Research Paper:
Improving the Performance of Voice Lie Detection Using Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients and Long Short Term Memory Models
Dewi Kusumawati*
 , Amil Ahmad Ilham**,†
, Amil Ahmad Ilham**,†
 , Andani Achmad***
, Andani Achmad***
 , and Ingrid Nurtanio**
, and Ingrid Nurtanio**

*Department of Informatics, STMIK Bina Mulia Palu
Jl. Soeprapto No.38, Palu, Sulawesi Tengah 94111, Indonesia
**Department of Informatics, Universitas Hasanuddin
Jl. Poros Malino Km. 6, Bontomarannu, Gowa, Sulawesi Selatan 92171, Indonesia
†Corresponding author
***Department of Electrical Engineering, Universitas Hasanuddin
Jl. Poros Malino Km. 6, Bontomarannu, Gowa, Sulawesi Selatan 92171, Indonesia
The objective of this study is to show that the combination of the Mel frequency cepstral coefficient (MFCC) and long short-term memory (LSTM) can be an effective approach for voice lie detection. To improve the performance of voice lie detection, a modified MFCC was used to extract important features in voice. An MFCC was modified by adding zero-crossing rate, audio entropy, and energy entropy parameters to detect changes in tone in each voice frame. LSTM was used to detect and classify voice-based lies. Datasets were obtained from the video recordings of the trial of a suspect. A total of 847 voice datasets were obtained after applying the time stretching augmentation technique where the audio duration was changed from 28.0 s to 4 s per video. The lie classification process was performed using the LSTM method that was equipped with additional dropout and dense layers and optimized using the adaptive moment estimation (Adam) optimizer. The results showed that the combination of the MFCC and LSTM achieved a classification accuracy level of 97% and an area under the curve value of 0.97 using epoch parameters of 200, Adam optimizer, and learning rate of 0.0001. This study concluded that the addition of zero-crossing rate, audio entropy, and energy entropy parameters to the MFCC extraction feature and the use of Adam optimizer in LSTM improved the accuracy of voice lie detection.
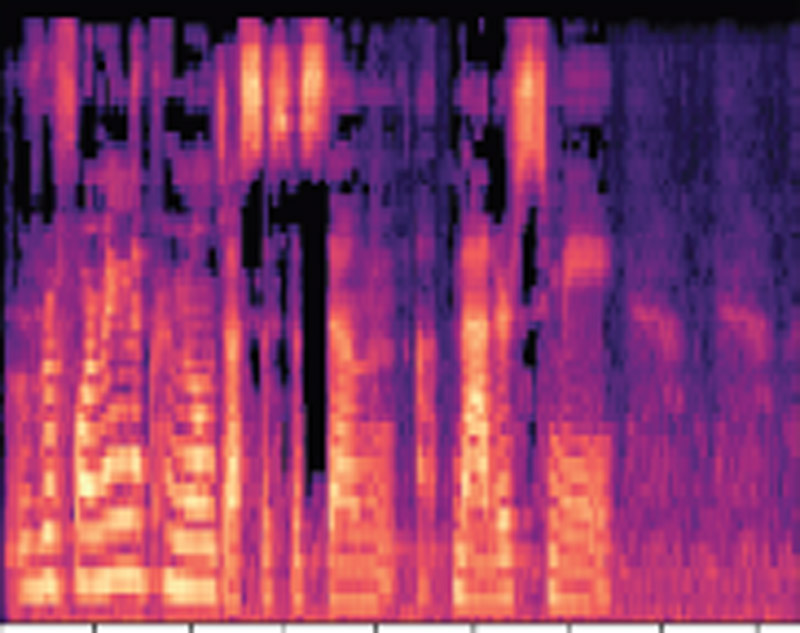
MFCC spectrogram of a lie data
- [1] V. Gupta, M. Agarwal, M. Arora, T. Chakraborty, R. Singh, and M. Vatsa, “Bag-of-lies: A multimodal dataset for deception detection,” IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. Work., pp. 83-90, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2019.00016
- [2] A. R. Bhamare, S. Katharguppe, and J. S. Nancy, “Deep neural networks for Lie detection with attention on bio-signals,” 2020 7th Int. Conf. Soft Comput. Mach. Intell. (ISCMI 2020), pp. 143-147, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCMI51676.2020.9311575
- [3] H. C. Chou, Y. W. Liu, and C. C. Lee, “Automatic deception detection using multiple speech and language communicative descriptors in dialogs,” APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process., Vol.10, Article No.e5, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1017/ATSIP.2021.6
- [4] A. Saxena, A. Khanna, and D. Gupta, “Emotion recognition and detection methods: A comprehensive survey,” J. Artif. Intell., Vol.2, pp. 53-79, 2020. https://doi.org/10.33969/AIS.2020.21005
- [5] A. Gallardo-Antolín and J. M. Montero, “Detecting deception from gaze and speech using a multimodal attention LSTM-based framework,” Appl. Sci., Vol.11, No.14, Article No.6393, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146393
- [6] S. V. Fernandes and M. S. Ullah, “Phychoacoustic masking of delta and time-difference cepstrum features for deception detection,” 2020 11th IEEE Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conf. (UEMCON 2020), pp. 213-217, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/UEMCON51285.2020.9298117
- [7] D. Avola, L. Cinque, M. De Marsico, A. Fagioli, and G. L. Foresti, “LieToMe: Preliminary study on hand gestures for deception detection via Fisher-LSTM,” Pattern Recognit. Lett., Vol.138, pp. 455-461, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2020.08.014
- [8] H. U. D. Ahmed, U. I. Bajwa, F. Zhang, and M. W. Anwar, “Deception detection in videos using the facial action coding system,” arXiv:2105.13659, 2021. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2105.13659
- [9] A. Vrij, L. Akehurst, S. Soukara, and R. Bull, “Detecting deceit via analyses of verbal and nonverbal behavior in children and adults,” Hum. Commun. Res., Vol.30, No.1, pp. 8-41, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1093/hcr/30.1.8
- [10] N. Srivastava and S. Dubey, “Moth monarch optimization-based deep belief network in deception detection system,” Sādhanā, Vol.45, Article No.166, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-020-01354-w
- [11] J.-T. Yang, G.-M. Liu, and S. C.-H Huang, “Emotion transformation feature: Novel feature for deception detection in videos,” 2020 IEEE Int. Conf. on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1726-1730, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP40778.2020.9190846
- [12] M. R. Ahmed, S. Islam, A. K. M. M. Islam, and S. Shatabda, “An ensemble 1D-CNN-LSTM-GRU model with data augmentation for speech emotion recognition,” Expert Syst. Appl., Vol.218, Article No.119633, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119633
- [13] J. Immanuel, A. Joshua, and S. T. George, “A study on using blink parameters from EEG data for Lie detection,” 2018 Int. Conf. on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI 2018), pp. 1-5, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCI.2018.8441238
- [14] A. Bablani, D. R. Edla, V. Kupilli, and R. Dharavath, “Lie detection using fuzzy ensemble approach with novel defuzzification method for classification of EEG signals,” IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., Vol.70, Article No. 2509413, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2021.3082985
- [15] E. P. F. Bareeda, B. S. S. Mohan, and K. V. A. Muneer, “Lie Detection using Speech Processing Techniques,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., Vol.1921, Article No.012028, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1921/1/012028
- [16] N. T. S. Saptadi, A. Suyuti, A. A. Ilham, and I. Nurtanio, “Optimization of briquette classification using deep learning,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.27, No.6, pp. 1200-1208, 2023. https://doi.org/10.20965/jaciii.2023.p1200
- [17] A. A. Masrur Ahmed et al., “Deep learning hybrid model with Boruta-Random forest optimizer algorithm for streamflow forecasting with climate mode indices, rainfall, and periodicity,” J. Hydrol., Vol.599, Article No.126350, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126350
- [18] J. S. Sepp Hochreiter, “LSTM can solve hard long time lag problems,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 473-479, 1997.
- [19] A. A. Ilham, I. Nurtanio, Ridwang, and Syafaruddin, “Applying LSTM and GRU methods to recognize and interpret hand gestures, poses, and face-based sign language in real time,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.28, No.2, pp. 265-272, 2024. https://doi.org/10.20965/jaciii.2024.p0265
- [20] H. Sak, A. W. Senior, and F. Beaufays, “Long short-term memory recurrent neural network architectures for large scale acoustic modeling,” Proc. Interspeech 2014, pp. 338-342, 2014. https://doi.org/10.21437/interspeech.2014-80
- [21] T. Yu and H. Zhu, “Hyper-parameter optimization: A review of algorithms and applications,” arXiv:2003.05689, 2020. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2003.05689
- [22] C. G. S. George and B. Sumathi, “Grid search tuning of hyperparameters in random forest classifier for customer feedback sentiment prediction,” Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl., Vol.11, No.9, pp. 173-178, 2020. https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2020.0110920
- [23] H. Nasri, W. Ouarda, and A. M. Alimi, “ReLiDSS: Novel Lie detection system from speech signal,” Proc. IEEE/ACS Int. Conf. Comput. Syst. Appl. (AICCSA), 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/AICCSA.2016.7945789
- [24] Y. Zhou and F. Bu, “An overview of advancements in lie detection technology in speech,” Int. J. Inf. Technol. Syst. Approach, Vol.16, No.2, 2023. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJITSA.316935
- [25] M. Abouelenien, V. Pérez-Rosas, R. Mihalcea, and M. Burzo, “Detecting deceptive behavior via integration of discriminative features from multiple modalities,” IEEE Trans. on Information Forensics and Security, Vol.12, No.5, pp. 1042-1055, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2016.2639344
- [26] G. Krishnamurthy, N. Majumder, S. Poria, and E. Cambria, “A deep learning approach for multimodal deception detection,” A. Gelbukh (Ed.), “Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing, Lecture Notes in Computer Science,” Vol.13396, pp. 87-96, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23793-5_8
- [27] A. Maiya, I. Sricharan, A. Pandey, and S. K. S, “Tom: Leveraging trend of the observed gradients for faster convergence,” arXiv:2109.03820, 2021. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2109.03820
- [28] L. Muda, M. Begam, and I. Elamvazuthi, “Voice recognition algorithms using mel frequency cepstral coefficient (MFCC) and dynamic time warping (DTW) techniques,” arXiv:1003.4083, 2010. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1003.4083
- [29] C. Millar, N. Siddique, and E. Kerr, “LSTM network classification of dexterous individual finger movements,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.26, No.2, pp. 113-124, 2022. https://doi.org/10.20965/jaciii.2022.p0113
- [30] S. Lasniari, S. Sanjaya, F. Yanto, and M. Affandes, “Pengaruh hyperparameter convolutional neural network arsitektur ResNet-50 pada klasifikasi citra daging sapi dan daging babi,” Vol.5, No.3, pp. 474-481, 2022. https://doi.org/10.32672/jnkti.v5i3.4424
- [31] R. Andonie and A. C. Florea, “Weighted random search for CNN hyperparameter optimization,” Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control, Vol.15, No.2, 2020. https://doi.org/10.15837/IJCCC.2020.2.3868
- [32] X. Deng, Q. Liu, Y. Deng, and S. Mahadevan, “An improved method to construct basic probability assignment based on the confusion matrix for classification problem,” Inf. Sci., Vols.340-341, pp. 250-261, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.033
- [33] A. Javeed, S. Zhou, L. Yongjian, I. Qasim, A. Noor, and R. Nour, “An intelligent learning system based on random search algorithm and optimized random forest model for improved heart disease detection,” IEEE Access, Vol.7, pp. 180235-180243, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2952107
- [34] A. J. Bowers and X. Zhou, “Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) area under the curve (AUC): A diagnostic measure for evaluating the accuracy of predictors of education outcomes,” J. Educ. Students Placed Risk, Vol.24, No.1, pp. 20-46, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/10824669.2018.1523734
- [35] F. Gorunescu, “Data Mining: Concepts, Models and Techniques,” Springer, 2011.
- [36] A. A. Ilham, I. Nurtanio, Ridwang, and Syafaruddin, “Applying LSTM and GRU methods to recognize and interpret hand gestures, poses, and face-based sign language in real time,” J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform., Vol.28, No.2, pp. 265-272, 2024. https://doi.org/10.20965/jaciii.2024.p0265
- [37] Z. Wu, B. Singh, L. S. Davis, and V. S. Subrahmanian, “Deception detection in videos,” 32nd AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell (AAAI 2018), pp. 1695-1702, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v32i1.11502
- [38] X. Guo, N. M. Selvaraj, Z. Yu, A. W.-K. Kong, B. Shen, and A. Kot, “Audio-visual deception detection: DOLOS dataset and parameter-efficient crossmodal learning,” Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 22078-22088, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.02023
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.