Research Paper:
Improved Pure Pursuit Algorithm Based Path Tracking Method for Autonomous Vehicle
Meng Wang*
 , Xue Lv*
, Xue Lv*
 , Juexuan Chen**,†
, Juexuan Chen**,†
 , and Xiaocong Su**
, and Xiaocong Su**
*Changjiang Institute of Technology
No.9 Wenhua Avenue, Jiangxia District, Wuhan, Hubei 430212, China
**Wuhan Goyu Intelligence Technology Co., Ltd.
No.1 Fenghuang Yuan 3rd Road, East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430200, China
†Corresponding author
Pure pursuit algorithm is commonly used in path tracking control of autonomous vehicle for its high real-time performance. Due to the problem of “taking shortcuts,” traditional pure pursuit algorithms usually have the problem of low path tracking accuracy in curved road scenarios. To address the issue, a path tracking control method based on improved pure pursuit algorithm is proposed. This method builds upon traditional pure pursuit theory and dynamically adjusts the look-ahead distance based on vehicle speed and road curvature radius information, allowing it to adapt to different road scenarios. This effectively addresses the problem of large path tracking errors in curved road scenarios. Furthermore, a fuzzy feedback control is employed to compensate for control variable and enhance tracking accuracy across various scenarios. Simulations and real-world experiments demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves path tracking accuracy compared to traditional pure pursuit methods, particularly in curved road scenarios. The maximum lateral deviation is reduced by over 50%, realizing the precise tracking of autonomous vehicle on the park roads.
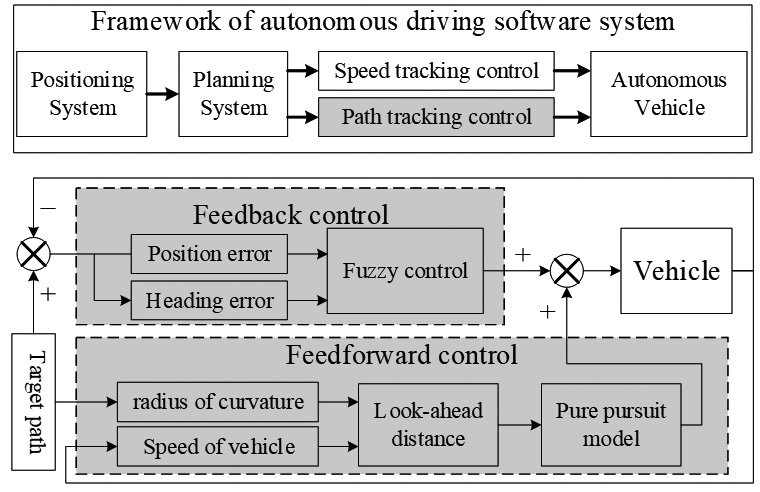
Lateral control block diagram
- [1] K.-Y. Kwon et al., “Autonomous vehicle path tracking based on natural gradient methods,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.16, No.7, pp. 888-893, 2012. https://doi.org/10.20965/jaciii.2012.p0888
- [2] S. Matsumoto and M. Saito, “Adaptive identification method for vehicle driving model capable of driving with large acceleration changes and steering,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.27, No.4, pp. 609-615, 2023. https://doi.org/10.20965/jaciii.2023.p0609
- [3] M. Samuel, M. Hussein, and M. B. Mohamad, “A review of some pure-pursuit based path tracking techniques for control of autonomous vehicle,” Int. J. of Computer Applications, Vol.135, No.1, pp. 35-38, 2016. https://doi.org/10.5120/ijca2016908314
- [4] W.-J. Wang, T.-M. Hsu, and T.-S. Wu, “The improved pure pursuit algorithm for autonomous driving advanced system,” 2017 IEEE 10th Int. Workshop on Computational Intelligence and Applications (IWCIA), pp. 33-38, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWCIA.2017.8203557
- [5] W. Lv et al., “An improved algorithm based on pure pursuit model for path tracking,” Measurement & Control Technology, Vol.30, No.7, pp. 93-96+100, 2011 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.19708/j.ckjs.2011.07.024
- [6] L. Yu et al., “Driverless bus path tracking based on fuzzy pure pursuit control with a front axle reference,” Applied Sciences, Vol.10, No.1, Article No.230, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010230
- [7] H. Wang et al., “Trajectory tracking and speed control of cleaning vehicle based on improved pure pursuit algorithm,” 2019 Chinese Control Conf., pp. 4348-4353, 2019. https://doi.org/10.23919/ChiCC.2019.8865255
- [8] B. Guo, X. Du, and X. Tao, “Algorithm improvement based on pure tracking model,” Automobile Applied Technology, Vol.2019, No.15, pp. 32-34, 2019 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.16638/j.cnki.1671-7988.2019.15.012
- [9] Q. Sun et al., “Path tracking control of wheeled mobile robot based on improved pure pursuit algorithm,” 2019 Chinese Automation Congress, pp. 4239-4244, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CAC48633.2019.8997258
- [10] M.-W. Park, S.-W. Lee, and W.-Y. Han, “Development of lateral control system for autonomous vehicle based on adaptive pure pursuit algorithm,” 2014 14th Int. Conf. on Control, Automation and Systems, pp. 1443-1447, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCAS.2014.6987787
- [11] Y. Huang et al., “Path tracking based on improved pure pursuit model and PID,” 2020 IEEE 2nd Int. Conf. on Civil Aviation Safety and Information Technology, pp. 359-364, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCASIT50869.2020.9368694
- [12] D. S. Lal, A. Vivek, and G. Selvaraj, “Lateral control of an autonomous vehicle based on Pure Pursuit algorithm,” 2017 Int. Conf. on Technological Advancements in Power and Energy, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAPENERGY.2017.8397361
- [13] R. C. Coulter, “Implementation of the pure pursuit path tracking algorithm,” Technical Report, Carnegie Mellon University, No.CMU-R1-TR-92-01, 1992.
- [14] E. Cocconi, “Enhanced pure pursuit algorithm & autonomous driving,” Bachelor’s thesis, The University of New South Wales, 2019. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.16776.44803/2
- [15] M. Samuel, M. Hussein, and M. B. Mohamad, “A review of some pure-pursuit based path tracking techniques for control of autonomous vehicle,” Int. J. of Computer Applications, Vol.135, No.1, pp. 35-38, 2016. https://doi.org/10.5120/ijca2016908314
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.