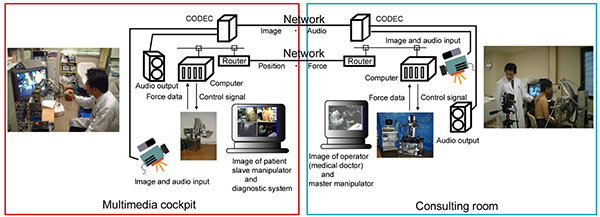 Remote Ultrasound Diagnostic System
Remote Ultrasound Diagnostic System- [1] M. Mitsuishi, S. Warisawa, T. Tsuda, T. Higuchi, N. Koizumi, H. Hashizume, and K. Fujiwara, “Remote Ultrasound Diagnostic Sys-Fig. 3. Slave manipulator configuration and coordinates.tem,” Proc. of 2001 Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation, Vol.2, pp. 1567-1573, 2001.
- [2] N. Koizumi, S. Warisawa, M. Nagoshi, H. Hashizume, and M. Mitsuishi, “Construction methodology for a remote ultrasound diagnostic system,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics, Vol.25, pp. 522-538, 2009.
- [3] N. Koizumi, J. Seo, T. Funamoto, A. Nomiya, A. Ishikawa, K. Yoshinaka, N. Sugita, Y. Homma, Y. Matsumoto, and M. Mitsuishi, “Technologizing and Digitalizing Medical Professional Skills for a Non-Invasive Ultrasound Theragnostic System,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.24, No.2, pp. 379-388, 2012.
- [4] N. Koizumi, H. Tsukihara, S. Takamoto, H. Hashizume, and M. Mitsuishi, “Robot Vision Technology for Technologizing and Digitalization of Medical Diagnostic and Therapeutic Skills,” Int. J. of Automation Technology, Vol.3, No.5, pp. 541-550, 2009.
- [5] N. Koizumi, T. Tsurumi, S. Warisawa, H. Hashizume, and M. Mitsuishi, “Probe positioning support utilizing shoulder model for ultrasound diagnosis,” Proc. of 2006 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intelligent Robotics and Systems, Vol.1, pp. 155-161, 2006.
- [6] N. Koizumi, S. Warisawa, M. Mitsuishi, and H. Hashizume, “Impedance Controller for a Remote Ultrasound Diagnostic System,” Proc. of 2002 Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation, Vol.1, pp. 651-656, 2002.
- [7] N. Koizumi, S. Warisawa, H. Hashizume, and M. Mitsuishi, “Dynamic Switching of a Controller Based on Diagnostic Tasks in Remote Ultrasound Diagnostics,” J. of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.16, No.2, pp. 146-154, 2004.
- [8] N. Koizumi, S. Warisawa, M. Mitsuishi, and H. Hashizume, “Continuous Path Controller of Slave Manipulator in Remote Ultrasound Diagnostic System,” Proc. of 2002 Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation, Vol.4, pp. 3368-3373, 2002.
- [9] N. Koizumi, S. Warisawa, H. Hashizume, and M. Mitsuishi, “Continuous path controller for the remote ultrasound diagnostic system,” IEEE/ASME Trans. on Mechatronics, Vol.12, No.2, pp. 206-218, 2008.
- [10] N. Koizumi, S. Warisawa, M. Mitsuishi, and H. Hashizume, “Impedance Controller and its Clinical Use of the Remote Ultrasound Diagnostic System,” Proc. of 2003 Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation, Vol.1, pp. 676-683, 2003.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.