Paper:
Research on the Method of Robot Arm Trajectory Planning Under Chaos Control
Zebin Li and Jiangdong Zhao
Center of Basic Experiment, West Anhui University
Lu’an, Anhui 237012, China
The robot’s arm trajectory can be used to improve the quality of the robot work. The current method utilizes the searching ability of the Alopex algorithm to perform a rough search of the robot’s path of action to achieve the trajectory planning of its arm, but the planning efficiency is low. To this end, this paper uses chaos control to plan the robot arm trajectory. Based on the description of the robot arm trajectory planning, the robotic arm trajectory planning is completed by using the obstacle to the intersection time, probability prediction, motion planning strategy and real-time obstacle avoidance. Experiments show that this method can carry on the efficient planning to the robot arm trajectory.
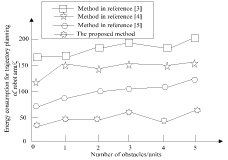
Number of obstacles
- [1] J. Liu, Q. Yan, and Z. Tang, “Research on Indoor Obstacle Avoidance of Mobile Robot Based on Laser Radar,” Computer Measurement & Control, Vol.23, No.3, pp. 787-790, 2015.
- [2] C. Cheng, “Energy-efficient Trajectory Planning Research for Protraction leg of a Hexapod Robot,” Computer Simulation, Vol.32, No.1, pp. 438-441, 2015.
- [3] K. Zheng and Q. Zhang, “Delta robot’s trajectory planning based on trajectory lattice and comprehensive dynamics dexterity,” J. of Vibration and Shock, Vol.35, No.22, pp. 31-37, 2016.
- [4] W. Zhang and W. Shang, “High-velocity Point-to-point Trajectory Planning of a 2-DOF Cable Driven Parallel Manipulator,” J. of Mechanical Engineering, Vol.52, No.3, pp. 1-8, 2016.
- [5] D. Zhao, R. Bai, C. Shen, et al., “Trajectory Planning Method of Point-to-Point Motion for SCARA Robot,” Computer Engineering, Vol.41, No.8, pp. 306-312, 2015.
- [6] G. Yang, Y. Zhang, J. Yang, et al., “Automated classification of brain images using wavelet-energy and biogeography-based optimization,” Multimedia Tools & Applications, Vol.75, No.23, pp. 15601-15617, 2016.
- [7] Y. Nakagawa and N. Nakagawa, “Relationship Between Human and Robot in Nonverbal Communication,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.21, No.1, pp. 20-24, 2017.
- [8] G. Yang, W. Tan, H. Jin, et al., “Review wearable sensing system for gait recognition,” Cluster Computing, pp. 1-9, 2018.
- [9] Q. Ai, Q. Yang, M. Lin et al., “Implementing Multi-DOF Trajectory Tracking Control System for Robotic Arm Experimental Platform,” 2018 10th Int. Conf. on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA), pp. 282-285, 2018.
- [10] L. Z. Quan, C. L. Li, Z. Y. Feng et al., “Algorithm of Works’ Decision for Three Arms Robot in Greenhouse Based on Control with Motion Sensing Technology,” Trans. of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, Vol.48, No.3, pp. 14-23, 2017.
- [11] T. H. Luo, C. Chen, and F. Y. Li, “Inverse solution of redundant robot arm based on glowworm swarm optimization algorithm of time-varying,” Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, Vol.22, No.2, pp. 576-582, 2016.
- [12] S. P. Liu, X. Y. He, L. L. Han et al., “Self-motion Optimization for Redundant Manipulator of Robonaut,” Manned Spaceflight, Vol.23, No.2, pp. 143-149, 2017.
- [13] Y. Meng, X. J. Li, Y. Guan et al., “Modeling and Verification for Robot Joint Bus Communication System,” J. of Software, Vol.29, No.6, pp. 1699-1715, 2018.
- [14] W. Zhang, “High-speed Point-to-point Trajectory Planning of a 2-DOF Cable Driven Parallel Manipulator,” J. of Mechanical Engineering, Vol.52, No.3, pp. 1-8, 2016.
- [15] D. B. Zhao, R. L. Bai, C. H. Shen et al., “Trajectory Planning Method of Point-to-Point Motion for SCARA Robot,” Computer Engineering, Vol.41, No.8, pp. 306-312, 2015.
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.