Paper:
DSFS: Dynamic Sensor Fusion System for Robust Localization with Diverse Sensing Information
Takumi Suzuki*, Yuki Funabora*
 , Shinji Doki*
, Shinji Doki*
 , Kae Doki**
, Kae Doki**
 , and Mitsuhiro Yamazumi***
, and Mitsuhiro Yamazumi***

*Nagoya University
Furo-cho, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya, Aichi 464-8603, Japan
**Aichi Institute of Technology
1247 Yachigusa, Yakusa-cho, Toyota, Aichi 470-0392, Japan
***Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
8-1-1 Tsukaguchi-Honmachi, Amagasaki, Hyogo 661-8661, Japan
Autonomous mobile robots are expected to demonstrate a high degree of adaptability, enabling effective operation across diverse environments. As sensor performance is largely influenced by environmental conditions, relying solely on a single sensor for localization makes robust localization challenging. To address this issue, various studies have enhanced the localization robustness using multiple sensors with different characteristics that complement each other’s weaknesses. However, conventional studies require the design of separate fusion systems for each type and numerous sensor observations. As future developments facilitate increased cooperation with environment-fixed sensors and external agents, the types and number of sensor observations accessible to robots are expected to dynamically change depending on location and time. Therefore, a pose fusion system that adapts to such changes is required. This paper proposes a fusion system that can adapt to changes in the type and number of sensor observations. This system dynamically fuses pose information obtained from onboard sensors, environment-fixed sensors, and external agents by extending the selective fusion method, one of the existing pose fusion methods for onboard sensors. Simulation experiments confirm that our system can adapt to changes in the type and number of sensor observations and robustly localize by dynamically fusing pose information from onboard sensors, environment-fixed sensors, and external agents.
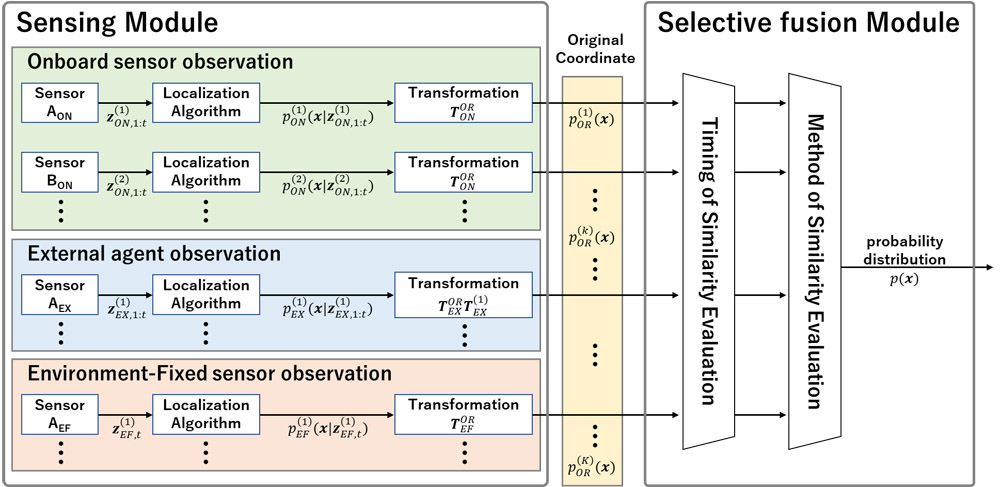
DSFS: dynamic sensor fusion system
- [1] J. Graeter, A. Wilczynski, and M. Lauer, “LIMO: Lidar-Monocular Visual Odometry,” 2018 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 7872-7879, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2018.8594394
- [2] S. Khan, D. Wollherr, and M. Buss, “Modeling Laser Intensities For Simultaneous Localization and Mapping,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Vol.1, Issue 2, pp. 692-699, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2016.2516592
- [3] J. Biswas and M. Veloso, “Depth camera based indoor mobile robot localization and navigation,” 2012 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1697-1702, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2012.6224766
- [4] J. A. Castellanos, J. Neira, and J. D. Tardós, “Multisensor fusion for simultaneous localization and map building,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics and Automation, Vol.17, Issue 6, pp. 908-914, 2001.
- [5] H. T. Niknejad, S. Mita, H. Long, and H. Quoc, “Multi-Sensor Data Fusion for Autonomous Vehicle Navigation and Localization Through Precise Map,” Int. J. of Automotive Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, pp. 19-25, 2012. https://doi.org/10.20485/jsaeijae.3.1_19
- [6] T. Shan and B. Englot, “LeGO-LOAM: Lightweight and Ground-Optimized Lidar Odometry and Mapping on Variable Terrain,” 2018 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 4758-4765, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2018.8594299
- [7] B. Yang and R. Yang, “Interactive particle filter with occlusion handling for multi-target tracking,” 2015 12th Int. Conf. on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD), pp. 1945-1949, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/FSKD.2015.7382246
- [8] A. Bajcsy, S. L. Herbert, D. Fridovich-Keil, J. F. Fisac, S. Deglurkar, A. D. Dragan, and C. J. Tomlin, “A Scalable Framework For Real-Time Multi-Robot, Multi-Human Collision Avoidance,” 2019 Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 936-943, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2019.8794457
- [9] S. Kohlbrecher, O. von Stryk, J. Meyer, and U. Klingauf, “A flexible and scalable SLAM system with full 3D motion estimation,” 2011 IEEE Int. Symp. on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics, pp. 155-160, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1109/SSRR.2011.6106777
- [10] R. Mur-Artal, J. M. M. Montiel, and J. D. Tardós, “ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics, Vol.31, Issue 5, pp. 1147-1163, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671
- [11] G. Huang, “Visual-Inertial Navigation: A Concise Review,” 2019 Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 9572-9582, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2019.8793604
- [12] L. Liu, Z. Liu, and B. E. Barrowes, “Through-Wall Bio-Radiolocation With UWB Impulse Radar: Observation, Simulation and Signal Extraction,” IEEE J. of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, Vol.4, Issue 4, pp. 791-798, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2011.2157461
- [13] S. He and S.-H. G. Chan, “Wi-Fi Fingerprint-Based Indoor Positioning: Recent Advances and Comparisons,” IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, Vol.18, Issue 1, pp. 466-490, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2015.2464084
- [14] R. Faragher and R. Harle, “Location Fingerprinting With Bluetooth Low Energy Beacons,” IEEE J. on Selected Areas in Communications, Vol.33, Issue 11, pp. 2418-2428, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2015.2430281
- [15] K. Kaemarungsi, R. Ranron, and P. Pongsoon, “Study of received signal strength indication in zigbee location cluster for indoor localization,” 2013 10th Int. Conf. on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTICon.2013.6559612
- [16] Y.-S. Shin and A. Kim, “Sparse Depth Enhanced Direct Thermal-Infrared SLAM Beyond the Visible Spectrum,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Vol.4, Issue 3, pp. 2918-2925, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2019.2923381
- [17] C. Freye, C. Bendicks, E. Lilienblum, and A. Al-Hamadi, “Multiple Camera Approach for SLAM Based Ultrasonic Tank Roof Inspection,” A. Campilho and M. Kamel (Eds.), “Image Analysis and Recognition, Proc. of 11th Int. Conf. on Image Analysis and Recognition (ICIAR 2014), Part II,” pp. 453-460, Springer, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11755-3_50
- [18] A. Zhang and M. M. Atia, “Comparison of 2D Localization Using Radar and LiDAR in Long Corridors,” 2020 IEEE SENSORS, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/SENSORS47125.2020.9278684
- [19] X. Deng, Z. Zhang, A. Sintov, J. Huang, and T. Bretl, “Feature-constrained Active Visual SLAM for Mobile Robot Navigation,” 2018 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 7233-7238, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2018.8460721
- [20] M. B. Alatise and G. P. Hancke, “A Review on Challenges of Autonomous Mobile Robot and Sensor Fusion Methods,” IEEE Access, Vol.8, pp. 39830-39846, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2975643
- [21] A. Ehambram, R. Voges, C. Brenner, and B. Wagner, “Interval-based Visual-Inertial LiDAR SLAM with Anchoring Poses,” 2022 Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 7589-7596, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA46639.2022.9812425
- [22] C. Zheng, Q. Zhu, W. Xu, X. Liu, Q. Guo, and F. Zhang, “FAST-LIVO: Fast and Tightly-coupled Sparse-Direct LiDAR-Inertial-Visual Odometry,” 2022 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 4003-4009, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9981107
- [23] D. Chen, S. Wang, W. Xie, S. Zhai, N. Wang, H. Bao, and G. Zhang, “VIP-SLAM: An Efficient Tightly-Coupled RGB-D Visual Inertial Planar SLAM,” 2022 Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5615-5621, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA46639.2022.9812354
- [24] H. Li, L. Pan, and J. Zhao, “LiDAR-Aided Visual-Inertial Localization with Semantic Maps,” 2022 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 910-916, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9982152
- [25] K. Koide, M. Yokozuka, S. Oishi, and A. Banno, “Globally Consistent and Tightly Coupled 3D LiDAR Inertial Mapping,” 2022 Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/icra46639.2022.9812385
- [26] H. Yaguchi, N. Zaoputra, N. Hatao, K. Yamazaki, K. Okada, and M. Inaba, “View-Based Localization Using Head-Mounted Multi Sensors Information,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.21, No.3, pp. 376-383, 2009. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2009.p0376
- [27] H. Kurita, M. Oku, T. Nakamura, T. Yoshida, and T. Fukao, “Localization Method Using Camera and LiDAR and its Application to Autonomous Mowing in Orchards,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.34, No.4, pp. 877-886, 2022. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2022.p0877
- [28] H. Zhang, Y. Wang, T. Zhong, F. Dong, and K. Chen, “FFD-SLAM: A Real-Time Visual SLAM Toward Dynamic Scenes with Semantic and Optical Flow Information,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.28, No.3, pp. 586-594, 2024. https://doi.org/10.20965/jaciii.2024.p0586
- [29] Y. Song, M. Guan, W. P. Tay, C. L. Law, and C. Wen, “UWB/LiDAR Fusion For Cooperative Range-Only SLAM,” 2019 Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 6568-6574, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2019.8794222
- [30] E. Martín-Gorostiza, M. A. García-Garrido, D. Pizarro, P. Torres, M. O. Miguel, and D. Salido-Monzú, “Infrared and Camera Fusion Sensor for Indoor Positioning,” 2019 Int. Conf. on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/IPIN.2019.8911812
- [31] A. Arun, R. Ayyalasomayajula, W. Hunter, and D. Bharadia, “P2SLAM: Bearing Based WiFi SLAM for Indoor Robots,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Vol.7, Issue 2, pp. 3326-3333, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2022.3144796
- [32] R. Han, S. Chen, Y. Bu, Z. Lyu, and Q. Hao, “Decentralized Cooperative Multi-Robot Localization with EKF,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:1811.07506, 2018. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1811.07506
- [33] C. C. Cossette, M. A. Shalaby, D. Saussié, J. Le Ny, and J. R. Forbes, “Optimal Multi-robot Formations for Relative Pose Estimation Using Range Measurements,” 2022 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 2431-2437, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9981301
- [34] T. H. Nguyen, T.-M. Nguyen, and L. Xie, “Flexible and resource-efficient multi-robot collaborative visual-inertial-range localization,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Vol.7, Issue 2, pp. 928-935, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2021.3136286
- [35] X. Yu, P. T. Morrn, S. Salimpour, J. P. Queralta, and T. Westerlund, “Loosely coupled odometry, uwb ranging, and cooperative spatial detection for relative monte-carlo multi-robot localization,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2304.06264, 2023.
- [36] A. G. Pires, P. A. F. Rezeck, R. A. Chaves, D. G. Macharet, and L. Chaimowicz, “Cooperative Localization and Mapping with Robotic Swarms,” J. of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, Vol.102, No.2, Article No.47, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-021-01397-z
- [37] H. Xu, L. Wang, Y. Zhang, K. Qiu, and S. Shen, “Decentralized Visual-Inertial-UWB Fusion for Relative State Estimation of Aerial Swarm,” 2020 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 8776-8782, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA40945.2020.9196944
- [38] Y. Qu, M. Yang, J. Zhang, W. Xie, B. Qiang, and J. Chen, “An Outline of Multi-Sensor Fusion Methods for Mobile Agents Indoor Navigation,” Sensors, Vol.21, Issue 5, Article No.1605, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051605
- [39] G. Nützi, S. Weiss, D. Scaramuzza, and R. Siegwart, “Fusion of IMU and Vision for Absolute Scale Estimation in Monocular SLAM,” J. of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, Vol.61, No.1, pp. 287-299, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-010-9490-z
- [40] E. López, R. Barea, A. Gómez, Á. Saltos, L. M. Bergasa, E. J. Molinos, and A. Nemra, “Indoor SLAM for Micro Aerial Vehicles Using Visual and Laser Sensor Fusion,” Robot 2015: Second Iberian Robotics Conf.: Advances in Robotics, Vol.1, pp. 531-542, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27146-0_41
- [41] P. Carrasco, F. Cuesta, R. Caballero, F. J. Perez-Grau, and A. Viguria, “Multi-Sensor Fusion for Aerial Robots in Industrial GNSS-Denied Environments,” Applied Sciences, Vol.11, Issue 9, Article No.3921, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093921
- [42] Y. Wang and X. Li, “The IMU/UWB Fusion Positioning Algorithm Based on a Particle Filter,” ISPRS Int. J. of Geo-Information, Vol.6, Issue 8, Article No.235, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6080235
- [43] R. Mascaro, L. Teixeira, T. Hinzmann, R. Siegwart, and M. Chli, “GOMSF: Graph-Optimization Based Multi-Sensor Fusion for Robust UAV Pose Estimation,” 2018 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1421-1428, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2018.8460193
- [44] Y. Jia, H. Luo, F. Zhao, G. Jiang, Y. Li, J. Yan, Z. Jiang, and Z. Wang, “Lvio-Fusion: A Self-adaptive Multi-sensor Fusion SLAM Framework Using Actor-critic Method,” 2021 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 286-293, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS51168.2021.9635905
- [45] K. Suyama, Y. Funabora, S. Doki, and K. Doki, “Divergence-Based Dynamic Sensor Fusion for Robust Localization Using Particle Filter,” Trans. of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers, Vol.53, Issue 2, pp. 169-177, 2017 (in Japanese). https://doi.org/10.9746/sicetr.53.169
- [46] N. Ohashi, Y. Funabora, S. Doki, and K. Doki, “Majority Rule Based Sensor Fusion System with Correlation Evaluation for Mobile Robot Localization,” Trans. of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers, Vol.55, Issue 7, pp. 439-446, 2019 (in Japanese). https://doi.org/10.9746/sicetr.55.439
- [47] N. Ohashi, Y. Funabora, S. Doki, and K. Doki, “Multisensor robust localization in various environment with correlation checking test,” ROBOMECH J., Vol.8, No.1, Article No.3, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40648-021-00190-9
- [48] T. Zhi, J. R. Xu, Y. Ma, W. Yu, S. Liu, and S. Yuan, “Uapgo: Uncertainty-Aware Pose Graph Optimization for Lidar-Based Slam Systems,” SSRN, 2024. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5076407
- [49] Y. Zhang, K. Yang, Z. Wang, and K. Wang, “P2U-SLAM: A Monocular Wide-FoV SLAM System Based on Point Uncertainty and Pose Uncertainty,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2409.10143, 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2409.10143
- [50] R. Mur-Artal and J. D. Tardós, “ORB-SLAM2: An Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo, and RGB-D Cameras,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics, Vol.33, Issue 5, pp. 1255-1262, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103
- [51] S. Morikawa, “A localization system for autonomous vehicles integrating self-location and external vehicle poses as heterogeneous information sources,” Master’s Thesis, Nagoya University, 2022 (in Japanese).
- [52] M. Takamatsu, “Localization and path planning for stable autonomous movement of mobile robots,” Master’s Thesis, Nagoya University, 2024 (in Japanese).
- [53] A. Yasuda, M. Hirata, K. Okuda, and H. Imazu, “The Error Distribution and GDOP in GPS,” The J. of Japan Institute of Navigation, Vol.79, pp. 25-31, 1988. https://doi.org/10.9749/jin.79.25
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.