Paper:
System Identification Under Multirate Sensing Environments
Hiroshi Okajima
 , Risa Furukawa, and Nobutomo Matsunaga
, Risa Furukawa, and Nobutomo Matsunaga

Kumamoto University
2-39-1 Kurokami, Chuo-ku, Kumamoto, Kumamoto 860-8555, Japan
This paper proposes a system identification algorithm for systems with multirate sensors in a discrete-time framework. It is challenging to obtain an accurate mathematical model when the ratios of the inputs and outputs are different. A cyclic reformulation-based model for multirate systems is formulated, and the multirate system can be reduced to a linear time-invariant system to derive the model under the multirate sensing environment. The proposed algorithm integrates a cyclic reformulation with a state coordinate transformation of the cycled system to enable precise identification of systems under the multirate sensing environment. The effectiveness of the proposed system identification method is demonstrated through numerical simulations.
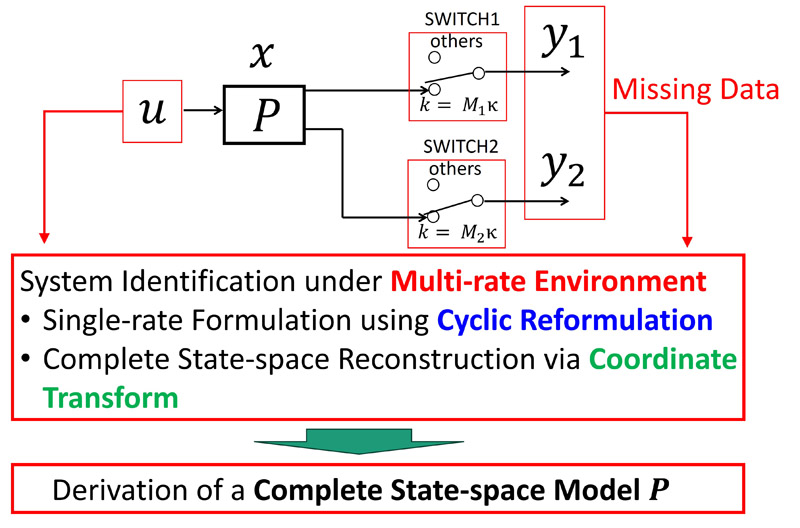
Multi-rate system identification sequence
- [1] L. Ljung, “System Identification: Theory for the User, 2nd Edition,” PTR Prentice Hall, 1998.
- [2] P. V. Overschee and B. D. Moor, “N4SID: Subspace algorithms for the identification of combined deterministic-stochastic systems,” Automatica, Vol.30, No.1, pp. 75-93, 1994. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-1098(94)90230-5
- [3] D. Bauer and M. Jansson, “Analysis of the asymptotic properties of the MOESP type of subspace algorithms,” Automatica, Vol.36, No.4, pp. 497-509, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-1098(99)00174-0
- [4] H. Tanaka and K. Ikeda, “Identification of linear stochastic systems taking initial state into account,” 56th Annual Conf. of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-1098(99)00174-0
- [5] Y. Fujimoto, I. Maruta, and T. Sugie, “Input design for kernel-based system identification from the viewpoint of frequency response,” IEEE Trans. on Automatic Control, Vol.63, No.9, pp. 3075-3082, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.2018.2791464
- [6] I. Maruta and T. Sugie, “Closed-loop subspace identification for stable/ unstable systems using data compression and nuclear norm minimization,” IEEE Access, Vol.10, pp. 21412-21423, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3154017
- [7] J. Sjöberg, Q. Zhang, L. Ljung, A. Benveniste, B. Delyon, P.-Y. Glorennec, H. Hjalmarsson, and A. Juditsky, “Nonlinear black-box modeling in system identification: A unified overview,” Automatica, Vol.31, Issue 12, pp. 1691-1724, 1995. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-1098(95)00120-8
- [8] F. Felici, J.-W. van Wingerden, and M. Verhaegen, “Subspace identification of MIMO LPV systems using a periodic scheduling sequence,” Automatica, Vol.43, No.10, pp. 1684-1697, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2007.02.027
- [9] M. Yin, A. Iannelli, and R. S. Smith, “Subspace identification of linear time-periodic systems with periodic inputs,” IEEE Control Systems Letters, Vol.5, No.1, pp. 145-150, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCSYS.2020.3000950
- [10] D. Karlsson and D. J. Hill, “Modelling and identification of nonlinear dynamic loads in power systems,” IEEE Trans. on Power Systems, Vol.9, Issue 1, pp. 157-166, 1994. https://doi.org/10.1109/59.317546
- [11] I. S. Apostolakis, “An estimation algorithm for multirate sampled digital control systems,” Int. J. of Control, Vol.56, Issue 4, pp. 813-830, 1992. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207179208934345
- [12] W. Lu, D. G. Fisher, and S. L. Shah, “Multirate constrained adaptive control,” Int. J. of Control, Vol.51, No.6, pp. 1439-1456, 1990. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207179008934145
- [13] R. Scattolini, “Multi-rate self-tuning predictive controller for multi-variable systems,” Int. J. of Systems Science, Vol.23, Issue 8, pp. 1347-1359, 1992. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207729208949388
- [14] T. Sato, “Parametric Design of a Dual-Rate Controller for Improvement in Steady-State Intersample Response,” SICE J. of Control, Measurement, and System Integration, Vol.1, Issue 4, pp. 329-334, 2008. https://doi.org/10.9746/jcmsi.1.329
- [15] Y. Minami, H. Okajima, K. Sawada, and K. Sekiguchi, “Special Issue on Navigation and Control Technologies for Autonomous Mobility,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.35, No.2, pp. 229-230, 2023. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2023.p0229
- [16] N. Matsunaga, I. Yamamoto, and H. Okajima, “Navigation System for Personal Mobility Vehicles Following a Cluster of Pedestrians in a Corridor Using Median of Candidate Vectors Observer,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.35, No.6, pp. 1562-1572, 2023. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2023.p1562
- [17] N. Matsunaga, K. Murata, and H. Okajima, “Robust Cooperative Transport System with Model Error Compensator Using Multiple Robots with Suction Cups,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.35, No.6, pp. 1583-1592, 2023. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2023.p1583
- [18] D. J. Yeong, G. V. Hernandez, J. Barry, and J. Walsh, “Sensor and Sensor Fusion Technology in Autonomous Vehicles: A Review,” Sensors, Vol.21, No.6, Article No.2140, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062140
- [19] Y. Kanuki, N. Ohta, and N. Nakazawa, “Development of autonomous moving robot using appropriate technology for Tsukuba Challenge,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol.35, No.2, pp. 279-287, 2023. https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2023.p0279
- [20] Q. M. Shao and A. Cinar, “System identification and distributed control for multi-rate sampled systems,” J. of Process Control, Vol.34, pp. 1-12, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2015.06.010
- [21] F. Ding and T. Chen, “Performance analysis of multi-innovation gradient type identification methods,” Automatica, Vol.43, No.1, pp. 1-14, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2006.07.024
- [22] J. Wang, T. Chen, and B. Huang, “Identification of Multirate Sampled-Data Systems,” IFAC Proc. Volumes, Vol.37, Issue 1, pp. 149-154, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-6670(17)38723-2
- [23] D. Li, S. L. Shah, T. Chen, and R. Patwardhan, “System identification and long-range predictive control of multi-rate systems,” Proc. of the 1999 American Control Conf., 1999.
- [24] H. Okajima, Y. Fujimoto, H. Oku, and H. Kondo, “Cyclic Reformulation Based System Identification for Periodically Time-varying Systems,” IEEE Access, Vol.13, pp. 26483-26493, 2025. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3537086
- [25] S. Bittanti and P. Colaneri, “Invariant representations of discrete-time periodic systems,” Automatica, Vol.36, Issue 12, pp. 1777-1793, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-1098(00)00087-X
- [26] S. Bittanti and P. Colaneri, “Periodic systems: Filtering and control,” Springer-Verlag, London, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84800-911-0
- [27] H. Okajima, Y. Hosoe, and T. Hagiwara, “State observer under multi-rate sensing environment and its design using l2-induced norm,” IEEE Access, Vol.11, pp. 20079-20087, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3249187
- [28] H. Okajima, K. Arinaga, and A. Hayashida, “Design of Observer-Based Feedback Controller for Multi-Rate Systems with Various Sampling Periods Using Cyclic Reformulation,” IEEE Access, Vol.11, pp. 121956-121965, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3329117
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.